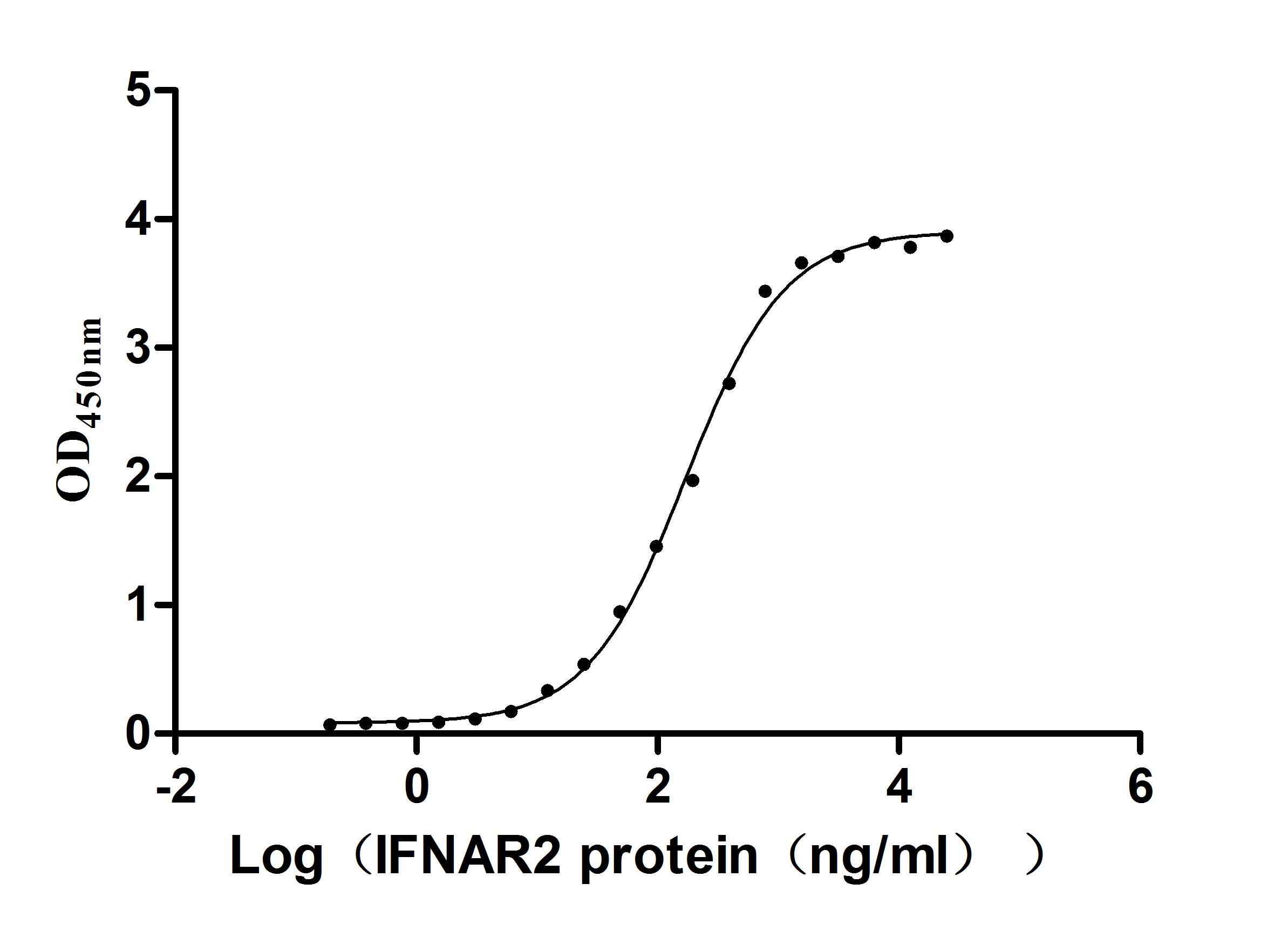
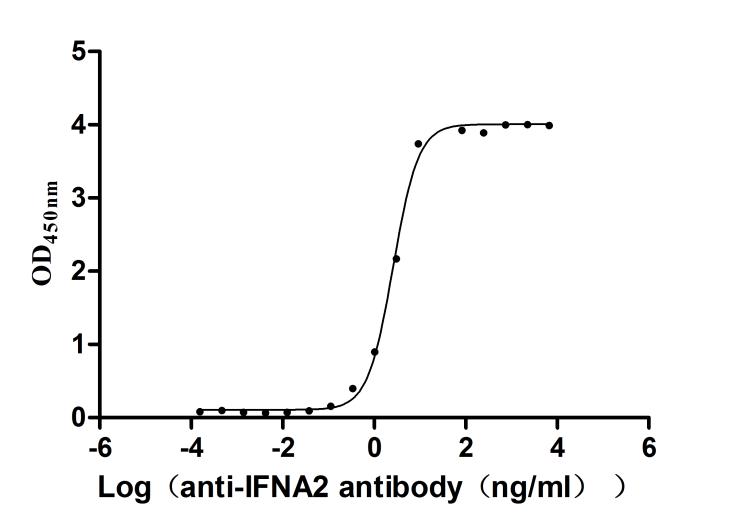
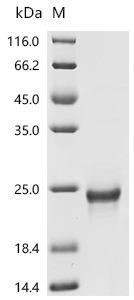
The recombinant human IFNA2 protein is a mammalian cell-derived cytokine construct encompassing amino acids 24-188 of mature human interferon alpha-2, featuring an N-terminal 10xHis affinity tag to optimize purification workflows while preserving C-terminal structural integrity critical for receptor engagement. This lyophilized formulation exhibits >95% purity verified by SDS-PAGE, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency for experimental applications requiring precise dosing. Functional validation through ligand and antibody interaction assays demonstrates its dual binding capabilities. When immobilized at 2 μg/mL, it engages both its receptor IFNAR2 (CSB-MP011047HU) and the anti-IFNA2 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA365593MA1HU) with an EC50 of 154.2-191.9 ng/mL and 2.366-2.818 ng/mL, respectively. This engineered IFNα2 variant serves as a versatile reagent for studying type I interferon signaling mechanisms, antiviral response pathways, and therapeutic antibody development, particularly in assays requiring simultaneous assessment of receptor engagement and immunodetection efficiency.
The human IFNA2 protein is part of the type I interferon family, which consists of thirteen subtypes in humans and is categorized as a cytokine that plays essential roles in the innate immune response against viral infections and certain tumors [1][2]. IFNA2's function in the immune response is primarily mediated through its interaction with specific receptors, triggering the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, which leads to the expression of various genes that possess antiviral and antiproliferative properties [3]. This mechanism of action underscores the significance of IFNA2 in both innate and adaptive immunity [4], and its roles include the enhancement of cytotoxic activities of natural killer (NK) cells and promoting the maturation of dendritic cells [4].
