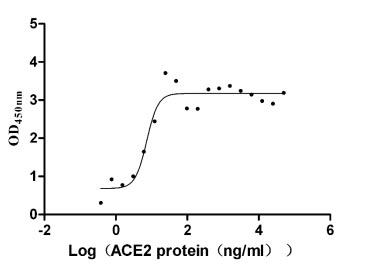
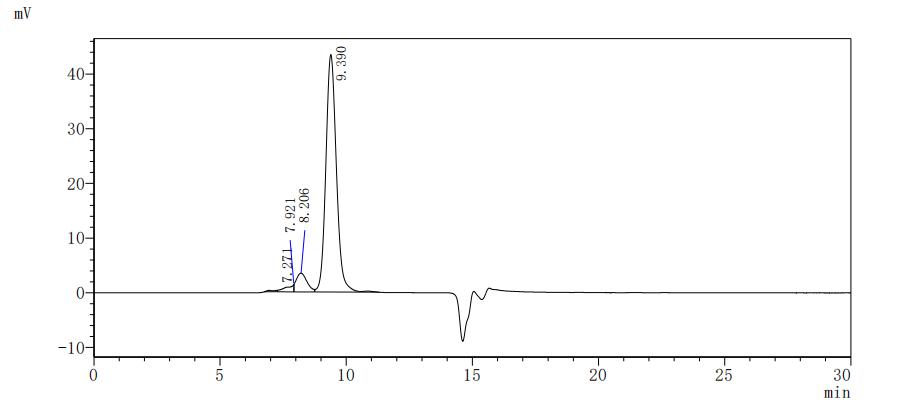
This recombinant protein is a high-purity (>90% measured by SDS-PAGE and SEC-HPLC) form of Macaca fascicularis angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), expressed in mammalian cells. It consists of the amino acids 18-741 of Macaca fascicularis ACE2 protein and is fused with a C-terminal hFc tag for enhanced stability and detection. This recombinant ACE2 protein contains low endotoxin levels (<1.0 EU/μg, LAL method), ensuring minimal interference in cell-based assays. Its functional activity has been confirmed by binding to SARS-CoV-2-S1-RBD (EC50: 5.638–9.496 ng/mL in ELISA), validating its relevance in COVID-19 and ACE2-related research. Its lyophilized formulation is convenient for long-term stability and reconstitution. Designed for cancer and virology studies, this recombinant ACE2 protein is a critical tool for investigating viral entry mechanisms (e.g., SARS-CoV-2), receptor- ligand interactions, and therapeutic development. Its mammalian cell expression ensures proper post-translational modifications, closely mimicking native protein behavior.
Macaca fascicularis, also referred to as the long-tailed or crab-eating macaque, presents a significant focus in biomedical research, notably concerning the ACE2. ACE2 acts as a receptor for the spike protein of coronaviruses such as SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, facilitating viral entry into host cells [1][2]. The biochemical properties and genetic variations of ACE2 in M. fascicularis have been explored, revealing insights into its susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, aligning with findings that multiple Old World monkeys, including M. fascicularis, can be infected and develop clinical symptoms akin to those seen in human COVID-19 cases [3][4][5].
The affinity of ACE2 for the receptor-binding domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is critical in evaluating the species' susceptibility to the virus. Studies indicate that the ACE2 of M. fascicularis exhibits strong binding interactions with the spike protein, suggesting a high potential for infection and consequent disease [2][3]. Comparatively, M. fascicularis, along with M. mulatta (Rhesus macaque), are established models for studying human diseases, particularly due to their similar ACE2 structure, which has been exploited in various preclinical studies [4][5]. Furthermore, the genetic composition of M. fascicularis is notably diverse, which may influence the patterns of ACE2 expression and further modulate responses to viral infections [5][6].
In addition to its role as a viral receptor, ACE2 possesses physiological functions that are highly relevant to cardiovascular health by regulating the renin-angiotensin system. It catalyzes the conversion of angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor, into angiotensin 1-7, which has vasodilatory effects. Alterations in ACE2 expression in the context of infection can lead to dysregulation of this system, contributing to aspects of disease pathology seen in infected individuals [1]. The nexus between ACE2's viral and physiological roles underscores the importance of M. fascicularis in comprehensive studies aimed at understanding both viral biology and cardiovascular implications stemming from infections [1].
References:
[1] J. Damas, G. Hughes, et al., Broad host range of sars-cov-2 predicted by comparative and structural analysis of ace2 in vertebrates. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.16.045302
[2] L. Lopes, N. Pina, A. Silva, & P. Bandiera‐Paiva. Evolutionary analysis of mammalian ace2 and the key residues involved in binding to the spike protein revealed potential sars-cov-2 hosts. Journal of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 1-9, 2022. https://doi.org/10.52547/jommid.10.1.1
[3] Y. Liu, G. Hu, et al. Functional and genetic analysis of viral receptor ace2 orthologs reveals a broad potential host range of sars-cov-2, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. vol. 118, no. 12, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2025373118
[4] S. Laila, D. Astuti, I. Suparto, E. Handharyani, T. Register, & D. Sajuthi. Atherosclerotic lesion of the carotid artery in indonesian cynomolgus monkeys receiving a locally sourced atherogenic diet. Veterinary Sciences, vol. 9, no. 3, p. 105, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030105
[5] S. Kanthaswamy, J. Ng, et al. The genetic composition of populations of cynomolgus macaques (macaca fascicularis) used in biomedical research. Journal of Medical Primatology, vol. 42, no. 3, p. 120-131, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmp.12043
[6] M. Abdul‐Latiff, F. Ruslin, et al. Continental monophyly and molecular divergence of peninsular malaysia’smacaca fascicularis fascicularis, Biomed Research International. vol. 2014, p. 1-18, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/897682