On July 18, 2021, the WHO COVID-19 Database updated Israel's phase II clinical data on EXO-CD24, a new treatment for COVID-19 (Click here to read more). The preliminary results uncovered that the 29 out of 30 patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 recovered within 5 days or even less. The clinical data has not yet been posted on the Clinical Trial website. Nevertheless, the news has attracted attention worldwide after it was posted in the Jerusalem Post, the Israel's most-read English news website. Now, as the COVID-19 continues to mutate, interest in emerging Israeli treatments EXO-CD24 is growing fast. It is not the first time that CD24 has been applied for the COVID-19. In earlier studies, soluble CD24-Fc drug has been designed for COVID-19 therapy, also suggesting greatly improved outcomes in patients. If EXO-CD24 proved to be safe and effective, CD24 will take the largely part for the COVID-19 therapy. Since then, what is CD24 and how might it work in COVID-19 treatment?
1. Heat-Stable Antigen-CD24
CD24 is a heat-stable antigen that belongs to the group of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored cell surface proteins. CD24 was originally thought to be a marker for B cells and is expressed in the early stages of B cell differentiation, while playing an important role in lymphocyte maturation, neurological development, and tissue renewal in biological process. Moreover, CD24 expression also has been largely identified in cells of the hematopoietic system, neural tissue and some specific epithelial cells. Importantly, CD24 is aberrantly expressed in solid tumors, inflammatory tissues and certain cells of autoimmune disorder. Numerous studies implied that CD24 can have dual and opposing effects on health states and deficient health states - in the health states, CD24 inhibits tissue growth, but in the deficient health states, CD24 promotes cell proliferation. The diverse physiological properties trigger the interest of CD24 in therapeutic studies of autoimmune diseases, inflammation, tumors, and other diseases.
2. "Don't Eat Me" Signaling Protein-CD24
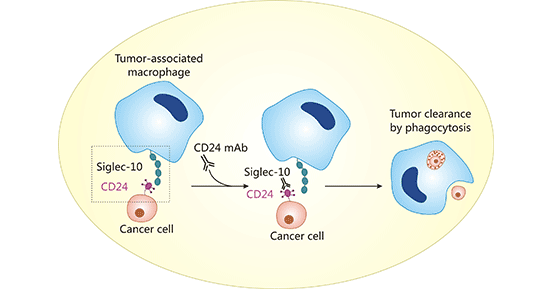
It is known that cancer cells avoid being killed by expressing a "don't eat me" signaling protein, which leads to tumor immune escape. This signaling protein is called as the "don't eat me" signaling protein. In 2019, a study revealed a significant role for the CD24/Siglec-10 signaling pathway in ovarian and breast cancer tumors, suggesting that CD24 interacts with Siglec-10 (sialic-acid- binding Ig-like lectin10) on macrophages. The binding of CD24 and Siglec-10 could inhibit phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages. On the contrary, knockdown of CD24 or Siglec-10 could promote phagocytosis (Figure 1). Therefore, CD24 as the novel immunotherapy target, is a newly discovered "don't eat me" signaling protein, like the popular molecular CD47. (Click for CD47 related article)
Figure 1. CD24/Siglec-10 signaling pathway
3. Why is CD24 an Important Target for COVID-19?
Let's go back to this new drug: EXO-C24. First of all, EXO-C24 is not an antiviral drug, but rather an immunotherapy drug that is still being tested. The essence of this drug is an exosome encapsulated in CD24. Exosomes (exosomes) are tiny cell-secreted membrane vesicles that are widely distributed in various body fluids. Exosomes can carry a variety of proteins, lipids, DNA and RNA messages, creating a form of cell-to-cell signaling. It is CD24, which regulates the body's immune response through a variety of mechanisms, that really works, and it is by virtue of its ability to restrain the cytokine storms that CD24 is being used to treat patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 disease. As previous mentioned, CD24 targeted drug-CD24 and Fc fusion protein (CD24-Fc) has been used for COVID-19 therapy before EXO-CD24.
