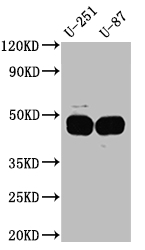
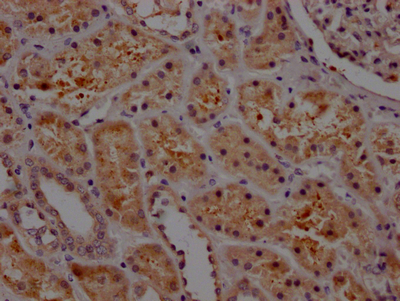
There are four main steps involved in the production of a SERPINE1 recombinant antibody: firstly, sequencing the SERPINE1 monoclonal antibody gene; secondly, cloning the gene into a plasmid vector; thirdly, introducing the recombinant vector into a host cell line; and finally, purifying the SERPINE1 recombinant monoclonal antibody from the cell culture supernatant via affinity chromatography. The SERPINE1 monoclonal antibody is derived from hybridomas that produce the SERPINE1 antibody, with a synthesized peptide from human SERPINE1 used as the immunogen during production. This SERPINE1 recombinant monoclonal antibody is recommended for ELISA, WB, and IHC applications in the detection of human SERPINE1 protein.
The SERPINE1 protein, also known as plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), is a type of serine protease inhibitor that plays a key role in the regulation of blood clotting and fibrinolysis. SERPINE1 regulates this process by inhibiting the activity of tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), which are responsible for the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin. By inhibiting these enzymes, SERPINE1 effectively blocks the fibrinolytic system and prevents the dissolution of the blood clot. SERPINE1 has also been implicated in a variety of other biological processes, including cell migration, adhesion, and proliferation. Dysregulation of SERPINE1 has been linked to a variety of diseases, including thrombosis, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.