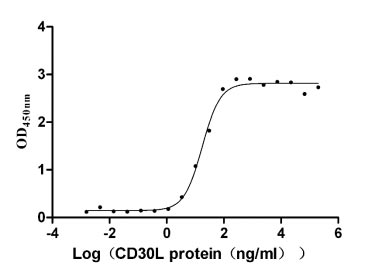
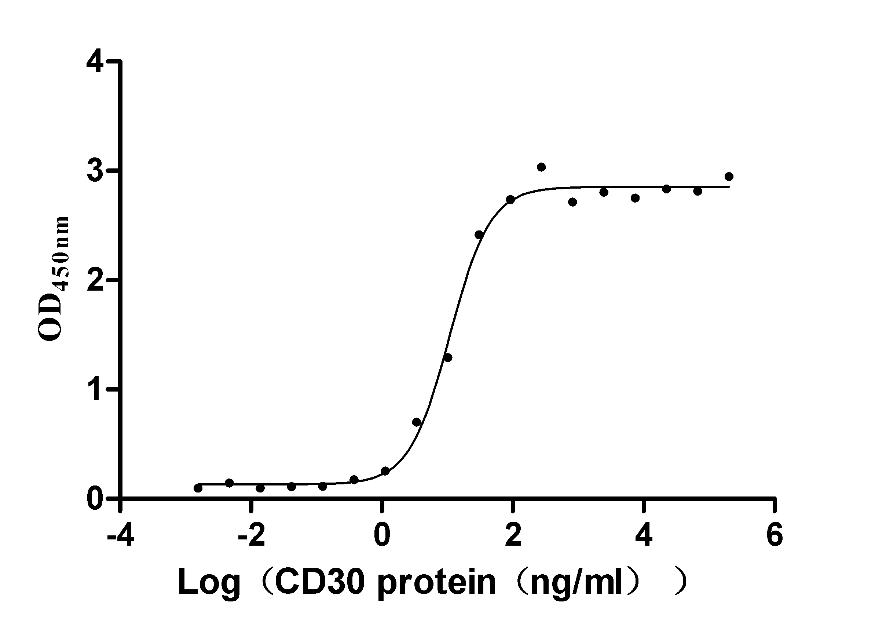
The recombinant human TNFRSF8 protein is expressed in mammalian cells. The gene segment encoding the 19-379aa of the human TNFRSF8 is co-ligated into a plasmid with an N-terminal 10xHis-tag gene and a C-terminal Myc-tag gene. Transfection of mammalian cells with the recombinant plasmid is followed by selective antibiotic treatment 24 hours later to identify successful transfections. The transfected cells are cultured for protein expression. The TNFRSF8 protein is purified from cell lysate using affinity chromatography. The recombinant TNFRSF8 protein's purity exceeds 95%, as determined by SDS-PAGE, and endotoxin levels are below 1.0 EU/μg, as measured by the LAL method. It is an active protein as confirmed in a functional ELISA, in which the TNFRSF8 binds to the TNFSF8 (CSB-MP023996HU1c9) with an EC50 of 14.96-20.25 ng/mL.
Human TNFRSF8 (or CD30) is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein primarily expressed on activated T and B lymphocytes, particularly in the context of immune activation and inflammation [1][2]. It is involved in various cellular processes, including cell proliferation, apoptosis, and immune responses.
The activation of TNFRSF8 occurs upon binding with its ligand, TNFSF8 (or CD30L). This interaction leads to receptor trimerization, which is essential for initiating downstream signaling pathways, particularly the NF-κB pathway that promotes cell survival and proliferation, as well as drives pro-inflammatory cytokine production [3][4]. Moreover, TNFRSF8 regulates apoptosis, with studies indicating that it can promote apoptotic signaling through the activation of NF-κB complexes [5][6].
TNFRSF8 is notably expressed in various hematological malignancies, including Hodgkin lymphoma and anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Its expression is associated with the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin lymphoma [2][4]. Additionally, TNFRSF8 has been identified as a potential therapeutic target, with monoclonal antibodies designed to engage CD30 showing promise in treating malignancies characterized by its overexpression [2][3]. TNFRSF8 is also involved in chronic inflammatory conditions. Its expression has been linked to the remodeling of pulmonary vascular endothelium in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [7].
References:
[1] Z. Li. Mechanism of action and therapeutic targeting of cd30 molecule in lymphomas, Frontiers in Oncology, vol. 13, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2023.1301437
[2] M. Veyri, J. Spano, F. Bras, A. Marcelin, & E. Todesco. cd30 as a therapeutic target in adult haematological malignancies: where are we now?, British Journal of Haematology, vol. 201, no. 6, p. 1033-1046, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.18841
[3] J. He. Antibody–drug conjugates in cancer therapy: mechanisms and clinical studies, Medcomm, vol. 5, no. 8, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1002/mco2.671
[4] E. Leroyer, C. Ziegler, C. Moulin, A. Campidelli, C. Jacquet, M. Rubio, et al. Filling the gap: the immune therapeutic armamentarium for relapsed/refractory hodgkin lymphoma, Journal of Clinical Medicine, vol. 11, no. 21, p. 6574, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11216574
[5] M. Wang, D. Windgassen, & E. Papoutsakis. A global transcriptional view of apoptosis in human t-cell activation, BMC Medical Genomics, vol. 1, no. 1, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1186/1755-8794-1-53
[6] M. Gaisawat, S. Lopez-Escalera, C. MacPherson, M. Iskandar, T. Tompkins, & S. Kubow. Probiotics exhibit strain-specific protective effects in t84 cells challenged with clostridioides difficile-infected fecal water, Frontiers in Microbiology, vol. 12, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.698638
[7] P. Sibilio. Correlation-based network integration of lung rna sequencing and dna methylation data in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Heliyon, vol. 10, no. 10, p. e31301, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31301