[1] Kipps T J. ROR1: an orphan becomes apparent[J]. Blood, 2022, 140(14): 1583-1591.
[2] Mellstedt H, Hojjat-Farsangi M, Daneshmanesh A H, et al. First generation of a small chemical molecule ROR1 RTK tyrosine kinase inhibitor[J]. Annals of Oncology, 2016, 27(Supplement 6): vi526-vi544.
[3] Anonymous. Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer score with ROR1[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(1): 3-12.
[4] Snell D, Kirk N, Bassler N, et al. An assessment of ROR1 expression across tumor tissue and the investigation of a ROR1-targeted T cell engager as a therapeutic strategy to target ROR1 positive tumors[J]. J Immunother Cancer, 2023, 11(Suppl 1): A1-A1731.
[5] Madani D, John M, Satgunaseelan L, et al. ROR1 mRNA expression in glioma - a novel prognostic biomarker[J]. Neuro-Oncology, 2022, 24(Supplement 7): vii6.
[6] Ghia E M, Rassenti L Z, Choi M Y, et al. High expression level of ROR1 and ROR1-signaling associates with venetoclax resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia[J]. Leukemia, 2022, 36(6): 1609-1618.
[7] Madani D, Satgunaseelan L, El-Hayek J, et al. ROR1 mRNA expression in glioma - a novel prognostic biomarker[J]. Neuro-Oncology, 2024, 26(Supplement 7): vii4-vii5.
