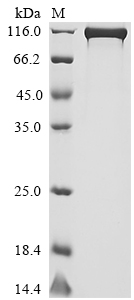
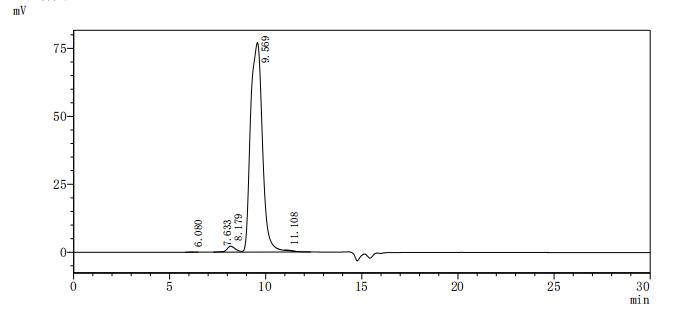
The recombinant human DPP4 protein with an N-terminal hFc-Flag-tag and a C-terminal Myc-tag is expressed using a mammalian cell system. The DPP4 gene fragment (29-766aa) with the tag gene is cloned into an expression vector and introduced into mammalian cells. Protein expression is induced by IPTG. The cells are lysed to extract the DPP4 protein. Ni-NTA affinity chromatography is employed to purify the recombinant DPP4 proteins, utilizing the His tag's affinity for nickel ions. The recombinant DPP4 protein is eluted and analyzed using SDS-PAGE, with a purity of exceeds 90%.
DPP4 is a serine protease enzyme that plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism and is primarily known for its involvement in the inactivation of incretin hormones, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) [1][2]. These incretin hormones are secreted in response to food intake and are essential for stimulating insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, thereby regulating blood glucose levels. The rapid degradation of these hormones by DPP4 results in a short half-life, which limits their effectiveness in glucose regulation [3].
DPP4 is expressed in various tissues, including the pancreas, liver, kidney, and immune cells, and exists in both membrane-bound and soluble forms [1][4]. Elevated DPP4 activity has been associated with inflammatory conditions, and its inhibition may have therapeutic implications in managing both diabetes and inflammatory diseases [5][6].
References:
[1] R. Yin, Y. Xu, X. Wang, L. Yang, & D. Zhao, Role of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in antidiabetic treatment, Molecules, vol. 27, no. 10, p. 3055, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27103055
[2] M. Kishimoto, Teneligliptin: a dpp-4 inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, Diabetes Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity Targets and Therapy, p. 187, 2013. https://doi.org/10.2147/dmso.s35682
[3] Y. Kang and C. Jung, Cardiovascular effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, Endocrinology and Metabolism, vol. 31, no. 2, p. 258, 2016. https://doi.org/10.3803/enm.2016.31.2.258
[4] H. Noels, W. Theelen, M. Sternkopf, V. Jankowski, J. Moellmann, S. Kraemer, et al. Reduced post-operative dpp4 activity associated with worse patient outcome after cardiac surgery, Scientific Reports, vol. 8, no. 1, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30235-w
[5] D. Abrahami, A. Douros, H. Yin, O. Yu, C. Renoux, A. Bittonet al., Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and incidence of inflammatory bowel disease among patients with type 2 diabetes: population based cohort study, BMJ, p. k872, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k872
[6] D. Avcı, Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and inflammation: dpp-4 inhibitors improve mean pleatelet volume and gamma glutamyl transferase level, Journal of Biosciences and Medicines, vol. 07, no. 02, p. 42-53, 2019. https://doi.org/10.4236/jbm.2019.72004