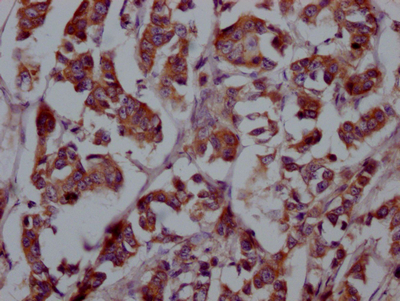
FGFR4 is highly expressed in embryonic tissues and is involved in embryonic development, angiogenesis, and tissue differentiation. The expression of FGFR4 in adult tissues is restricted to actively developing tissues. In adults, FGFR4 regulates bile acid synthesis, metabolism, muscle development, and tissue healing, among other things. FGFR4 performs these functions via interacting with FGF19. FGFR4 dysregulation has been linked to the development of a variety of cancers. Overexpression of FGFR4 has been found in multiple human cancers, including breast cancer, liver cancer, and colon cancer, and has been associated with a shorter life expectancy. Furthermore, high FGFR4 expression is related to cancer resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Mammalian cells are transfected with plasma vectors containing FGFR4 antibody genes, allowing for both recombinant FGFR4 antibody expression and secretion to the medium. Collecting the cell supernatant and purifying to obtain the recombinant FGFR4 antibody by Affinity-chromatography. This recombinant FGFR4 antibody has been validated to detect the FGFR4 protein of Human in the ELISA, IHC.