What are Tumor Markers?
Tumor markers are biomarkers that exist in tumor cells or non-tumor cells in blood, urine, bone, and other organs indicating the occurrence, progression and recurrence of cancers. Most tumor markers are proteins, however, more recently, patterns of gene expression or changes of DNA and even long non-coding RNA are used as tumor markers. Meanwhile, tumor marker test is looked as a companion diagnostic test and its result should be further proved by biopsy or other ways.
The Functions of Tumor Markers
Tumor markers are applied in the following fields:
Detection: You can screen specific symptoms with specific tumor markers to dig out the invaders in time.
Diagnosis: To help the verification of specific tumors like some brain tumors.
Staging: You can supervise the stage of the tumor through the location of tumor markers, which are used to metastasis and monitor the escapers of tumor after treatment to prevent recurrence.
Confirmation of personalized medicine: To guide the drugs and reduce the damage of unnecessary treatments.
Prognosis: To verify the effect of the treatment and help to plan the future of patients after operation.
How to Classify Tumor Markers?
According to their chemical and immunological characteristics, tumor markers can be classified as oncofetal proteins like AFP (alpha-fetoprotein), tumor-associated antigens or carbohydrate antigens like CA (carcinoma antigen), hormones like HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), enzymes and isoenzymes like PAP (prostatic acid phosphatase), special serum proteins like ferritin, proto-oncogenes and anti-oncogenes like p53, others like BCR-ABL fusion gene.
According to their source, tumor markers can be also classified as markers produced by original tumor tissues like AFP or by the subsequent tissues like the receptor of interleukin and Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF).
The Mechanism and Detection of Tumor Markers
The traditional ways to check tumors include magnetic resonance imaging scans, mammography, ultrasonography, computed tomography, tumor marker test and biopsy. When taking a tumor marker test, some specific tumor markers will be tested in multiple samples taken over time by laboratory technicians using different immunoassay, biological assay or chemical assay. The mechanism and detections are as follows:
Activated or elevated expression of tumor markers indicates the existence of a cancer. We can employ qPCR or FISH technology to detect the expression of DNA/RNA, and WB, IHC or ELISA technology to detect the expression of protein.
Structural mutation of tumor markers indicates the existence of a cancer. Structural mutation includes amplification, translocation and inversion of genes which can be detected by qPCR or FISH technology. For the level of protein, we can adopt WB, ELISA or IHC technology to detect.
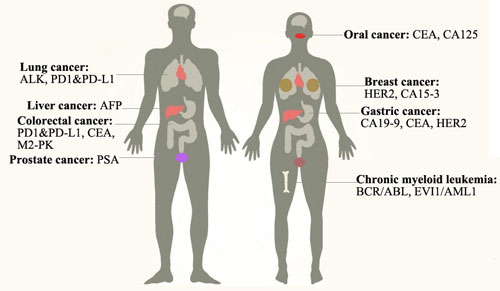
Commonly Used Tumor Markers for Cancers
Tumor markers are widely used for testing in labs although some of them are specific that meet the standards set and some are not. Here, we list the common tumor markers as completely as possible (Table 1).
Table 1. Commonly Used Tumor Markers in the Clinic
|
Type of cancer
|
Tumor marker
|
Uniprot
|
Protein name
|
|
Breast cancer
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
CA15-3
|
P15941
|
Carcinoma antigen 15-3
|
|
HER2
|
P04626
|
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2
|
|
ER
|
P03372
|
Estrogen receptor
|
|
PR
|
P06401
|
Progestrone receptor
|
|
PAI
|
P05121
|
Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1
|
|
β-HCG
|
P0DN86
|
Human chorionic gonadotropin beta subunit
|
|
Prostate cancer
|
PSA
|
P07288
|
Prostate-specific antigen
|
|
PCA3
|
Q8WUY3
|
Protein prune homolog 2
|
|
Lung cancer
|
ACTH
|
P01189
|
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
|
|
NSE
|
P09104
|
Gamma-enolase
|
|
Cyfra21-1
|
P08727
|
Cytokeratin-19
|
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
SCC
|
P29508
|
Squamous carcinoma antigen
|
|
TPA
|
P00750
|
Tissue-type plasminogen activator
|
|
CT
|
P01258
|
Calcitonin
|
|
ALK
|
Q9UM73
|
Anaplastic lymphoma receptor tyrosine kinase
|
|
PD-L1
|
Q9NZQ7
|
