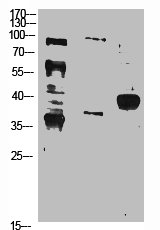
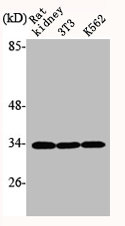
Alternative Names
I kappa B alpha antibody; I-kappa-B-alpha antibody; IkappaBalpha antibody; IkB-alpha antibody; IKBA antibody; IKBA_HUMAN antibody; IKBalpha antibody; MAD 3 antibody; MAD3 antibody; Major histocompatibility complex enhancer-binding protein MAD3 antibody; NF kappa B inhibitor alpha antibody; NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha antibody; NFKBI antibody; NFKBIA antibody; Nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B cells antibody; Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B cells inhibitor alpha antibody
Species Reactivity
Human,Mouse,Rat
Immunogen
Synthesized peptide derived from the N-terminal region of Human IκB-α.
Immunogen Species
Homo sapiens (Human)
Purification Method
The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
Concentration
It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
Buffer
Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
Tested Applications
WB, ELISA
Recommended Dilution
| Application |
Recommended Dilution |
| WB |
1:500-1:2000 |
| ELISA |
1:40000 |
Storage
Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
Lead Time
Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
Usage
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.