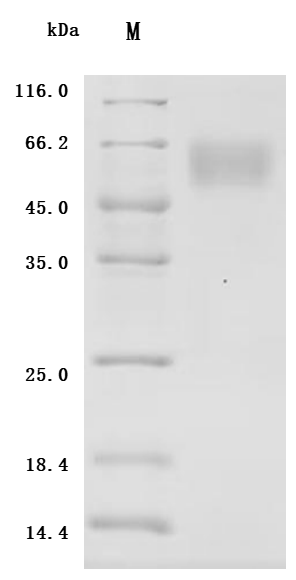
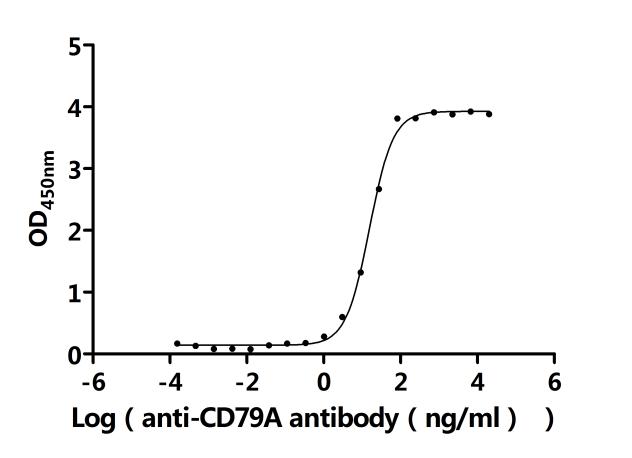
A DNA fragment corresponding to the human CD79A (33-143aa) was expressed with a mFC-flag tag at the C-terminus in mammalian cells. The product is the recombinant human CD79A protein. It carries a C-terminal mFC-flag-tag. Its purity is greater than 95% as measured by SDS-PAGE. Its endotoxin is less than 1.0 EU/ug as determined by the LAL method. In a functional ELISA, this recombinant CD79A protein is validated to be biologically active as it can bind to the anti-CD79A recombinant antibody(CSB-RA004957MA1HU), with the EC50 of 14.44-16.80 ng/mL.
The CD79A protein plays a crucial role in B-cell biology, primarily functioning as an integral component of the B-cell receptor (BCR) complex. CD79A is essential for B-cell development, differentiation, and activation upon antigen binding, which is critical for the adaptive immune response. CD79A, along with its partner CD79B, forms a heterodimer that transmits signals from the BCR to intracellular signaling pathways, thereby facilitating B-cell activation and proliferation [1][2].
During the early stages of B-cell development, CD79A is expressed in nearly all B-cell stages, from pro-B cells to mature B cells, and its expression diminishes in plasma cells [3][4]. This expression pattern highlights its role as a pan-cell marker for B-lineage assignment, making it a valuable tool in the characterization of B-cell malignancies [3]. Furthermore, CD79A is implicated in tonic signaling, which is a continuous low-level signaling necessary for the survival and maintenance of mature B cells [5][6]. The tonic signaling is crucial for the development of mature follicular B cells and has been shown to influence the progression of various B-cell malignancies, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) [1][7].
In the context of cancer, CD79A has been identified as a significant factor in the prognosis of several B-cell neoplasms. High expression levels of CD79A are associated with poorer outcomes in classical Hodgkin's lymphoma and other B-cell malignancies, indicating its potential as a therapeutic target [8][9]. In pediatric B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (BCP-ALL), CD79A is crucial for CNS infiltration and leukemia engraftment, underscoring its role in tumor biology and metastasis [10]. Moreover, mutations in the CD79A gene have been linked to enhanced BCR signaling, contributing to the pathogenesis of aggressive forms of DLBCL [2][7].
Additionally, CD79A's role extends beyond B-cell activation to include interactions with myeloid cells, where it can influence immune responses and tumor microenvironments. CD79A expression on myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) has been shown to enhance their immunosuppressive capabilities, promoting tumor growth [11]. This multifaceted role of CD79A in both normal B-cell physiology and in the context of malignancy highlights its importance as a target for therapeutic interventions aimed at modulating immune responses and treating B-cell-related diseases.
References:
[1] V. Xiao. Discovery of novel targets for diffuse large b-cell lymphoma, J Emerg Invest, 2021. https://doi.org/10.59720/21-102
[2] O. Ducharme, M. Beylot‐Barry, A. Pham‐Ledard, É. Bohers, P. Viailly, T. Bandres, et al. Mutations of the b-cell receptor pathway confer chemoresistance in primary cutaneous diffuse large b-cell lymphoma leg type, Journal of Investigative Dermatology, vol. 139, no. 11, p. 2334-2342.e8, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2019.05.008
[3] A. Berhili, M. Bensalah, J. Elmalki, A. Elyagoubi, & R. Seddik. Immunophenotypic challenges in diagnosis of cd79a negativity in a patient with b acute lymphoblastic leukemia harboring intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21: a case report, Journal of Medical Case Reports, vol. 15, no. 1, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-021-03128-2
[4] S. Sirivisoot, S. Techangamsuwan, S. Tangkawattana, & A. Rungsipipat. Pax5 as a potential candidate marker for canine b-cell lymphoma, Veterinární Medicína, vol. 62, no. 2, p. 74-80, 2017. https://doi.org/10.17221/100/2016-vetmed
[5] X. Huang, K. Takata, Y. Sato, T. Tanaka, K. Ichimura, M. Tamura, et al. Downregulation of the b‐cell receptor signaling component cd79b in plasma cell myeloma: a possible post transcriptional regulation, Pathology International, vol. 61, no. 3, p. 122-129, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1827.2010.02634.x
[6] J. Müller-Winkler, R. Mitter, J. Rappe, L. Vanes, E. Schweighoffer, H. Mohammadi, et al. Critical requirement for bcr, baff, and baffr in memory b cell survival, The Journal of Experimental Medicine, vol. 218, no. 2, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20191393
[7] O. Havránek, J. Xu, S. Köhrer, Z. Wang, L. Becker, J. Comer, et al. Tonic b-cell receptor signaling in diffuse large b-cell lymphoma, Blood, vol. 130, no. 8, p. 995-1006, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-10-747303
[8] S. Yao, Z. Huang, C. Wei, Y. Wang, H. Xiao, S. Chen, et al. Cd79a work as a potential target for the prognosis of patients with oscc: analysis of immune cell infiltration in oral squamous cell carcinoma based on the cibersortx deconvolution algorithm, BMC Oral Health, vol. 23, no. 1, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12903-023-02936-w
[9] S. Yao, Z. Huang, C. Wei, Y. Wang, H. Xiao, S. Chen, et al. Cd79a work as a potential target for the prognosis of patients with hnscc: analysis of immune cell infiltration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma based on the cibersortx deconvolution algorithm,, 2022. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2177047/v1
[10] L. Lenk, M. Carlet, F. Vogiatzi, L. Spory, D. Winterberg, A. Cousins, et al. Cd79a promotes cns-infiltration and leukemia engraftment in pediatric b-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia, Communications Biology, vol. 4, no. 1, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-01591-z
[11] D. Luger, Y. Yang, A. Raviv, D. Weinberg, S. Banerjee, M. Lee, et al. Expression of the b-cell receptor component cd79a on immature myeloid cells contributes to their tumor promoting effects, Plos One, vol. 8, no. 10, p. e76115, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076115