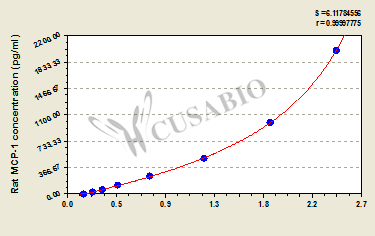
CUSABIO's rat CCL2 ELISA kit is an in vitro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the quantitative determination of CCL2 concentrations in serum, plasma, and tissue homogenates. This assay exclusively recognizes rat CCL2. The quantitative sandwich ELISA technique of this kit is based on CCL2 antibody-CCL2 antigen interactions and an HRP colorimetric detection system to detect the levels of CCL2 in samples. The intensity of the color is positively proportional to the amount of bound CCL2 in the initial step.
CCL2 is the most powerful chemoattractant involved in macrophage recruitment and a potentinitiator of inflammation. It exerts potent chemotactic, stimulatory, and mitogenic effects on mononuclear cells. CCL2 also plays an important role in coordinating the immune response after microbial infection by regulating T cell polarization as well as leukocyte migration and accumulation within infected tissues. CCL2/CCR2 signaling has multiple pro-tumorigenic roles, including mediating tumor growth and angiogenesis as well as recruiting and usurping host stromal cells to support tumor progression. CCL2 upregulation has been linked to tumor metastasis, invasion, and immune resistance.