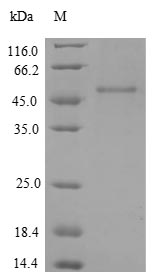
Recombinant human IGF1R production in E. coli starts with co-cloning the target gene into an expression vector with an N-terminal GST-tag gene, which is introduced into E. coli cells. The target gene encodes the 763-931aa of human IGF1R. These cells are grown and induced for protein expression. The cells are lysed to release the protein, which is purified using affinity chromatography. Protein purity is checked using SDS-PAGE, exceeding 90%.
The IGF1R is a transmembrane glycoprotein with an intrinsic kinase moiety [1]. IGF1R is crucial in various physiological processes, including growth, development, and metabolism. Studies have shown that mutations in the IGF1R gene can lead to growth retardation both during intrauterine development and postnatally [2][3]. IGF1R can influence longevity. Evidence has indicated that certain mutations in the IGF1R gene are associated with increased lifespan [4][5].
IGF1R regulates cellular signaling pathways, such as the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway [6]. IGF1R is implicated in cancer progression. Research has demonstrated that IGF1R is linked to breast cancer metastasis and is a potential target for cancer vaccines [7][8]. IGF1R has been related to have a dual role in breast cancer, where both activation and inhibition of IGF1R can impact tumor development [9].
References:
[1] T. Kruis, J. Klammt, A. Galli-Tsinopoulou, T. Wallborn, M. Schlicke, E. Mülleret al., Heterozygous mutation within a kinase-conserved motif of the insulin-like growth factor i receptor causes intrauterine and postnatal growth retardation, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, vol. 95, no. 3, p. 1137-1142, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2009-1433
[2] F. Peng, I. Schwartz, B. Johnson, M. Derr, C. Roberts, V. Hwaet al., Familial short stature caused by haploinsufficiency of the insulin-like growth factor i receptor due to nonsense-mediated messenger ribonucleic acid decay, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, vol. 94, no. 5, p. 1740-1747, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-1903
[3] J. Choi, M. Kang, G. Kim, M. Hong, H. Jin, B. Leeet al., Clinical and functional characteristics of a novel heterozygous mutation of theigf1rgene and igf1r haploinsufficiency due to terminal 15q26.2->qter deletion in patients with intrauterine growth retardation and postnatal catch-up growth failure, The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, vol. 96, no. 1, p. E130-E134, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-1789
[4] Y. Suh, G. Atzmon, M. Cho, D. Hwang, B. Liu, D. Leahyet al., Functionally significant insulin-like growth factor i receptor mutations in centenarians, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 105, no. 9, p. 3438-3442, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0705467105
[5] C. Tazearslan, J. Huang, N. Barzilai, & Y. Suh, Impaired igf1r signaling in cells expressing longevity-associated human igf1r alleles, Aging Cell, vol. 10, no. 3, p. 551-554, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00697.x
[6] S. Wei, K. Wang, X. Yang, W. Dai, & Z. Fan, Long non‑coding rna bancr mediates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by regulating the�igf1r/raf/mek/erk pathway via mir‑338‑3p, International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2020.4687
[7] A. Obr, J. Bulatowicz, Y. Chang, V. Ciliento, A. Lemenze, K. Maingretteet al., Breast tumor igf1r regulates cell adhesion and metastasis: alignment of mouse single cell and human breast cancer transcriptomics, Frontiers in Oncology, vol. 12, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.990398
[8] C. Giovanni, L. Landuzzi, A. Palladini, M. Ianzano, G. Nicoletti, F. Ruzziet al., Cancer vaccines co-targeting her2/neu and igf1r, Cancers, vol. 11, no. 4, p. 517, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040517
[9] J. Bulatowicz and T. Wood, Activation versus inhibition of igf1r: a dual role in breast tumorigenesis, Frontiers in Endocrinology, vol. 13, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.911079