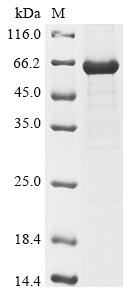
Recombinant Human Intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase (ALPI) is produced in E.coli and includes the complete mature protein sequence from amino acids 20 to 503. The protein carries an N-terminal 6xHis-tag that makes purification and detection more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms the purity exceeds 85%. This product is intended for research use only and maintains low endotoxin levels that appear suitable for various experimental work.
Intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase (ALPI) is an enzyme that primarily handles dephosphorylation processes in the gastrointestinal tract. It seems to play an important role in maintaining intestinal balance and acts as a key part of the body's defense against microbial invasion. ALPI is also being studied for its possible involvement in lipid absorption and detoxification pathways, which makes it an interesting target for gastrointestinal and enzyme research.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Expression in E. coli does not guarantee proper folding or native post-translational modifications required for alkaline phosphatase activity, and there is no direct evidence of enzymatic activity or correct folding validated in the description. Therefore, it is uncertain whether the protein is correctly folded or biologically active without functional assays. The presence of a His-tag and bacterial expression could affect folding or activity, particularly for enzymes that rely on disulfide bonds or glycosylation, which are not typical of bacterial expression systems.
1. Biochemical Characterization and Enzyme Kinetics Studies
This recombinant ALPI protein allows researchers to examine basic biochemical properties of human intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase. Scientists can investigate substrate specificity, optimal pH and temperature conditions, and kinetic parameters. The N-terminal 6xHis tag facilitates purification and potential immobilization for enzymatic assays. Researchers may compare this recombinant enzyme's behavior with other alkaline phosphatase types to elucidate tissue-specific differences. The full-length mature protein (20-503aa) provides a model for studying the catalytic domain and any regulatory regions, provided that the protein is properly folded and active; if activity is not demonstrated, these studies should acknowledge potential folding limitations due to bacterial expression.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
The purified recombinant ALPI protein can serve as an antigen for generating antibodies against human intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase. The >85% purity and His-tag can aid in antibody development, with options for producing polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. However, antibody specificity should be validated using orthogonal methods and, if possible, with native or properly folded antigen to ensure relevance. The recombinant protein can function as a positive control in antibody-based assays, contingent on verified antigenicity and conformation.
3. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The His-tagged recombinant ALPI can be employed in pull-down assays to identify interacting partners, using nickel-affinity matrices for capture. While this approach is feasible, the reliability of detected interactions depends on ALPI adopting a native-like conformation in the bacterial system. Co-immunoprecipitation with anti-His antibodies can help confirm interactions, but follow-up validation in more physiological systems is recommended.
4. Structural and Biophysical Analysis
The recombinant ALPI provides material for structural and biophysical studies if it is correctly folded and stable. Techniques such as X-ray crystallography or cryo-EM require homogeneous, native-like protein. If folding is uncertain, data interpretation should consider potential misfolding or non-native conformations arising from E. coli expression. Complementary analyses (DSC, CD, DLS) can inform on stability and folding status.
5. Inhibitor Screening and Drug Discovery Research
This recombinant ALPI can serve as a target for in vitro inhibitor screening, enabling standard assay development for preliminary inhibitor evaluation. The His-tag supports straightforward purification and assay setup. The suitability of hits for therapeutic development will depend on validating activity and physiological relevance in subsequent studies using a properly folded and active enzyme.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Proceed with a prioritized validation workflow: (1) confirm enzymatic activity under conditions typical for ALPI, (2) assess folding and stability using biophysical methods, (3) compare activity to known ALPI benchmarks and to ALPI from other tissues, and (4) validate antibody and interaction-based claims using both the recombinant protein and a secondary, more native-positive control. If activity or proper folding cannot be demonstrated, explicitly revise the application descriptions to reflect a non-validated, putative model, and consider alternative expression systems (eukaryotic or insect cells) or refolding protocols to achieve native-like conformation before proceeding with functional studies.