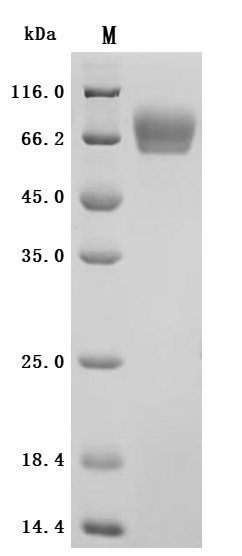
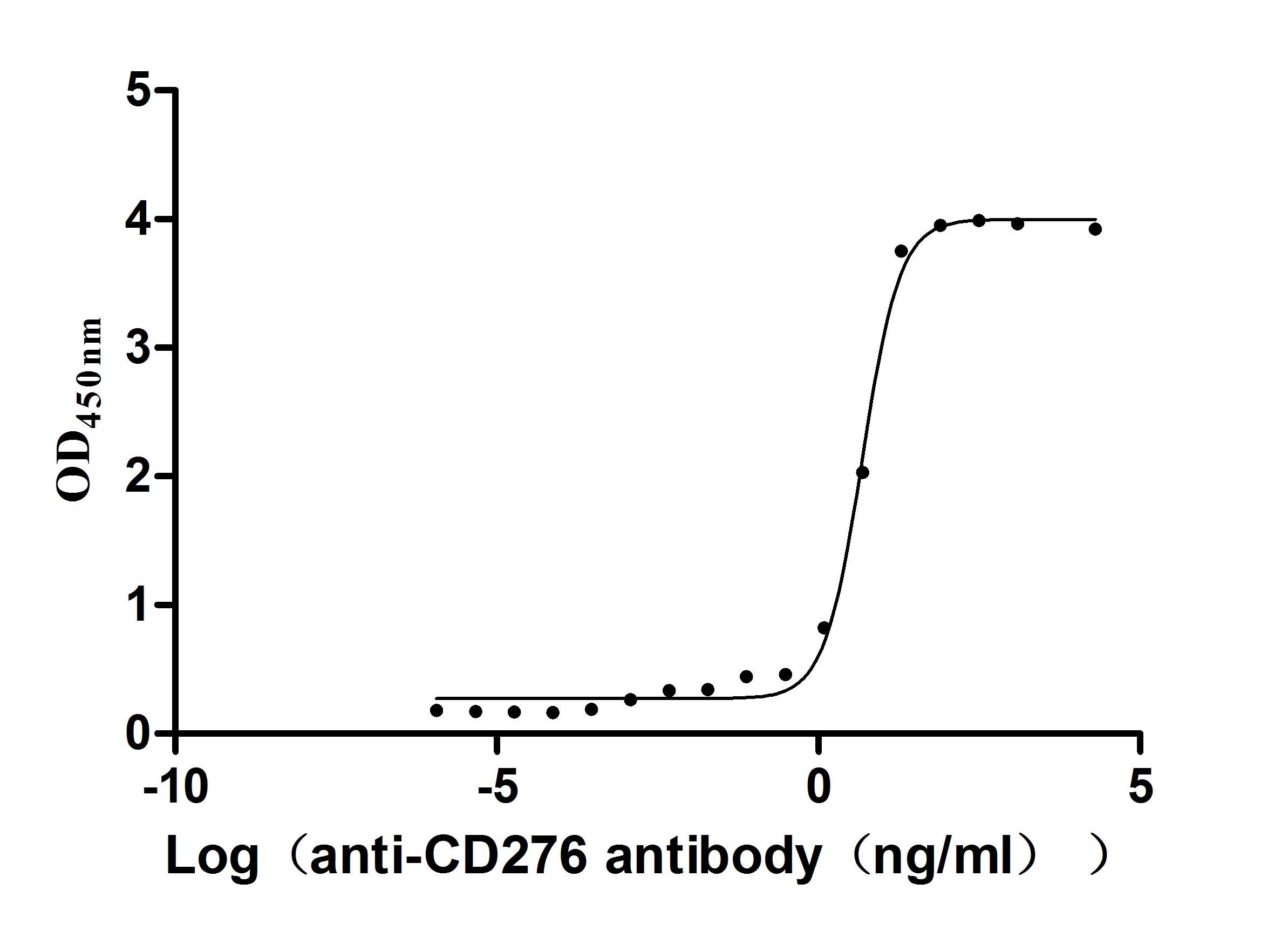
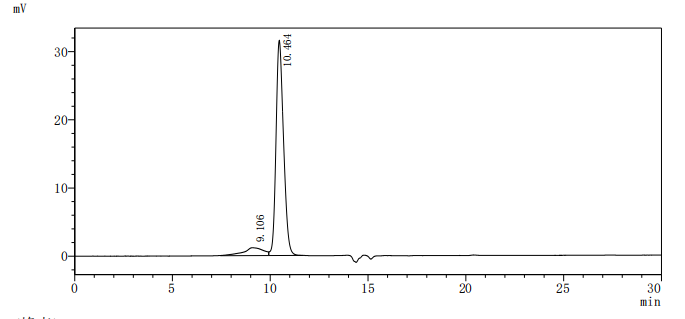
The recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD276 protein is a functionally active molecule produced in a mammalian expression system to ensure proper folding and post-translational modifications. Covering amino acids 29 to 465 of the native sequence, it is designed with a C-terminal 10xHis tag to support efficient purification and analytical detection. Supplied as a lyophilized powder, the recombinant CD276 protein demonstrates high purity, greater than 95% by SDS-PAGE and over 90% by SEC-HPLC. Endotoxin content is strictly controlled to be less than 1.0 EU/µg, as verified by the LAL assay. Its activity has been validated through a binding ELISA, where the immobilized protein at 2 μg/mL specifically interacts with the anti-CD276 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA733578MA1HU), producing an EC50 in the range of 4.299 to 5.373 ng/mL. These features make it a dependable reagent for studies focused on immune regulation, tumor immunology, or therapeutic antibody development involving CD276.
