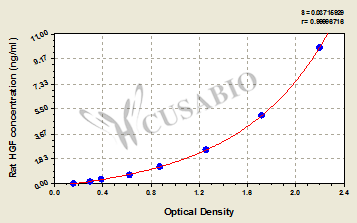
This rat hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) ELISA kit employs the quantitative sandwich enzyme immunoassay technique to measure the levels of rat HGF in multiple samples, including serum, plasma, or tissue homogenates. The enzyme-substrate chromogenic reaction is also used to amplify the signal and quantify the levels of the analyte through the intensity of the colored product. The color intensity positively correlates with the amount of HGF bound in the initial step.
HGF is synthesized by stromal and mesenchymal cells and functions as a pleiotropic cytokine on cells of mainly epithelial origin. It regulates cell motility and morphogenesis, induces angiogenesis, and promotes cell proliferation and migration by activating a tyrosine kinase signaling cascade after engagement to the proto-oncogenic c-Met receptor. The HGF-Met signaling pathway contributes to the development of epithelial organs in a paracrine manner, exerts regenerative effects on the epithelium, and facilitates the regression of fibrosis in numerous organs. The signaling of HGF through Met is associated with the biology of cancer types, neurons, and immunity. HGF is known to promote tumor progression and inhibit the development of fibrosis after tissue injury.