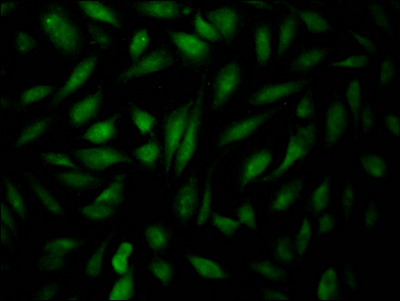
B cells isolated from the animal that was immunized with a synthesized peptide derived from human EPAS1 were fused with myeloma cells to form hybridomas. The cDNA for the variable light (VL) and variable heavy (VH) domains of the EPAS1 antibody-producing hybridomas was sequenced and used as a model for vector construction in the recombinant generation. The vector containing the EPAS1 monoclonal antibody gene was then transfected into cells for culture. The EPAS1 recombinant monoclonal antibody was purified from the cell culture supernatant using affinity chromatography, and its specificity was tested in ELISA and IF applications, with the antibody proving to detect only human EPAS1 protein.
The EPAS1 (also known as HIF-2 alpha) protein plays a critical role in cellular adaptation to hypoxic environments. In normal oxygen levels, EPAS1 is rapidly degraded by hydroxylation, which targets the protein for degradation by the proteasome. However, in hypoxic environments, the hydroxylation process is inhibited, allowing EPAS1 to accumulate and activate the expression of genes involved in angiogenesis, erythropoiesis, and metabolism. EPAS1 also plays a role in the development and function of certain organs, such as the lungs and kidneys. Mutations in EPAS1 have been associated with various diseases, including cancer, pulmonary hypertension, and erythrocytosis.