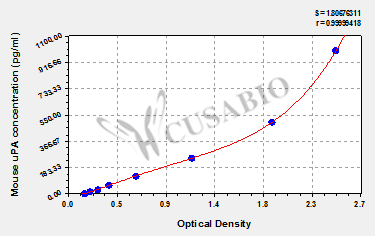
CUSABIO's mouse urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) ELISA kit is an in vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative measurement of mouse uPA in serum, plasma, or tissue homogenates. This assay uses the sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique in combination with the enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction to quantify the analyte in the sample. The color develops positively to the amount of uPA in samples. The color intensity is measured at 450 nm via a microplate reader.
uPA (PLAU) is a serine protease that cleaves and activates plasminogen, which triggers a proteolytic cascade to regulate extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins. The uPA and uPAR interaction is involved in various cellular activities, including cell proliferation, adhesion, invasion, and survival but is also linked to a broad range of pathological conditions including cancer, atherosclerosis, and kidney disease. In cancer, enhanced levels of the tumor-associated serine protease uPA and its receptor uPAR are linked to tumor progression, metastasis, and shortened survival in patients afflicted with this disease.