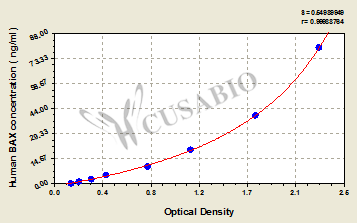
The human BAX ELISA kit (CSB-E09344h) is designed for the quantitative measurement of human BAX protein in serum, plasma, or tissue homogenates. It quantitates human BAX with 0.312 ng/ml sensitivity and shows excellent specificity for human BAX. It uses the bi-antibody sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique. This assay employs a biotin-conjugated BAX antibody that recognizes the analyte bound by the immobilized BAX antibody, forming an antibody-analyte-antibody complex. The immune complex is further detected by avidin-conjugated HRP. The TMB solution is added into the wells and turns blue and finally turns yellow after the addition of the stop solution. Solution color develops in proportion to the amount of BAX in the sample. The O.D. value is measured using a microplate reader at 450 nm and is used to determine the concentration of the human BAX in the sample.
BAX is one of the pro-apoptotic proteins of the BCL2 gene family that mediates mitochondrial fusion. BAX is essential for mitochondrial fusion in healthy cells. During apoptosis, BAX is recruited and oligomerized at mitochondrial foci. BAX is involved in the formation of pores that enables the mitochondrion to cytochrome c and subsequent activation of caspase cascade release, finally leading to apoptosis.