Programmed death ligand 1
|
|
PD1
|
Q15116
|
Programmed cell death protein 1
|
|
Cervical cancer
|
SCC
|
P29508
|
Squamous carcinoma antigen
|
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
CA125
|
Q8WXI7
|
Carcinoma antigen125
|
|
CA19-9
|
Q969X2
|
Carcinoma antigen19-9
|
|
Colorectal cancer
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
CA19-9
|
Q969X2
|
Carcinoma antigen19-9
|
|
PD-L1
|
Q9NZQ7
|
Programmed death ligand 1
|
|
PD1
|
Q15116
|
Programmed cell death protein 1
|
|
M2-PK
|
P14618
|
Pyruvate kinase M2 isozyme
|
|
Gastric cancer
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
CA19-9
|
Q969X2
|
Carcinoma antigen19-9
|
|
HER2
|
P04626
|
Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2
|
|
Liver cancer
|
AFP
|
P02771
|
Alpha-fetoprotein
|
|
Pancreatic cancer
|
CA19-9
|
Q969X2
|
Carcinoma antigen19-9
|
|
CA125
|
Q8WXI7
|
Carcinoma antigen125
|
|
Ovarian cancer
|
CA125
|
Q8WXI7
|
Carcinoma antigen125
|
|
Lymphoma
|
LDHA, LDHB, LDHC, LDHD
|
P00338, P07195, P07864, Q86WU2
|
Lactate dehydrogenase
|
|
PAP
|
P15309
|
Prostatic acid phosphatase
|
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
thymidine kinase
|
P04183
|
Thymidine kinase
|
|
B2M
|
P61769
|
Beta-2-microglobulin
|
|
Pituitary tumor
|
ACTH
|
P01189
|
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
|
|
PRL
|
P01236
|
Prolactin
|
|
FASA, FSHB
|
P01215, P01225
|
Follicle-stimulating hormone
|
|
TSHB
|
P01222
|
Thyroid-stimulating hormone
|
|
Bladder cancer
|
NMP22
|
Q14980
|
Human nuclear matrix protein 22
|
|
Cyfra21-1
|
P08727
|
Cytokeratin-19
|
|
TPA
|
P00750
|
Tissue-type plasminogen activator
|
|
Bone cancer
|
PAP
|
P15309
|
Prostatic acid phosphatase
|
|
B2M
|
P61769
|
Beta-2-microglobulin
|
|
Testicular cancer
|
ALPP
|
P05187
|
Placental alkaline phosphatase
|
|
AFP
|
P02771
|
Alpha-fetoprotein
|
|
β-HCG
|
P0DN86
|
Human chorionic gonadotropin beta subunit
|
|
LDHA, LDHB, LDHC, LDHD
|
P00338, P07195, P07864, Q86WU2
|
Lactate dehydrogenase
|
|
NSE
|
P09104
|
Gamma-enolase
|
|
Uterine cancer
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
CA125
|
Q8WXI7
|
Carcinoma antigen125
|
|
CA19-9
|
Q969X2
|
Carcinoma antigen19-9
|
|
TPA
|
P00750
|
Tissue-type plasminogen activator
|
|
Head & neck cancer
|
SCC
|
P29508
|
Squamous carcinoma antigen
|
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
CA125
|
Q8WXI7
|
Carcinoma antigen125
|
|
Kidney cancer
|
TPA
|
P00750
|
Tissue-type plasminogen activator
|
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
M2-PK
|
P14618
|
Pyruvate kinase M2 isozyme
|
|
Bile duct cancer
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
CA19-9
|
Q969X2
|
Carcinoma antigen19-9
|
|
Thyroid cancer
|
TG
|
P01266
|
Thyroglobulin
|
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
CT
|
P01258
|
Calcitonin
|
|
Choriocarcinoma
|
β-HCG
|
P0DN86
|
Human chorionic gonadotropin beta subunit
|
|
Neuroendoc-rine tumor
|
Chromogranin
|
P10645
|
Chromogranin
|
|
NSE
|
P09104
|
Gamma-enolase
|
|
Melanoma
|
CEA
|
P06731
|
Carcinoembryoric antigen
|
|
LDHA, LDHB, LDHC, LDHD
|
P00338, P07195, P07864, Q86WU2
|
Lactate dehydrogenase
|
We will introduce the applications of tumor markers for several most common cancers particularly as follows:
Breast cancer: It is the second most common type of cancer among American women. There are three types of breast cancer to this day: Luminal type, HER2 type and basal-like type. The tumor markers for it include: HER2 which gene amplification or protein overexpression leads to the tumor; CA15-3 which elevates its expression when tumor happens or when women are pregnant[1]. Only 8% breast cancer is hereditary[2]. The treatments include radiation therapy and mastectomy, etc.
HER2 is also known as receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 which is one of the human epidermal growth factor receptor. The abnormal number of gene copies makes 20-30% breast cancers[3]. We can use specific FISH probe to check the gene copies or specific antibody to detecting the protein level. HER2 positive type will stimulate the PI3K/AKT pathway and RAS/RAF/MAPK pathway and can be blocked by using monoclonal antibody Herceptin. Besides, overexpressing HER2 can be occurred in ovarian, lung, stomach cancers.
