CUSABIO’s Human lipopolysaccharide-binding protein (LBP) ELISA Kit is suitable for the quantitative detection of LBP content in human serum, plasma, or tissue homogenates. LBP is a carrier protein of the endotoxins' recognition by the host. It is produced by hepatocytes and released into the bloodstream as a consequence of Gram-negative infection. LBP conveys LPS to the cellular surface, forming a ternary complex with a cluster of CD14. CD14 facilitates the transfer of LPS to the TLR4/MD2 complex, activating LPS-TLR4 signaling that elicits proinflammatory responses. It is significantly up-regulated during acute-phase reaction following the initial inflammatory responses, promoting, along with (bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein), non-inflammatory clearance of LPS, and ultimate resolution of LPS-induced inflammation. Additionally, LBP mediates endothelial dysfunction and is required for apoptosis in tubular cells.
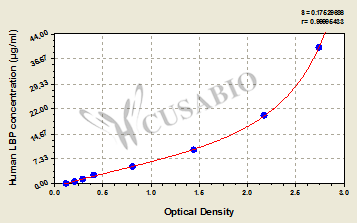
The detection mechanism of this kit is based on the sandwich ELISA technique and enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction. The formed pre-coated LBP antibody/LBP/Biotin-conjugated LBP antibody complex is labeled by HRP-avidin and then develops a color reaction after the addition of The TMB substrate solution. The color intensity can be measured at 450 nm via a microplate reader.