In November 2020, Merck announced the acquisition of the US company OncoImmune's drug CD24-Fc for an upfront payment of $425 million. But given the new trial and correspondingly sized production, it will not be completed until at least the first half of 2022, and in April 2021, Merck announced the suspension of CD24-Fc for the treatment of COVID-19 clinical studies in patients, but no other indications for CD24-Fc are affected. Earlier last year, OncoImmune published interim data from clinical III, where patients having respiratory failure were reduced over 50%.
Other drugs like tocilizumab and hormonal agents are also used for COVID-19 treatment. However, for tocilizumab, which targets a single cytokine pathway. There is limited evidence on the clinical benefit for patients with severe disease. Technically, CD24 has greater potential as a target than IL-6/IL-6R, but the specific clinical benefit of either CD24-Fc or EXO-C24 for COVID-19 continues to require more clinical validation.
4. How's the Recent Clinical Research Advances in CD24?
Data from Clinical Trials have shown that there are four CD24-based clinical agents, with indications primarily for COVID-19. Data from Pharmacodia implied that two of these are in the clinical phase, which is CD24-Fc and EXO-CD24. In addition to being used for COVID-19, the drug CD24-Fc is also used for myelodysplastic syndrome, acute lymphoblastic leukemia, leukemia and many other autoimmune diseases. Thus, CD24 as a novel immune regulator, does not only act on COVID-19, but a large number of studies have shown that CD24 is highly expressed in various tumors and involved in regulating immune response. Overall, CD24 might be served as a potential target for antitumor therapy. Certainly, we expect more breakthroughs in clinical studies of COVID-19 or other diseases as more CD24-based agents developed, which will make CD24 stand out.
|
Program Title
|
Status
|
Indications
|
Phase
|
Enrollment
|
Company
|
|
CD24Fc (MK-7110) as a Non-antiviral Immunomodulator in COVID-19 Treatment (MK-7110-007)
|
Completed
|
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19);
Myelodysplastic syndrome;
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia ;
Acute myeloid leukemia;
Graft-versus-host disease;
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation;
Leukemia;
HIV infection;
Melanoma;
|
Phase 3
|
234
|
OncoImmune, Inc.
|
|
A Phase II Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Exosomes Overexpressing CD24 to Prevent Clinical Deterioration in Patients With Moderate or Severe COVID-19 Infection
|
Active, not recruiting
|
COVID-19 Disease
|
Phase 2
|
155
|
Eli Sprecher, MD
|
|
Safety and Efficacy of Exosomes Overexpressing CD24 in Two Doses for Patients With Moderate or Severe COVID-19
|
Recruiting
|
Covid19
|
Pre-clinical
|
90
|
Athens Medical Society
|
|
Evaluation of the Safety of CD24-Exosomes in Patients With COVID-19 Infection
|
Recruiting
|
SARS-CoV-2
|
Pre-clinical
|
35
|
Tel-Aviv Sourasky Medical Center
|
Source: Clinical Trials
To fully assist pharmaceutical companies in the CD24 research for COVID-19 or immune diseases, CUSABIO offers CD24 active protein products Recombinant Human CD24 -Nanoparticle (Active) (Code: CSB-MP004902HU). You are welcome to contact us.
The Validated Data of CD24-Nanoparticle (Active)
High Purity Validated by SDS-PAGE
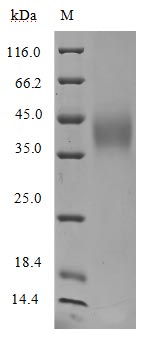
Purity was greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
Excellent Bioactivity Validated by Functional ELISA.
