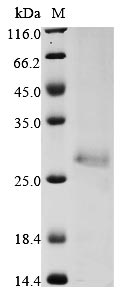
Recombinant Human E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ZNRF3 is produced through the baculovirus expression system and contains amino acids 56 to 219 of the protein. A C-terminal 6xHis-tag is attached to this partial protein, which makes purification and detection more straightforward. The product achieves purity levels above 90%, confirmed by SDS-PAGE analysis. This appears to provide high-quality material for research focused on understanding ubiquitin-mediated processes.
ZNRF3 functions as an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that's involved in regulating Wnt signaling pathways. The protein promotes ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of Frizzled receptors. This activity seems critical for modulating cellular signaling and maintaining tissue homeostasis. Studying this protein may be important for understanding how cells communicate and how signaling pathways contribute to various physiological processes.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Human ZNRF3 is a large transmembrane E3 ubiquitin ligase whose catalytic activity depends on its C-terminal RING domain, which is responsible for ubiquitin transfer. The 56-219aa fragment represents the extracellular portion of the full-length protein and almost certainly does not contain the critical RING domain. Therefore, this fragment itself lacks E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. While the baculovirus expression system may support proper folding of this extracellular domain fragment, its biological function remains unknown, and it is incapable of catalytic activity.
1. Antibody Development and Validation
This application is highly suitable as antibody development relies on antigenic sequence recognition rather than functional activity. The fragment can generate antibodies specific to the 56-219aa region of ZNRF3's extracellular domain.
2. Biochemical Characterization and Stability Studies
These studies can characterize physical properties but cannot assess E3 ligase activity. Thermal stability, solubility, and oligomerization state can be analyzed, but results will only reflect this fragment's behavior, not the full protein's functionality.
3. ELISA-Based Quantitative Assays
This application is well-suited as it depends on immunoreactivity rather than catalytic function. The fragment can serve as an antigen for detection assays targeting the extracellular domain.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This ZNRF3 fragment (56-219aa) is a partial, functionally undefined protein portion that lacks the critical RING domain required for E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. It is suitable for Applications 1 and 3 (antibody development and ELISA), which rely on immunoreactivity rather than function. Application 2 can proceed, but only for basic biophysical characterization of this specific fragment. While the extracellular domain may mediate some interactions, without the full protein context and known functional domains, any interaction data would be difficult to interpret biologically. There is a high risk of identifying non-specific or biologically irrelevant binding partners. Researchers should be aware that this fragment represents only a small portion of ZNRF3, and results cannot be extrapolated to understand the full protein's biological functions. For ZNRF3 functional studies, a full-length protein containing the RING domain is essential.