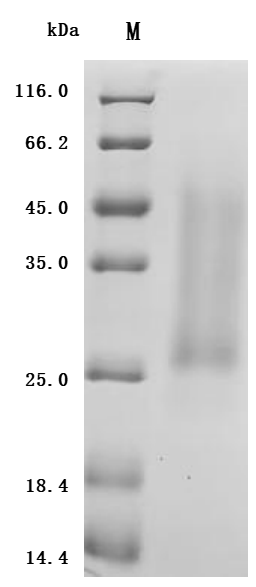
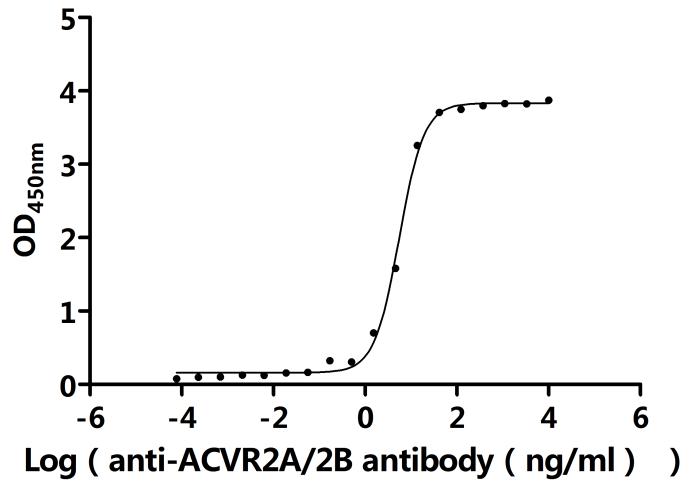
The product CSB-YP001260HU1 is a recombinant human ACVR2A protein produced in a eukaryotic expression system (yeast). Its expression region codes for the 20-135aa of the human ACVR2A protein. Its purity is over 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE. The endotoxin content of this ACVR2A protein is less than 1.0 EU/ug as measured by the LAL method. This recombinant human ACVR2A protein has been validated to be biologically active through a functional ELISA, where immobilized human ACVR2A at 2 μg/mL can bind the anti-ACVR2A&ACVR2B recombinant antibody (CSB-RA623829MA1HU), with the EC50 of 5.139-5.959 ng/mL.
The human ACVR2A protein is a crucial component of the TGF-β superfamily of receptors. It is a transmembrane receptor that plays a significant role in various cellular processes, including cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. ACVR2A is primarily involved in mediating the effects of activins, which regulate numerous biological functions such as embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and immune responses [1][2].
Structurally, ACVR2A consists of an extracellular domain, a single transmembrane domain, and an intracellular kinase domain. The binding of activin to ACVR2A initiates a cascade of intracellular signaling events, primarily through the phosphorylation of downstream Smad proteins and other non-Smad signaling pathways, which are critical for the regulation of genes involved in various physiological processes, including the synthesis of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) [1][3][4].
Mutations in the ACVR2A gene are notably prevalent in various cancers, particularly colorectal cancer (CRC). Studies have identified ACVR2A as one of the most frequently mutated genes in hypermutated colorectal cancers, with a significant association with microsatellite instability (MSI) [2][5]. The mutations often result in truncated proteins that fail to activate downstream signaling pathways, contributing to tumor progression and metastasis [3][5]. Loss of ACVR2A expression has been linked to advanced stages of cancer, lymphatic invasion, and poor prognosis, highlighting its potential role as a tumor suppressor gene [2][6][7].
ACVR2A is also implicated in other physiological and pathological conditions. It has been shown to be involved in the regulation of Th17 cell differentiation, which is crucial for immune responses [8]. Furthermore, ACVR2A expression levels can vary in different tissues and under various pathological conditions, such as asthma, where its expression may decrease in epithelial cells [9].s
References:
[1] L. Roten, M. Johnson, S. Forsmo, E. Fitzpatrick, T. Dyer, S. Brennecke, et al. Association between the candidate susceptibility gene acvr2a on chromosome 2q22 and pre-eclampsia in a large norwegian population-based study (the hunt study), European Journal of Human Genetics, vol. 17, no. 2, p. 250-257, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejhg.2008.158
[2] O. Menyhárt, T. Kakisaka, H. Uetake, A. Goel, & B. Győrffy. Uncovering potential therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer by deciphering mutational status and expression of druggable oncogenes, Cancers, vol. 11, no. 7, p. 983, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070983
[3] L. Zhao, J. Zhang, X. Qu, Y. Yang, Z. Gong, Y. Yang, et al. Microsatellite instability-related ACVR2A Mutations Partially Account for Decreased Lymph Node Metastasis in MSI-H Gastric Cancers, Oncotargets and Therapy, vol. Volume 13, p. 3809-3821, 2020. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s247757
[4] O. Olsen, K. Wader, H. Hella, A. Mylin, I. Turesson, I. Nesthus, et al. Activin a inhibits bmp-signaling by binding acvr2a and acvr2b, Cell Communication and Signaling, vol. 13, no. 1, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-015-0104-z
[5] Z. Li, Y. Jia, H. Zhu, H. Yuan, X. Xing, Y. Xin, et al. Genomic landscape of microsatellite instability in chinese tumors: a comparison of chinese and tcga cohorts, International Journal of Cancer, vol. 151, no. 8, p. 1382-1393, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.34119
[6] C. Zhuo, D. Hu, J. Li, H. Yu, X. Lin, Y. Chen, et al. Downregulation of activin a receptor type 2a is associated with metastatic potential and poor prognosis of colon cancer, Journal of Cancer, vol. 9, no. 19, p. 3626-3633, 2018. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.26790
[7] J. Bauer, Ö. Özden, N. Akagi, T. Carroll, D. Principe, J. Staudacher, et al. Activin and tgfβ use diverging mitogenic signaling in advanced colon cancer, Molecular Cancer, vol. 14, no. 1, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-015-0456-4
[8] H. Ihn, D. Kim, S. Oh, C. Moon, J. Chung, H. Song, et al. Identification ofacvr2aas a th17 cell-specific gene induced during th17 differentiation, Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry, vol. 75, no. 11, p. 2138-2141, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.110436
[9] G. Tang, C. Li, Y. Yao, Z. Xu, M. Deng, S. Wang, et al. Micrornas involved in asthma after mesenchymal stem cells treatment, Stem Cells and Development, vol. 25, no. 12, p. 883-896, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2015.0339