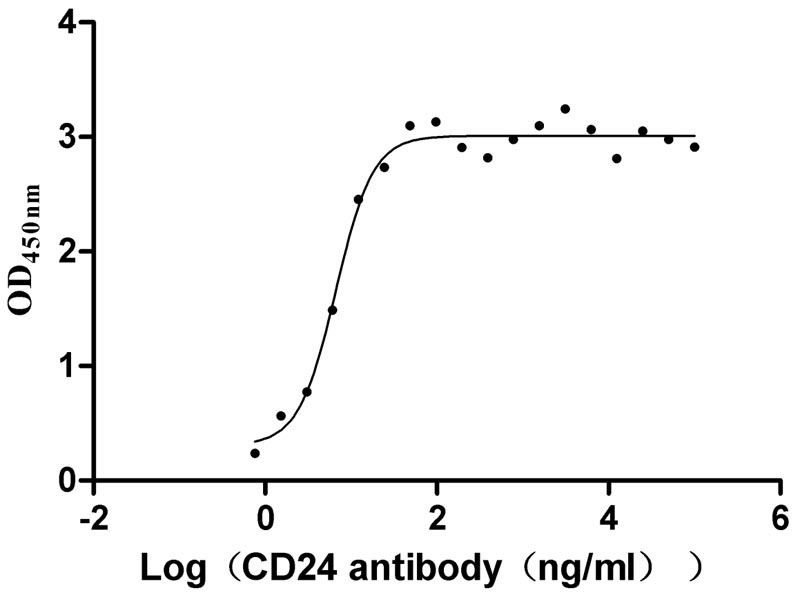
Immobilized human CD24 at 2 μg/ml can bind anti-CD24 recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (CSB-RA004902A0HU). The EC50 is 5.409-8.219 ng/ml.
References
[1] Sprecher, Eli. "A Phase II Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Exosomes Overexpressing CD24 to Prevent Clinical Deterioration in Patients With Moderate or Severe COVID-19 Infection."(2021).
[2] Altevogt, Peter, et al. "Novel insights into the function of CD24: A driving force in cancer." International Journal of Cancer 148.3 (2021): 546-559.
[3] Aroldi, Andrea, et al. "CD24/Siglec-10 Don't Eat Me Signal Blockade Is a Potential Immunotherapeutic Target in Mantle-Cell Lymphoma." Blood 138. Supplement 1 (2021): 2276-2276.
[4] Shapira, Shiran, et al. "Integrase-derived peptides together with CD24-targeted lentiviral particles inhibit the growth of CD24-expressing cancer cells." Oncogene 40.22 (2021): 3815-3825.
[5] Wu, Hao, et al. "Prospects of antibodies targeting CD47 or CD24 in the treatment of glioblastoma." CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics 27.10 (2021): 1105-1117.
[6] Kelley, Shannon M., and Kodi S. Ravichandran. "Putting the brakes on phagocytosis: "don't-eat-me " signaling in physiology and disease." EMBO reports (2021): e52564.
[7] Ghasempour Dabaghi, G., M. Rabiee Rad, and L. Saberian. "Treatment of COVID-19 by CD24FC; a mini-review to the current knowledge. "J Prev Epidemiol 6.1 ( 2021): e04.
[8] Song, No-Joon, et al. "Immunological Insights Into the Therapeutic Roles of CD24Fc Against Severe COVID-19." medRxiv (2021).
[9] Sagiv, Eyal, and Michael A. Portman. "CD24 for Cardiovascular Researchers: a Key Molecule in Cardiac Immunology, Marker of Stem Cells and Target for Drug Development." Journal of Personalized Medicine 11.4 (2021): 260.
[10] Song, No-Joon, et al. "Treatment with Soluble CD24 Attenuates COVID-19-Associated Systemic Immunopathology." medRxiv (2021): 2021-08.
[11] Barkal, Amira A., et al. "CD24 signalling through macrophage Siglec-10 is a target for cancer immunotherapy." Nature 572.7769 (2019): 392-396.
CUSABIO team. CD24: A Key Element in the EXO-CD24 Technique for Combating COVID-19. https://www.cusabio.com/c-21055.html






Comments
Leave a Comment