Additionally, among the Basal-like type patients, the Notch and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathways are deregulated, EGFR is identified as a marker of this pathway. While the patients with Luminal type breast cancer bear a misregulation of estrogen (ER) pathway.
Prostate cancer: It is the most common type of cancer among men and the second leading cause of male cancer deaths. Deficient levels of PTEN and NKX3.1 result in a reduction in p27 levels, decreased apoptosis and increased proliferation. A tumor marker for it is: PSA which is elevated in the blood when cancer happens. The treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, etc. It is the most common type of cancer among men and the second leading cause of male cancer deaths. Deficient levels of PTEN and NKX3.1 result in a reduction in p27 levels, decreased apoptosis and increased proliferation. A tumor marker for it is: PSA which is elevated in the blood when cancer happens. The treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, etc.
PSA is also known as prostate-specific antigen. It can be tested by specific antibody. The increased amount of PSA in the blood can be found in people who have prostate cancer and non-prostate cancer but inflammation.
Lung cancer: There are two kinds of lung cancers: non-small cell lung cancer (85%) and small cell lung cancer (15%). Smoking is the key cause of this disease. The tumor markers for it include ALK which rearrange causing ALK to fuse with the EML4 gene[4]; PD1 and its ligand PD-L1 which elevate their expression when tumor happens and accounts for 53%-62% of NSCLC cases[5]. The treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, etc. Targeted therapy like monoclonal antibodies and tyrosine kinase inhibitors can reduce the harm for normal cells.
Non-small cell lung's molecular mechanism includes activation of some genes like ALK, EGFR, RAS and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes like p53. When ALK-EML4 fused together making ALK activation continuously which will lead to invasion, increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis. Mutation or overexpression of EGFR makes increased proliferation. Mutation of RAS transmits growth signal. Inactivation of p53 makes increased proliferation and decreased apoptosis.
Anaplastic lymphoma receptor tyrosine kinase (ALK) gene located at 2p23 which is a hot spot to break apart, and it can inverse with EML4 to cause a non-small cell lung. Meanwhile, it can rearrange with other genes to cause other malignancies[4][6]. We can use specific FISH probes to check the mutation.
Chronic myeloid leukemia: It is a disease of bone marrow as it produces too many white cells in bone marrow and may progressively affect blood cells. It is a disease mostly among people more than 55 years old and rarely among childhood. More than 90% of CML has a Philadelphia chromosome that makes BCR-ABL fusion gene leading to a ABL activation continuously which in term regulates the downstream genes through JAK-STAT and MAPK signaling pathway[7]. The treatments are targeted therapy with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor like imatinib, surgery, etc. The tumor markers for it are: BCR/ABL, EVI1/AML1, etc.
BCR, also known as break cluster region, is located at 22q11. ABL (abelson), which encodes non-receptor Tyrosine kinase, is located at 9q34. The fusion of BCR/ABL eliminates the negative regulation of ABL leading to the phosphorylation of serial genes and inhibition of apoptosis. We can use specific FISH probes to check the mutation. Additionally, the abnormal also exists among ALL and AML patients.
EVI1, also known as ecotropic virus integration site 1, is located at 3q26.2. It may increase gene copies leading to overexpression or rearrange leading to fusion with AML1 gene which will prevent differentiation and apoptosis. We can use specific FISH probes or specific antibody to check the mutation[8].
Liver cancer: It is one of the most deadly cancer which includes bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma) and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HCC, which makes up 80% of cases, includes chronic infection with hepatitis B or C and cirrhosis of the liver. Hepatitis B accounts for 90% of hepatocellular carcinoma which can be prevented by specific vaccine. The tumor marker for it is: AFP. The treatments include surgery, chemotherapy, etc.
AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) is a glycoprotein produced by a fetus derived from embryonic endoderm cells and can not be detected in the blood of healthy adult men or women. AFP is consistent with it receptor. The AFP/AFPR brings about the Ca2+ influx which in term gives a rise of CAMP enhancing the protease A activity and DNA amplification, then tumor proliferates[9]. What is more, AFP could induce the immune escapes through inhibiting the function of dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and T lymphocytes, so that the elevated level indicates a primary liver cancer or a germ cell tumor and it has attracted more attention on liver cancer immunotherapy[10]. It can be detected by specific antibody.
Colorectal cancer: Colorectum helps us absorb nutrients and pass waste out of the body while colorectal cancer including colon and rectal cancer is a second deadly killer among cancers in western countries. It may be caused by heredity, etc. If you find and remove the polyp in time, it will not develop worse. The tumor markers for it are CEA, M2-PK, PD-L1, etc. The treatments include targeted therapy, surgery, etc.
