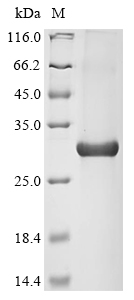
The production of the recombinant human aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) involves several steps. The gene encoding the 220-420aa of the human AHR is co-inserted into a vector with N-terminal 10xHis-tag gene. The recombinant vector is transfected into the E.coli cell for expression. The product is the recombinant human AHR, which is subject to affinity chromatogeaphy purification. Its purity reaches up to than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
The human AHR, a member of the bHLH/PAS family of transcription factors, is primarily activated by binding to ligands such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), dioxins, and other environmental pollutants [1][2][3]. Upon ligand binding, AhR translocates to the nucleus, where it heterodimerizes with the ARNT, facilitating the transcription of target genes involved in xenobiotic metabolism, immune response, and cellular differentiation [4][5].
The activation of AHR has been shown to regulate the expression of various cytochrome P450 enzymes, particularly CYP1A1 and CYP1B1, which are crucial for the metabolism of carcinogens [6][7]. This regulation is vital for detoxifying harmful substances. AHR is also implicated in the pathogenesis of diseases such as cancer, as its activation can lead to the expression of genes that promote cell proliferation and survival in response to toxic insults [8].
References:
[1] C. Gutiérrez-Vázquez and F. Quintana, Regulation of the immune response by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor, Immunity, vol. 48, no. 1, p. 19-33, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2017.12.012
[2] H. Zhao, T. Yang, Y. Feng, N. Vaziri, B. Liu, Q. Liuet al., Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation mediates kidney disease and renal cell carcinoma, Journal of Translational Medicine, vol. 17, no. 1, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-019-2054-5
[3] T. Peng, J. Chen, W. Mao, X. Liu, T. Yu, L. Chenet al., Potential therapeutic significance of increased expression of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in human gastric cancer, World Journal of Gastroenterology, vol. 15, no. 14, p. 1719, 2009. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.15.1719
[4] N. Yamashita, Y. Kanno, M. Yoshikawa, M. Ozawa, N. Sanada, K. Nemotoet al., Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons induce cyp3a5 gene expression via aryl hydrocarbon receptor in hepg2 cells, The Journal of Toxicological Sciences, vol. 46, no. 1, p. 25-29, 2021. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.46.25
[5] L. Bourner, I. Muro, A. Cooper, B. Choudhury, A. Bailey, W. Russellet al., Ahr promotes phosphorylation of arnt isoform 1 in human t cell malignancies as a switch for optimal ahr activity, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 119, no. 12, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2114336119
[6] M. Roth, J. Marques-Magallanes, M. Yuan, W. Sun, D. Tashkin, & O. Hankinson, Induction and regulation of the carcinogen-metabolizing enzyme cyp1a1 by marijuana smoke and δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, vol. 24, no. 3, p. 339-344, 2001. https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb.24.3.4252
[7] Y. Tsuchiya, M. Nakajima, S. Takagi, T. Taniya, & T. Yokoi, Microrna regulates the expression of human cytochrome p450 1b1, Cancer Research, vol. 66, no. 18, p. 9090-9098, 2006. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-06-1403
[8] J. Hukkanen, A. Lassila, K. Päivärinta, S. Valanne, S. Sarpo, J. Hakkolaet al., Induction and regulation of xenobiotic-metabolizing cytochrome p450s in the human a549 lung adenocarcinoma cell line, American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology, vol. 22, no. 3, p. 360-366, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb.22.3.3845