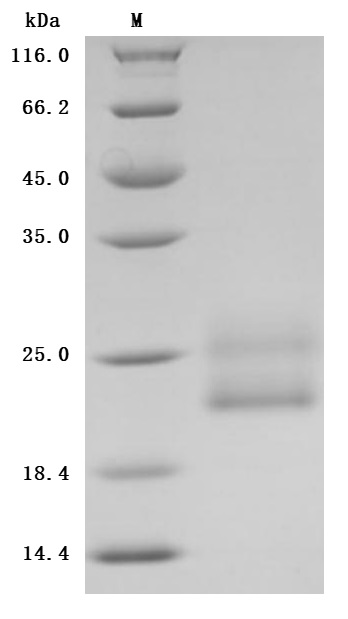
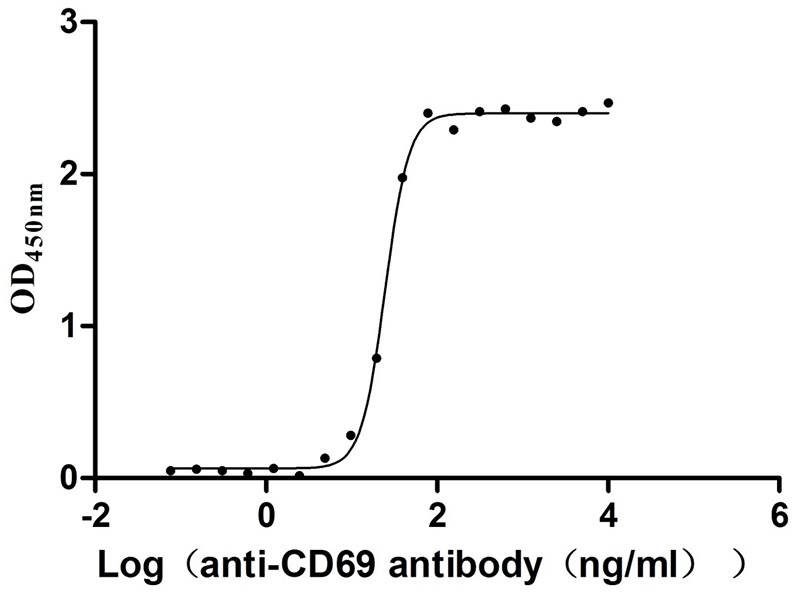
This Human CD96 recombinant protein was produced in Mammalian cell, where the gene sequence encoding Human CD96 (62-199aa) was expressed with the C-terminal 10xHis tag. The purity of this CD96 protein was more than 95%. Its endotoxin content is less than 1.0 EU/ug as determined by the LAL method. The activity was validated. In a functional ELISA, immobilized human CD69 at 2 μg/mL can bind Anti-CD69 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA004952MA1HU) with the EC50 of 23.17-26.04 ng/mL.
CD69 was discovered in 1981. It was also known as an activation-inducing molecule (AIM), Leu23 and MLR-3 in the early stage. It is the earliest expressed membrane surface molecule for lymphocyte activation and is usually used as a marker of T cell activation in many studies. CD69 is a pleiotropic immune regulatory molecule that plays an important role in the activation and differentiation of various hematopoietic cells. Since CD69 was discovered, its initial research is basically about its role in cell activation. Early research mainly focused on its expression in T cells and NK cells. The mechanism of inducing CD69 expression is mainly the activation of PKC and the activation of cells. The continuous increase of internal Ca2+ level, blocking the PKC pathway can directly inhibit the expression of CD69. The rapid expression of CD69 in activated cells is not only a marker molecule, in fact, its more important role is to further enhance cell activation or proliferation and differentiation as a cell costimulatory signal. CD69 is not expressed in the quiescent state of T cells and NK cells, but expresses rapidly after cell activation, indicating that CD69 has an important regulatory effect on the immune system, so CD69 can be used as a therapeutic agent for blood system diseases and immune-related diseases potential therapeutic target. However, at present, there are few clinical drug studies on CD69 and the progress is slow. The development of CD69 active protein can help CD69 clinical drug development and testing.