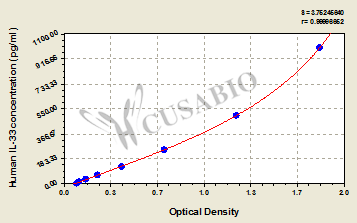
The human IL-33 ELISA Kit is engineered for accurate measurement of human IL-33 levels from samples including serum, plasma, or urine. It uses the Sandwich-ELISA mechanism in combination with the enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction to measure the IL-33 content in the sample. The color intensity is positively correlated with IL-33 content in the sample. The IL-33 concentration can be calculated according to the standard curve. This kit is tested with high sensitivity, strong specificity, good linearity, high precision and recovery, as well as lot-to-lot consistency.
IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of epithelial, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts and participates in innate and adaptive immunity by enhancing Th2 cytokines generation. It is secreted secondary to cell apoptosis and necrosis. It functions as an 'alarmin' released following cell necrosis to alert the immune system to tissue damage or stress. IL-33 binds to a heterodimeric receptor ST2/IL-1R4 and forms a complex with the IL-1RAcP, recruiting the adaptor protein MyD88 and activating transcription factors such as NF-κB via TRAF6, IRAK-1/4, and MAP kinases and inducing the generation of inflammatory mediators. IL-33 drives the pathogenesis of Th2-related diseases such as asthma, atopic dermatitis, and anaphylaxis because it strongly induces Th2 cytokine production. However, IL-33 has shown various protective effects on cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, obesity, and type 2 diabetes.