What is T lymphocytes?
T lymphocytes are an important part of the body's immune system. The activation of T cells can resist the invasion of tumor cells and pathogenic bodies, but also lead to autoimmune diseases due to overactivation.
Activation of T Cells
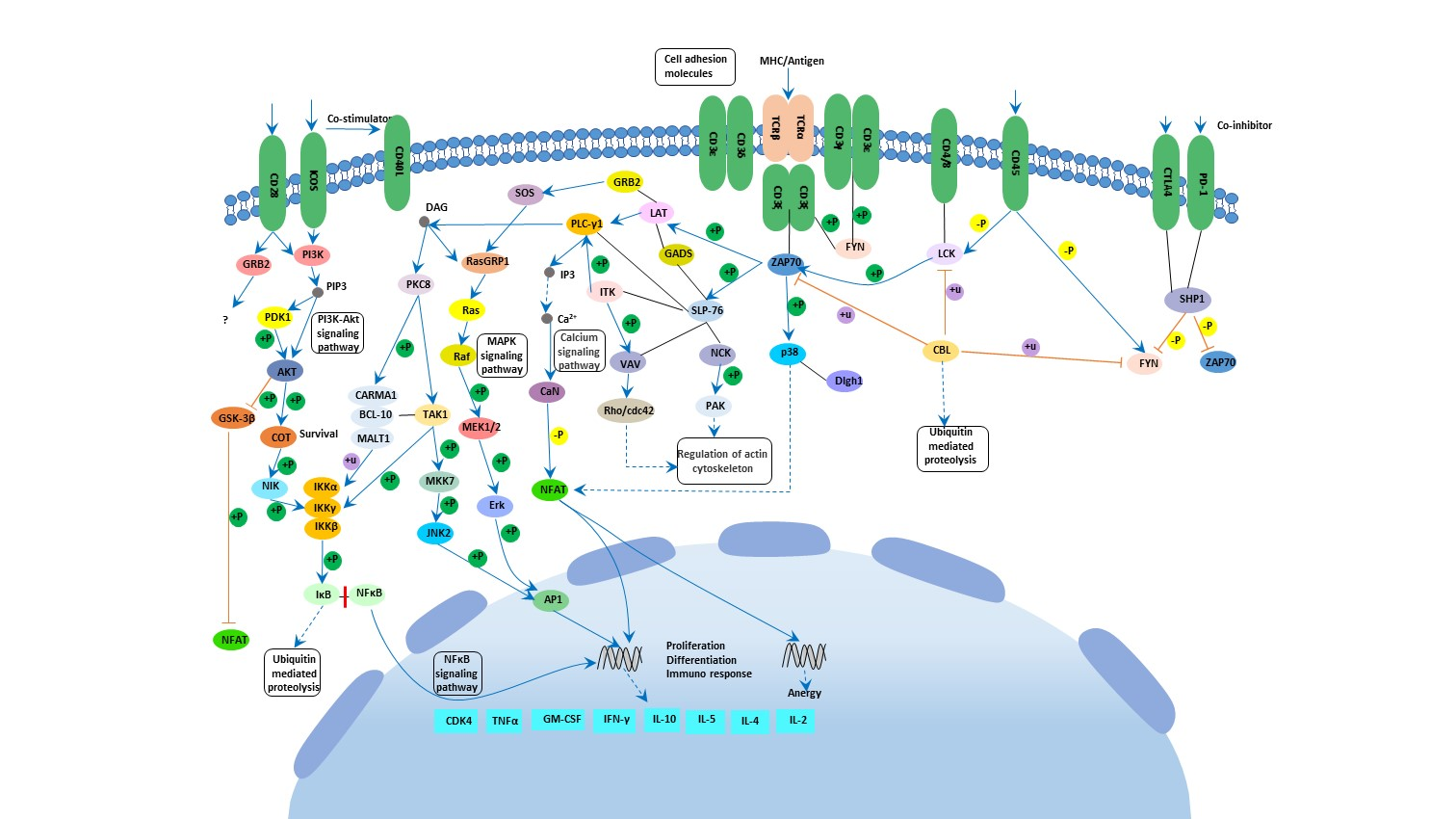
T cell activation is a complex process, including receiving signal stimulation, signal transduction, intracellular enzyme activation, gene transcription expression and cell amplification.
T cell activation requires dual signal stimulation.
First signal: antigen peptide -MHC molecular complex on antigen presenting cells binds to TCR specifically.
Second signal: interaction between T cells and costimulatory molecules present on the surface of antigen presenting cells produces costimulatory signals, of which CD28 and B7(CD80/CD86) are relatively important.
The integration of the two signals was the most effective way to induce T cell activation, while the lack of costimulation signals resulted in decreased T cell response, and in some cases can induce tolerance or T cell anergy. Blocking the co-stimulus signal of T cell activation can negatively regulate T cell activity and induce T cell immune tolerance.
The Signals Transduction Molecules of TCR Signaling Pathway
Intracellular signaling is accomplished by the following kinases and phosphatases. The molecules involved in TCR signal transduction mainly include upstream kinases (Lck, Fyn, ZAP-70, Itk), scaffold proteins (LAT, Gads, SLP-76, Grb2), phospholipases, phosphatases, etc. Activation of TCR signals not only induces T cell proliferation and cytokine production, but also promotes T cell differentiation and T cell function.
The Function T Cell Receptor Signaling
The T cell receptor is located on the surface of T cells, which specifically recognizes antigenic peptides presented by MHC on the surface of antigen-presenting cells, and activates signal pathways such as ERK, JNK, and NF-κB in T cells. Through several different signaling pathways, many transcription factors associated with cell division and differentiation are activated to regulate cell functions such as T cell proliferation, differentiation, death, and cytokine release. Typical intracellular signals activated by TCR also include: MAPK (Mitogen-activated protein kinase), PKC (Protein Kinase C), calcium signal pathways.