[8] Lin W, Niu R, Park S M, et al. IGFBP5 is an ROR1 ligand promoting glioblastoma invasion via ROR1/HER2-CREB signaling axis[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 1578.
[9] Piki E, Dini A, Raivola J, et al. ROR1-STAT3 signaling contributes to ovarian cancer intra-tumor heterogeneity[J]. Cell Death Discovery, 2023, 9(1): 222.
[10] Nie L, Jiang V C Y, Liu Y, et al. Dual Targeting of ROR1 and BTK Augments the Anti-Lymphoma Activity in Mantle[J]. Blood, 2023, 142(Supplement 1): 4366-4367.
[11] Wei R, Liao X, Li J, et al. Novel humanized monoclonal antibodies against ROR1 for cancer therapy[J]. Molecular Cancer, 2024, 23(1): 165.

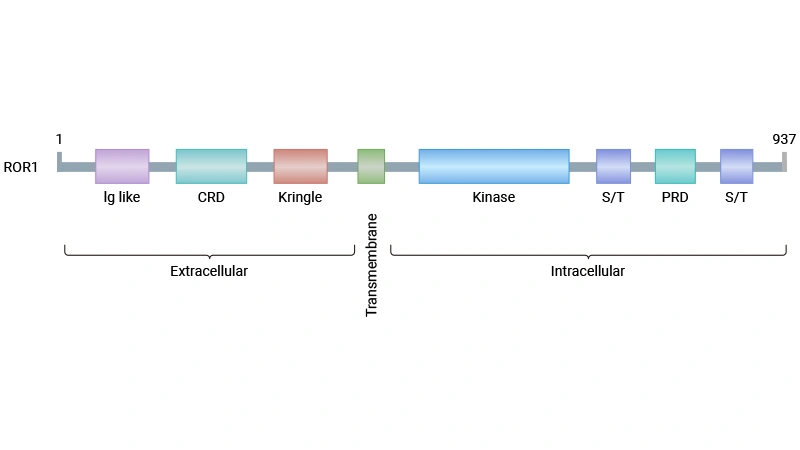
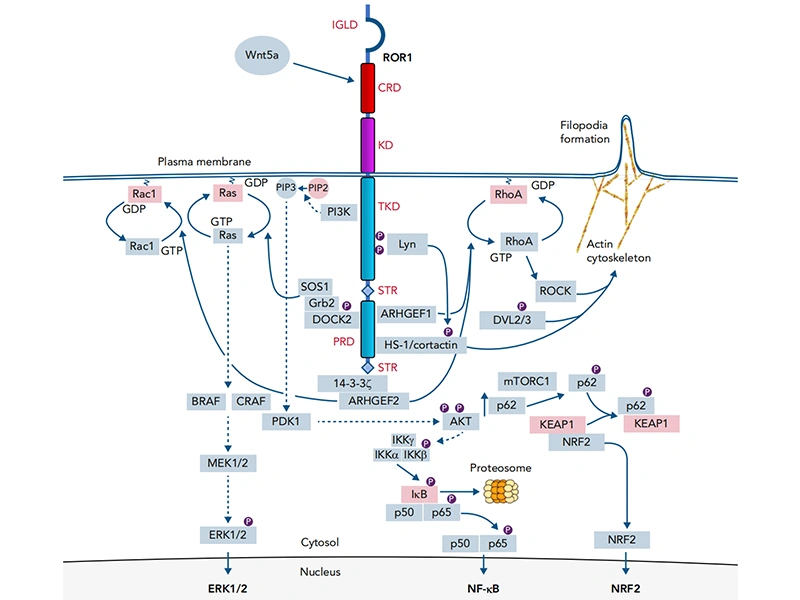
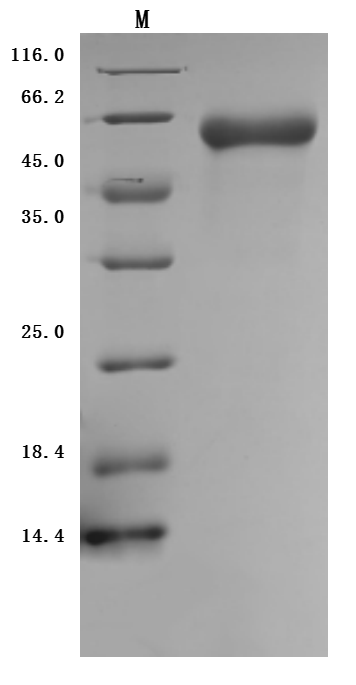
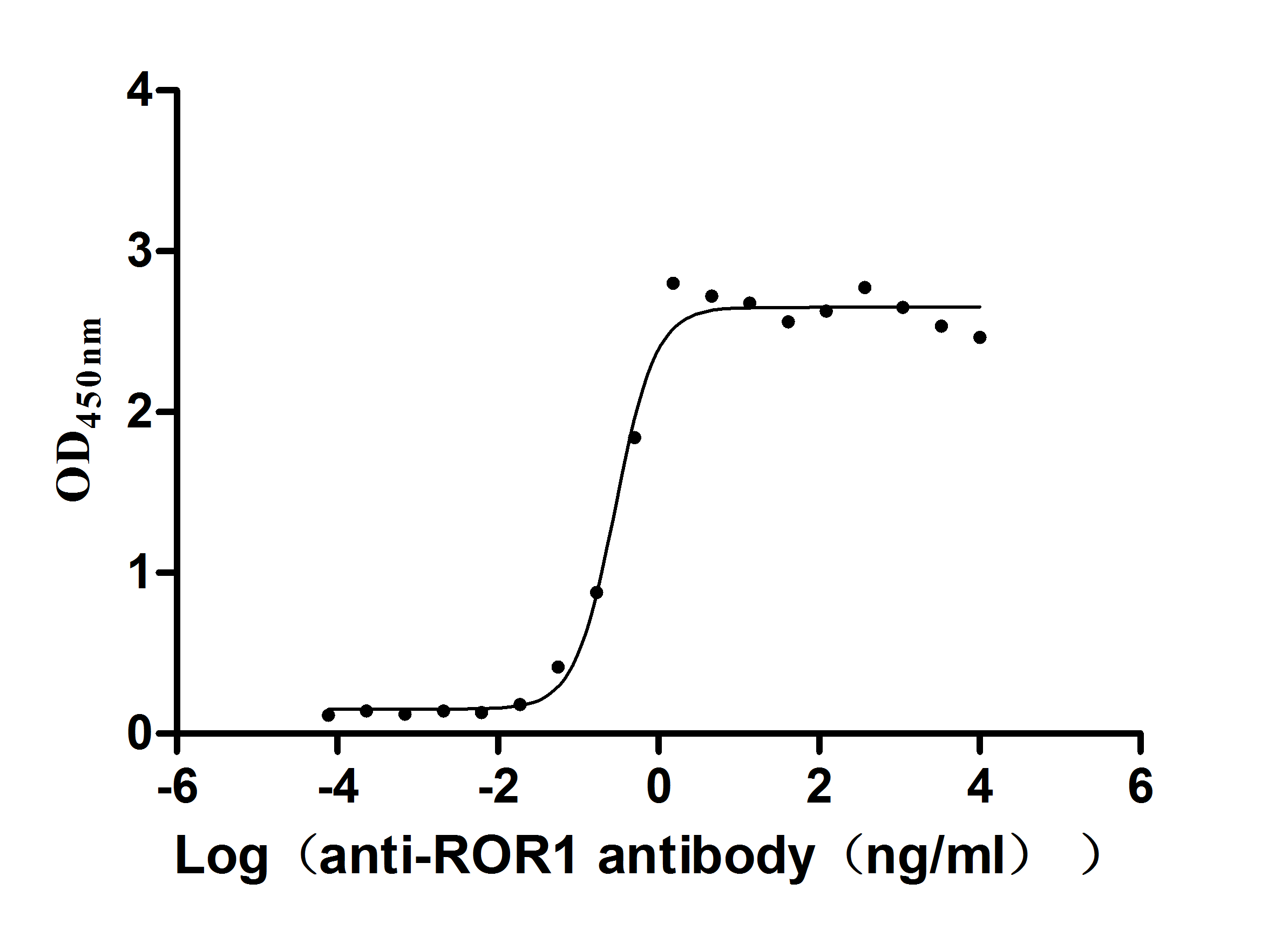
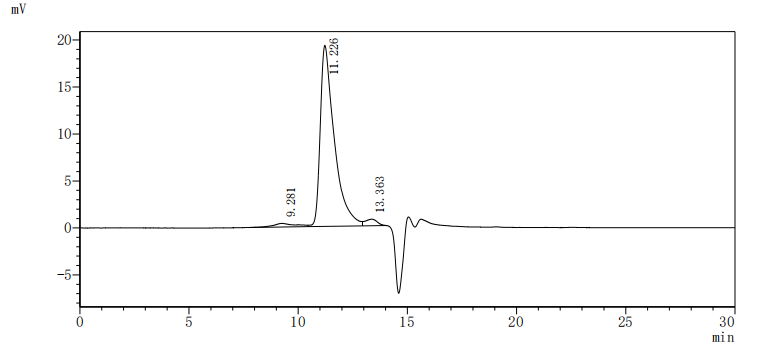
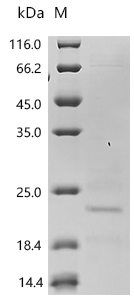
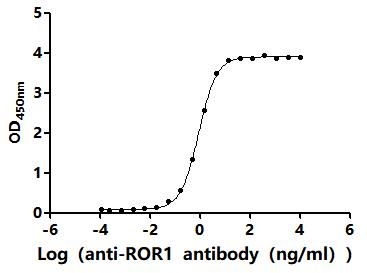
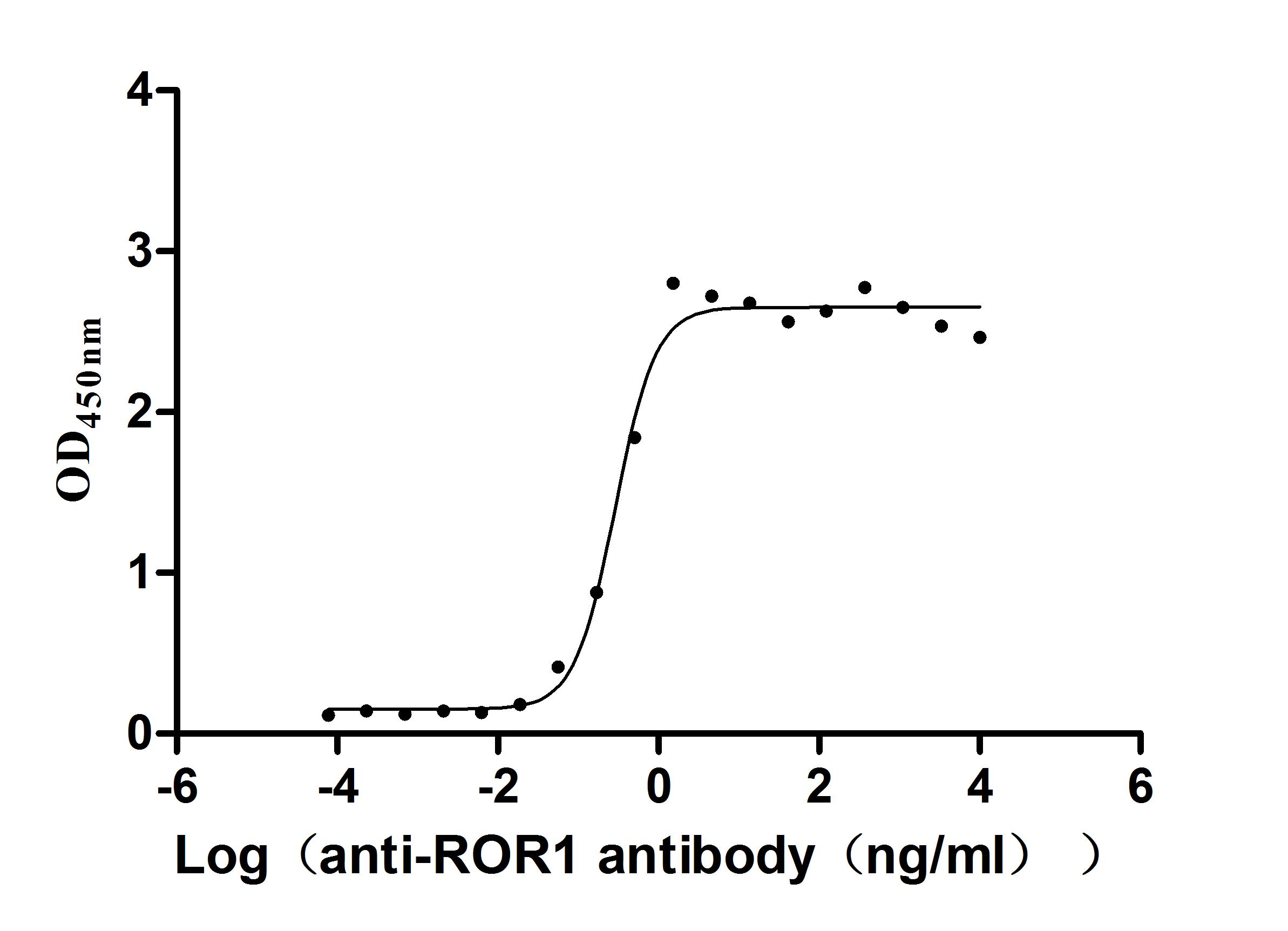
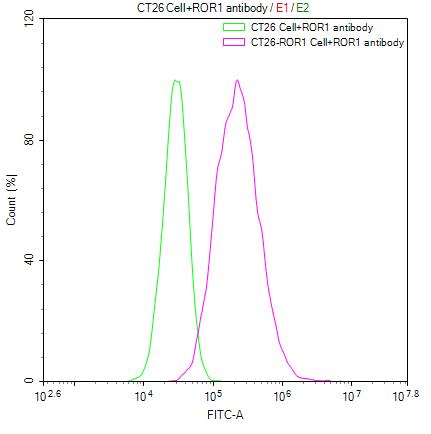
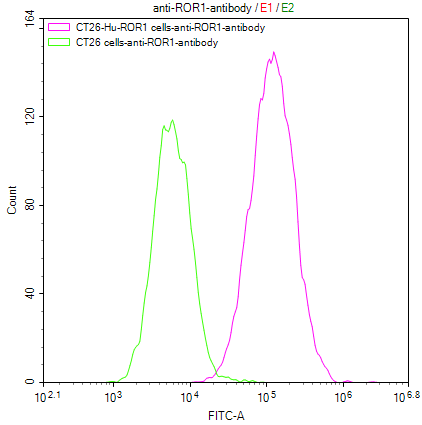
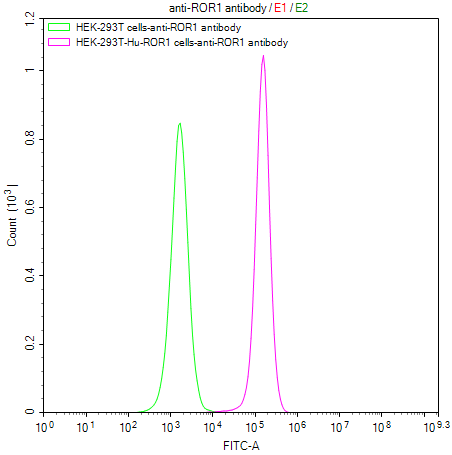
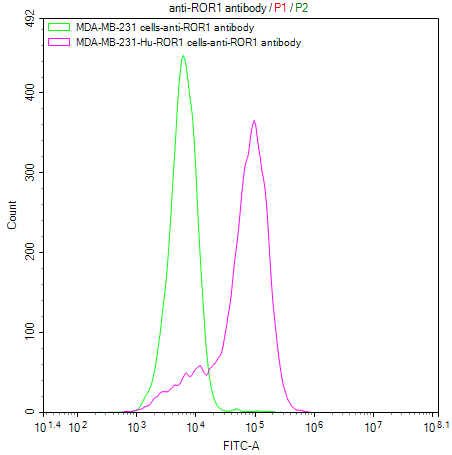


Comments
Leave a Comment