Research indicates that IFNA2 is not only critical for antiviral defense but also exhibits potential antitumor activities. It has been found to inhibit tumor proliferation in various experimental models, suggesting its use as a therapeutic agent in cancer treatment [5][3]. The modulatory functions of IFNA2 imply that it can impact tumor microenvironments and promote apoptosis in malignant cells, further warranting its investigation in cancer immunotherapy [6].
References:
[1] R. Bis, S. Singh, J. Cabello‐Villegas, & K. Mallela. Role of benzyl alcohol in the unfolding and aggregation of interferon α-2a. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, vol. 104, no. 2, p. 407-415, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.24105
[2] Z. Karakoese, M. Ingola, B. Sitek, U. Dittmer, & K. Sutter. Ifnα subtypes in hiv infection and immunity. Viruses, vol. 16, no. 3, p. 364, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16030364
[3] E. Fernandes, E. Soans, J. Xu, M. Kieliszewski, & S. Evan. Novel fusion proteins of interferon α2b cause growth inhibition and induce jak-stat signaling in melanoma. Journal of Immunotherapy, vol. 33, no. 5, p. 461-466, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1097/cji.0b013e3181d32e59
[4] M. Strengell, I. Julkunen, & S. Matikainen. Ifn-α regulates il-21 and il-21r expression in human nk and t cells. Journal of Leukocyte Biology, vol. 76, no. 2, p. 416-422, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.1003488
[5] Z. Liu, Y. Huang, et al. Establishment of an immunogenic cell death-related model for prognostic prediction and identification of therapeutic targets in endometrial carcinoma. Aging, 2024. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.205647
[6] K. Frey, A. Zivanovic, K. Schwager, & D. Neri. Antibody-based targeting of interferon-alpha to the tumor neovasculature: a critical evaluation. Integrative Biology, vol. 3, no. 4, p. 468-478, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0ib00099j