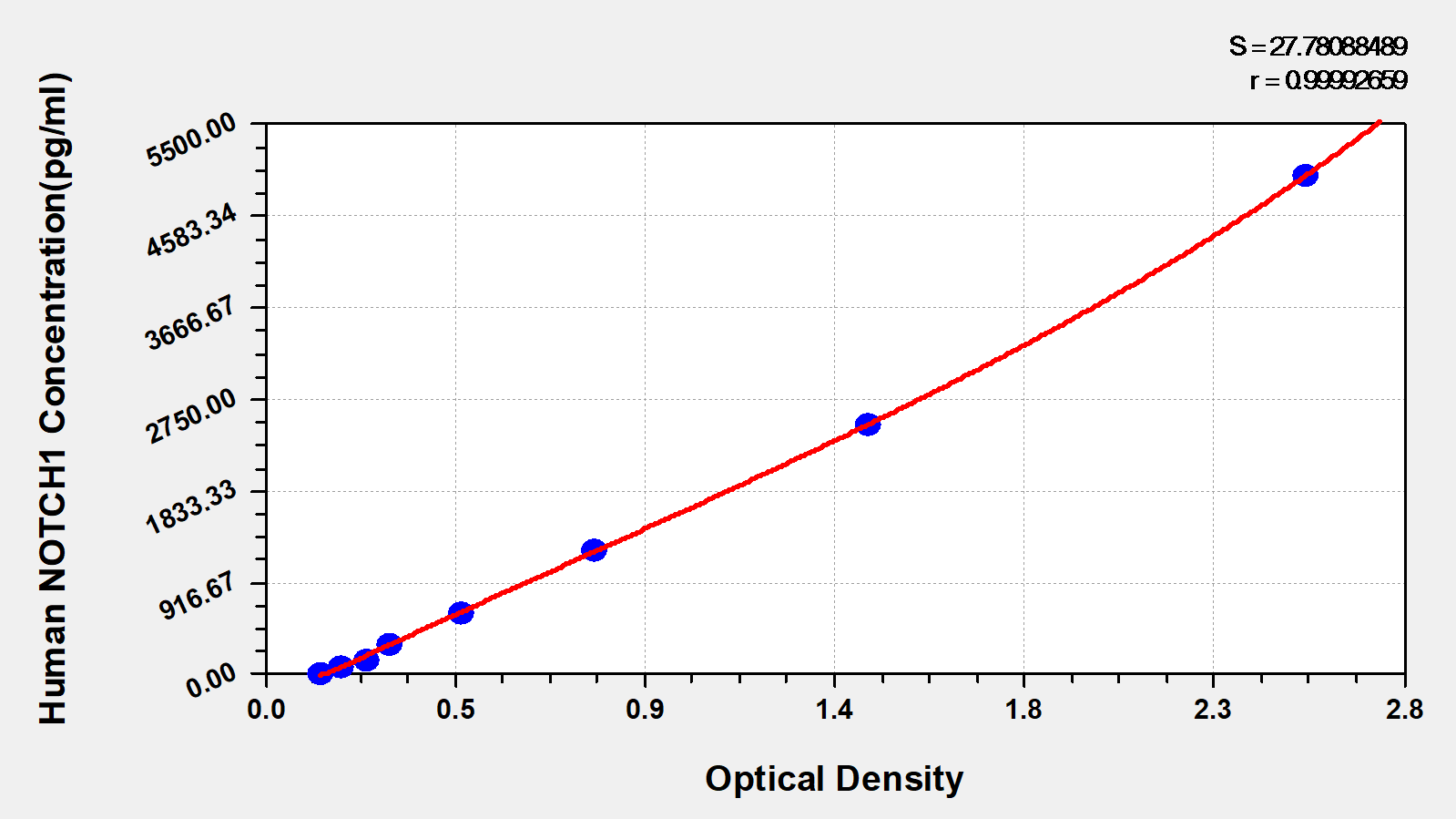
The human neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 (NOTCH1) ELISA kit is suitable for quantitatively determining human NOTCH1 in serum, plasma, or tissue homogenates. This assay employs the bi-antibody sandwich technique and enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction to quantify human NOTCH1 levels in the sample. The amount of synthesized colored product is positively related to the analyte of interest in the sample.
NOTCH1 plays an essential role in angiogenic vascular remodeling and embryonic development. Loss of either NOTCH1 or components of the Notch signaling pathway leads to early embryonic demise related to defects in vasculogenesis, somitogenesis, and cardiogenesis. Recent studies have shown that NOTCH1 is involved in numerous human cancers, including breast cancer, leukemias, brain tumors, and many others. NOTCH1 promotes cell growth, survival, apoptosis, migration, and invasion of tumor cells which are essential for cancer development and progression.