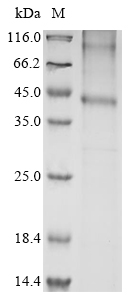
The mouse Ccr1 protein-encoding gene (1-355aa) is linked to an N-terminal 10xHis tag gene to create the target gene. This target gene is amplified by PCR and then cloned into expression vectors, constructing recombinant plasmids. Following the transfection of plasmids into an in vitro E.coli expression system, target proteins are induced to express during culture. The supernatant from the culture is purified by affinity chromatography, harvesting the recombinant mouse Ccr1 protein with purity exceeding 85%, as validated by SDS-PAGE.
The CCR1 is a G protein-coupled receptor that plays a significant role in various physiological and pathological processes, particularly in immune responses and inflammation. CCR1 is primarily activated by its ligands, such as CCL3, CCL5, and CCL9, which are crucial for mediating chemotaxis and the recruitment of immune cells, including monocytes, neutrophils, and T cells, to sites of inflammation [1][2][3].
In the context of neuroinflammation, CCR1 is expressed in various cell types, including microglia and astrocytes, and is implicated in the disruption of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) during neuroinflammatory diseases [1][4]. Activation of CCR1 in the central nervous system (CNS) can lead to increased neuroinflammation, which is associated with conditions such as cerebral hemorrhage and multiple sclerosis [1][4]. Studies have demonstrated that CCR1 activation promotes neuroinflammation through specific signaling pathways, such as the ERK1/2 pathway, highlighting its role in the pathogenesis of neuroinflammatory disorders [4].
Moreover, CCR1 is involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses in other tissues, including the lungs and cardiovascular system. In asthma, CCR1 expression on airway smooth muscle cells has been linked to the modulation of immune responses and inflammation [5]. Similarly, in acute myocardial infarction, CCR1 signaling pathways are activated, contributing to the inflammatory process that exacerbates tissue damage [2].
References:
[1] J. Yan, W. Xu, C. Lenahan, L. Huang, U. Ocak, J. Wen, et al., Met-rantes preserves the blood–brain barrier through inhibiting ccr1/src/rac1 pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice, Fluids and Barriers of the CNS, vol. 19, no. 1, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12987-022-00305-3
[2] D. Chen, X. Kong, X. Shen, M. Huang, J. Zheng, J. Sun, et al., Identification of differentially expressed genes and signaling pathways in acute myocardial infarction based on integrated bioinformatics analysis, Cardiovascular Therapeutics, vol. 2019, p. 1-13, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8490707
[3] Y. Sang, Y. Li, L. Xu, J. Chen, D. Li, & M. Du, Dysfunction of ccr1+ decidual macrophages is a potential risk factor in the occurrence of unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss, Frontiers in Immunology, vol. 13, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1045532
[4] J. Yan, G. Zuo, P. Sherchan, L. Huang, U. Ocak, W. Xu, et al., Ccr1 activation promotes neuroinflammation through ccr1/tpr1/erk1/2 signaling pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice, Neurotherapeutics, vol. 17, no. 3, p. 1170-1183, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13311-019-00821-5
[5] P. Joubert, S. Lajoie-Kadoch, M. Welman, S. Dragon, S. Létuvée, B. Tolloczko, et al., Expression and regulation of ccr1 by airway smooth muscle cells in asthma, The Journal of Immunology, vol. 180, no. 2, p. 1268-1275, 2008. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.180.2.1268