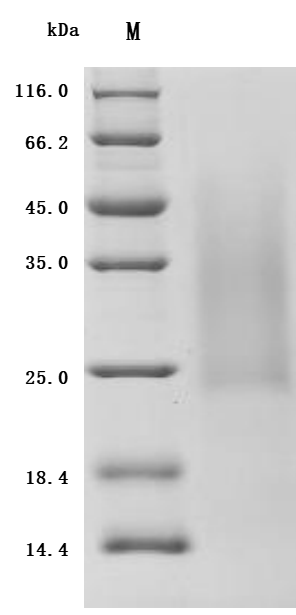
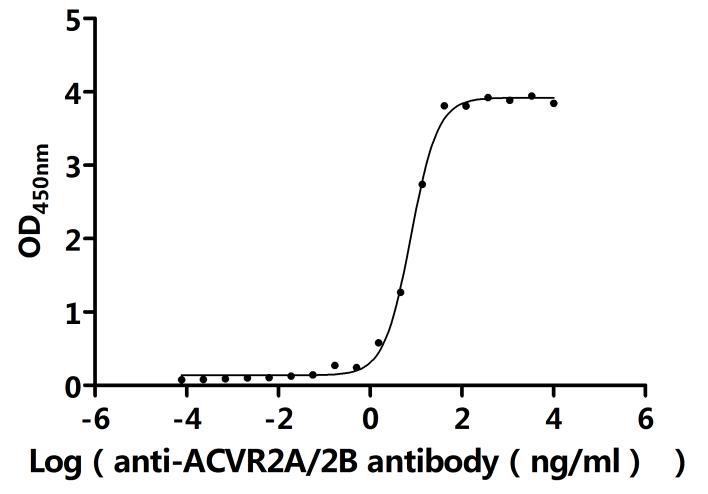
The recombinant mouse ACVR2B is produced by our yeast expression system. The target gene encoding the Ser19-Thr137 of mouse ACVR2B protein is expressed with a 10*His tag at the C-terminus. The purity of this recombinant mouse ACVR2B protein is over 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE. It contains low endotoxin less than 1.0 EU/ug as measured by the LAL method. It is an active protein. In a functional ELISA, this mouse ACVR2B at 2 μg/mL can bind the anti-ACVR2A&ACVR2B recombinant antibody (CSB-RA623829MA1HU), with the EC50 of 7.196-8.315 ng/mL.
The mouse ACVR2B protein, a member of the activin receptor family, plays a critical role in various physiological processes, particularly in muscle and bone homeostasis. ACVR2B functions primarily as a receptor for myostatin and activin A, both of which are negative regulators of muscle growth. The inhibition of ACVR2B signaling has been shown to promote muscle hypertrophy and improve bone mass, making it a significant target for therapeutic interventions in conditions such as cachexia, muscle wasting, and osteoporosis.
ACVR2B is mainly involved in muscle growth regulation. Studies have demonstrated that the blockade of ACVR2B signaling, particularly through the use of soluble ACVR2B (sACVR2B-Fc), leads to significant increases in muscle mass. Lee et al. reported that sACVR2B-Fc treatment resulted in greater than 50% muscle growth in mice within two weeks of administration, highlighting its potency as a myostatin inhibitor [1]. This decoy receptor effectively disrupts the myostatin/activin signaling pathway, which is crucial for maintaining muscle homeostasis [2].
ACVR2B is also implicated in bone metabolism. Research indicates that ACVR2B acts as a negative regulator of bone mass, with its inhibition leading to increased trabecular bone volume [3]. The administration of sACVR2B in mouse models of androgen deprivation led to significant bone mass increases, suggesting that targeting this receptor could be beneficial in treating osteoporosis [3].
In models of cancer cachexia, systemic blockade of ACVR2B ligands has been shown to improve survival rates by restoring muscle protein synthesis without adversely affecting oxidative capacity [4][5]. This suggests that ACVR2B plays a role not only in muscle maintenance but also in the broader context of metabolic health during disease states. Furthermore, the regulation of ACVR2B by microRNAs, such as miR-21, highlights its complex regulatory network and potential as a therapeutic target in various diseases, including cancer [6].
References:
[1] S. Lee, A. Lehar, C. Ly, Q. Pham, M. Michaud, R. Rydzik, et al. Functional redundancy of type i and type ii receptors in the regulation of skeletal muscle growth by myostatin and activin a, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 117, no. 49, p. 30907-30917, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2019263117
[2] S. Lee, T. Huynh, Y. Lee, S. Sebald, S. Wilcox-Adelman, N. Iwamori, et al. Role of satellite cells versus myofibers in muscle hypertrophy induced by inhibition of the myostatin/activin signaling pathway, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 109, no. 35, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1206410109
[3] B. Goh, V. Singhal, A. Herrera, R. Tomlinson, S. Kim, M. Faugère, et al. Activin receptor type 2a (acvr2a) functions directly in osteoblasts as a negative regulator of bone mass, Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 292, no. 33, p. 13809-13822, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m117.782128
[4] T. Nissinen, J. Degerman, M. Räsänen, A. Poikonen, S. Koskinen, E. Mervaala, et al. Systemic blockade of acvr2b ligands prevents chemotherapy-induced muscle wasting by restoring muscle protein synthesis without affecting oxidative capacity or atrogenes, Scientific Reports, vol. 6, no. 1, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32695
[5] T. Nissinen, J. Hentilä, F. Penna, A. Lampinen, J. Lautaoja, V. Fachada, et al. Treating cachexia using soluble acvr2b improves survival, alters mtor localization, and attenuates liver and spleen responses, Journal of Cachexia Sarcopenia and Muscle, vol. 9, no. 3, p. 514-529, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12310
[6] X. Gao, P. Zhao, J. Hu, H. Zhu, J. Zhang, Z. Zhou, et al. Microrna‐194 protects against chronic hepatitis b‐related liver damage by promoting hepatocyte growth via acvr2b, Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, vol. 22, no. 9, p. 4534-4544, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13714