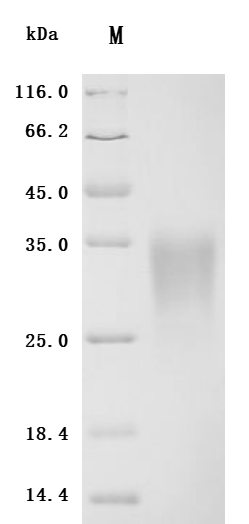
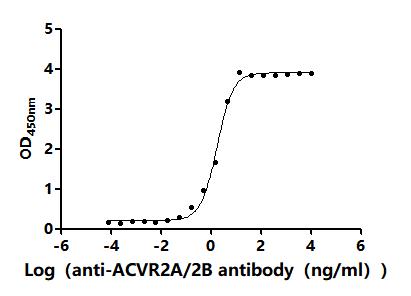
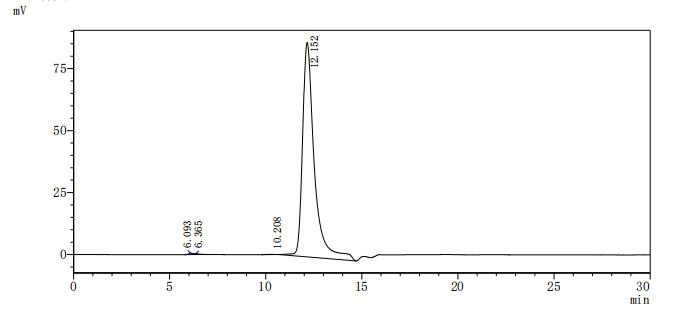
The recombinant mouse ACVR2A protein is expressed in mammalian cells with ten C-terminal His-tags. Its expression region encodes the Ala20-Pro135 of the mouse ACVR2A protein. Its purity is over 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE and SEC-HPLC. It is an active protein as validated in a functional ELISA where immobilized mouse ACVR2A at 2 μg/mL can bind the anti-ACVR2A recombinant antibody (CSB-RA623829MA1HU), with the EC50 of 1.562-1.966 ng/mL.
The mouse ACVR2A protein, a member of the activin receptor family, plays a multifaceted role in various biological processes, including apoptosis, immune response, and development. ACVR2A functions primarily as a transmembrane receptor that mediates signal transduction pathways initiated by activins, which are involved in numerous physiological and pathological processes.
One significant role of ACVR2A is its involvement in apoptosis regulation. Research indicates that ACVR2A is targeted by microRNA-21, leading to its downregulation in asthmatic models. This downregulation is reversed upon treatment with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which suggests that ACVR2A has protective effects against cell injury, particularly in bronchial epithelial cells [1]. The anti-apoptotic role of ACVR2A is further supported by findings that its expression levels correlate with the recovery of injured cells, indicating its importance in cell survival mechanisms [1].
In the context of cancer, ACVR2A has been implicated in tumor progression and metastasis. Studies have shown that mutations in the ACVR2A gene can lead to a loss of function, which is associated with increased metastatic potential in colorectal cancer [2][3]. Specifically, ACVR2A inhibits bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling, which is known to promote cancer cell migration and invasion. This suggests that ACVR2A acts as a tumor suppressor by regulating pathways that control cell proliferation and migration [2][3]. Furthermore, its downregulation has been linked to poor prognosis in various cancers, highlighting its critical role in tumor biology [2].
ACVR2A also plays a crucial role in developmental processes. In mouse models, ACVR2A is essential for craniofacial development, where it is involved in maintaining cell viability and proper patterning of cranial structures [4]. The ACVR2A-mediated signaling pathways are vital for the differentiation and function of various cell types during embryogenesis and tissue development [5]. Additionally, ACVR2A's interaction with other receptors, such as ACVR2B, is necessary for normal bone formation and homeostasis, further emphasizing its importance in developmental biology [6]. Moreover, ACVR2A has been shown to modulate immune responses. In liver fibrosis models, the blockade of ACVR2A signaling has been associated with reduced activation of hepatic stellate cells, indicating its role in regulating inflammatory responses within the liver [7].
References:
[1] C. Li, Z. Xu, X. Fan, H. Chen, Q. Yu, S. Fang, et al. Microrna-21 mediates the protective effects of mesenchymal stem cells derived from ipscs to human bronchial epithelial cell injury under hypoxia, Cell Transplantation, vol. 27, no. 3, p. 571-583, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963689718767159
[2] C. Zhuo, D. Hu, J. Li, H. Yu, X. Lin, Y. Chen, et al. Downregulation of activin a receptor type 2a is associated with metastatic potential and poor prognosis of colon cancer, Journal of Cancer, vol. 9, no. 19, p. 3626-3633, 2018. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.26790
[3] J. Wang. Identification of 8 candidate microsatellite instability loci in colorectal cancer and validation of the acvr2a mechanism in the tumor progression, Scientific Reports, vol. 14, no. 1, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-62753-1
[4] R. Albertson, T. Payne-Ferreira, J. Postlethwait, & P. Yelick. Zebrafish acvr2a and acvr2b exhibit distinct roles in craniofacial development, Developmental Dynamics, vol. 233, no. 4, p. 1405-1418, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.20480
[5] A. Weiß and L. Attisano. The tgfbeta superfamily signaling pathway, Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews Developmental Biology, vol. 2, no. 1, p. 47-63, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1002/wdev.86
[6] M. Zhao, S. Harris, D. Horn, Z. Geng, R. Nishimura, G. Mundy, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein receptor signaling is necessary for normal murine postnatal bone formation, The Journal of Cell Biology, vol. 157, no. 6, p. 1049-1060, 2002. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200109012
[7] H. Zhou, B. Ju, Y. Nie, B. Song, Y. Xu, & P. Gao. Adenovirus‑mediated knockdown of activin a receptor type�2a attenuates immune‑induced hepatic fibrosis in mice and inhibits interleukin‑17‑induced activation of primary hepatic stellate cells, International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2018. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3600