The CD276 protein, also known as B7-H3, plays an essential role in immunological regulation, with significant implications in physiological processes and pathological conditions, particularly in cancer biology. In Macaca fascicularis, CD276 is recognized for its ability to modulate immune responses, influencing tumor progression and immune evasion.
CD276 is implicated in immunosuppressive pathways predominantly mediated by the mTORC1 pathway, which has been shown to upregulate CD276 expression in response to pathological stimuli, such as infections [1]. Elevated levels of CD276 in the tumor microenvironment correlate with poor immune responses, facilitating tumor growth and metastasis by impairing the function of T cells and other immune cells [1][2]. The differential expression of CD276 in malignant tissues compared to normal tissues reinforces its potential as a valuable target for immunotherapy, notably utilizing CAR-T cell technologies, which have demonstrated effectiveness in animal models [3][4].
Furthermore, CD276 is involved in immune checkpoint regulation, akin to other members of the B7 family of immune modulators [5]. Its overexpression in various cancers suggests its role in immune evasion, supporting tumor survival against host immune responses [6]. In experiments utilizing CD276-targeting therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies, a significant reduction in tumor growth has been observed, linking CD276 to enhanced anti-tumor immunity through targeted approaches [7].
Studies indicate that CD276 serves not only as a tumor marker but also plays a mechanistic role in vascular processes associated with tumor development. In hepatocellular carcinoma models, CD276 was found to promote vasculogenic mimicry, aiding tumor nutrient acquisition while simultaneously reducing immune surveillance [6].
From an evolutionary biology perspective, the genetic and molecular characteristics of CD276 in Macaca fascicularis provide insights into its functionality across different species, affirming its conserved role in immune processes critical to both human and primate health. Understanding CD276's structure and signal transduction pathways reveals evolutionary adaptations that enhance its immunoregulatory functions, reflecting the evolutionary pressures shaping immune system diversity [8][9].
References:
[1] Q. Dong, Y. Sun, et al. Lamtor1/mtorc1 promotes cd276 to induce immunosuppression via pi3k/akt/mmp signaling pathway in clostridium perfringens–induced necrotic enteritis of laying hens. Poultry Science, vol. 103, no. 12, p. 104216, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psj.2024.104216
[2] B. Amend, L. Buttgereit, et al. Regulation of immune checkpoint antigen cd276 (b7-h3) on human placenta-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in gmp-compliant cell culture media. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 24, no. 22, p. 16422, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216422
[3] Y. Xuan, Y. Sheng, et al. Targeting cd276 by car-t cells induces regression of esophagus squamous cell carcinoma in xenograft mouse models. Translational Oncology, vol. 14, no. 8, p. 101138, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101138
[4] S. Grote, K. Chan, et al. Cd276 as a novel car nk‐92 therapeutic target for neuroblastoma. Advances in Cell and Gene Therapy, vol. 4, no. 1, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/acg2.105
[5] S. Seaman, Z. Zhu, et al. Eradication of tumors through simultaneous ablation of cd276/b7-h3-positive tumor cells and tumor vasculature. Cancer Cell, vol. 31, no. 4, p. 501-515.e8, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2017.03.005
[6] R. Cheng, W. Bi, et al. <p>cd276 promotes vasculogenic mimicry formation in hepatocellular carcinoma via the pi3k/akt/mmps pathway. Oncotargets and Therapy, vol. Volume 13, p. 11485-11498, 2020. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s271891
[7] D. Loo, R. Alderson, et al. Development of an fc-enhanced anti–b7-h3 monoclonal antibody with potent antitumor activity. Clinical Cancer Research, vol. 18, no. 14, p. 3834-3845, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-12-0715
[8] N. Osada, K. Matsudaira, Y. Hamada, & S. Malaivijitnond. Testing sex-biased admixture origin of macaque species using autosomal and x-chromosomal genomic sequences. Genome Biology and Evolution, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evaa209
[9] L. Tian, Y. Xia, H. Flores, M. Campbell, S. Moerlein, & J. Perlmutter. Neuroimaging analysis of the dopamine basis for apathetic behaviors in an mptp-lesioned primate model. Plos One, vol. 10, no. 7, p. e0132064, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132064