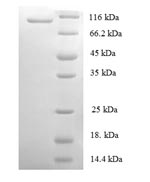
The generation of recombinant human DNA replication licensing factor MCM2 starts with the isolation of the target gene that codes for the 2-904aa of the human MCM2. This gene is cloned into an expression vector and transformated into E. coli cells. The successfully transformed E. coli cells are selected and induced to express the recombinant MCM2 protein, which is harvested from the cell lysate. The recombinant MCM2 protein is purified using affinity chromatography. The final step involves analyzing the purity of the recombinant MCM2 protein using SDS-PAGE. Its purity exceeds 90%.
Human DNA replication licensing factor MCM2 is a crucial component involved in the initiation of DNA replication. MCM2 is part of the MCM2-7 complex, which plays a vital role in the licensing of DNA replication origins, ensuring that DNA is replicated only once per cell cycle [1]. This licensing process involves the loading of the MCM2-7 complex onto DNA, which is a prerequisite for DNA replication to occur [2]. This loading process is essential for restricting DNA replication to once per cell cycle. The MCM2-7 proteins, including MCM2, bind to replication origins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle, along with other proteins like ORC, Cdc6, and Cdt1, to form the prereplication complex necessary for replication origin activation [3].
Furthermore, MCM2 interacts with other factors like ESRG to regulate cell survival, self-renewal, and pluripotency [4]. The loading of the MCM2-7 complex onto DNA is a coordinated process that involves the assembly of double-hexameric MCM2-7 complexes around DNA during DNA replication origin licensing [5].
References:
[1] D. Remus, F. Beuron, G. Tolun, J. Griffith, E. Morris, & J. Diffley, Concerted loading of mcm2–7 double hexamers around dna during dna replication origin licensing, Cell, vol. 139, no. 4, p. 719-730, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.015
[2] C. Evrin, P. Clarke, J. Zech, R. Lurz, J. Sun, S. Uhleet al., A double-hexameric mcm2-7 complex is loaded onto origin dna during licensing of eukaryotic dna replication, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 106, no. 48, p. 20240-20245, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0911500106
[3] M. Snyder, X. Huang, & J. Zhang, The minichromosome maintenance proteins 2-7 (mcm2-7) are necessary for rna polymerase ii (pol ii)-mediated transcription, Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 284, no. 20, p. 13466-13472, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m809471200
[4] S. Li, H. Liu, W. Liu, N. Shi, M. Zhao, S. Wanggouet al., esrg is critical to maintain the cell survival and self-renewal/pluripotency of hpscs by collaborating with mcm2 to suppress p53 pathway, International Journal of Biological Sciences, vol. 19, no. 3, p. 916-935, 2023. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.79095
[5] Y. Ishimi, T. Sugiyama, R. Nakaya, M. Kanamori, T. Kohno, T. Enomotoet al., Effect of heliquinomycin on the activity of human minichromosome maintenance 4/6/7 helicase, Febs Journal, vol. 276, no. 12, p. 3382-3391, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07064.x