It makes series of genetic changes involving the activation of oncogenes such as K-Ras and inactivation of TSG such as p53, DCC/Smad4, and APC. It also associates with gene mutations and hereditary syndrome.
Currently, PD1, PD-L1 and CTLA4 are approved to be checkpoint inhibitors. PD1 pathway is signaling to escape for tumors. PD-L1 (Programmed death ligand 1) as its ligand can inhibit T effector cells from killing tumor cells is quantified by IHC. However, it sometimes misses some candidate patients for immunotherapy as a standard because of the hetergeneity or other causes. Accompanied with TMB (tumor mutational burden, a neo-antigen as a result of somatic mutation can produce some immune response blocked by immune checkpoint which is predicted by next generation resequencing), we can argument or supplant the datas. PD-L1 is expressed on a variety of tumor types including NSCLC and colon cancer. We can use specific antibody to check the mutation and use Pembrolizumab to stop this pathway[5].
Gastric cancer: It is formed in the inner layer of stomach and spreads to the outer layer. Elevated age, stomach disease and unhealthy diet can raise the risk of gastric cancer. The tumor markers for it include CA19-9, CEA and HER2, so that we can use specific antibody for detecting the cancer[11][12]. Ramucirumab can prevent the growth of new blood vessels that tumor need to grow. The additional treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, etc. The molecular mechanism is that gastric cancer is associated with mutation in p53, APC, CDH1 and overexpression of c-ErbB2, MET, FGFR2F.
The tumor markers CA19-9 (carcinoma antigen 19-9), CA72-4 (carcinoma antigen 72-4), CEA (carcinoembryoric antigen) have good tips on monitoring and prognosis. The elevated level of them may indicate the recurrence[12].
Oral cancer: It is one of the head and neck cancer. Unhealthy diet like areca nut, tobacco use, alcohol use, human papillomavirus infection can raise the risk of oral cancer which should be avoided as possibly as we can. The signs of this disease are a lump in the mouth, bleeding and pain in the mouth or throat, a score that can not be healed in a long time. While the signs do not mean you have oral cancer already, we can further detect it by using CT scan, endoscopy, etc. The tumor markers for this disease include CEA, CA125[13]. The treatments depend on the stage of the cancer including chemotherapy, surgery, etc.
Conclusions
Thanks to the abundant researches on tumor markers, personalized cancer care is now rapidly becoming a reality in the clinical assessment and management of patients. We hope the application will benefit more people with efficacy and lower price in the future. Furthermore, we should try our best effort to protect ourselves from the risk factors for tumors.
References
[1] Feizic H, Mujagic S, etc. Tumor marker CA 15-3 in breast cancer patients[J]. Acta Med Acad, 2015(44): 39-46
[2] Calarf GM, Zepeda AB, etc. Molecular aspects of breast cancer resistance to drugs[J]. Int J Oncol, 2015(47): 437-445
[3] Slamon DJ, Clark GM, etc. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene[J]. Science, 1987(235): 177-182
[4] Takeuchi K, Choi YL, etc. Multiplex reverse transcription-PCR screening for EML4-ALK fusion transcripts[J]. Clin Cancer Res. 2008(14):6618-6624
[5] Cyriac G, Gandhi L. Emerging biomarkers for immune checkpoint inhibition in lung cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2018 May
[6] Lin E, Li L, etc. Exon array profiling detects EML4-ALK fusion in breast, colorectal, and non-small cell lung cancers[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2009(7): 1466-1476
[7] Shteper PJ, Siegfried Z, etc. ABL1 methylation in Ph-positive ALL is exclusively associated with the P210 form of BCR-ABL[J]. Leukemia, 2001(15): 575-582
[8] Glass C, Wilson M, etc. The role of EVI1 in myeloid malignancies[J]. Blood Cell Mol Dis, 2014(53): 67-76
[9] Li MS, Li PF, etc. The promoting molecular mechanism of alpha-fetoprotein on the growth of human hepatoma Bel7402 cell line[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2002(8): 469-475
[10] Wang XP, Wang QH. Alpha-fetoprotein and hepatocellular carcinoma immunity[J]. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018 Apr
[11] Gravalos C, Jimeno A. HER2 in gastric cancer: a new prognostic factor and a novel therapeutic target[J]. Ann Oncol 2008(19): 1523-1529
[12] Shimada H, Noie T, etc. Clinical significance of serum tumor markers for gastric cancer: a systematic review of literature by the Task Force of the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2014(17): 26-33
[13] Zhou YG, Liu CM, etc. Diagnostic values of detection on individual different tumor markers in oral cancer at different stages[J]. J Beihua Univ, 2016(17): 217-221
CUSABIO team. Tumor markers. https://www.cusabio.com/c-20631.html




Comments
Leave a Comment