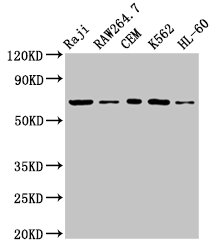
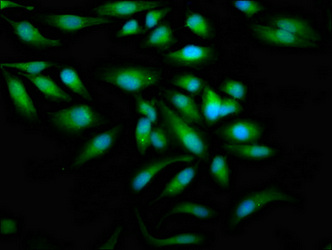
Tyrosine kinase that plays an essential role in regulation of the adaptive immune response. Regulates motility, adhesion and cytokine expression of mature T-cells, as well as thymocyte development. Contributes also to the development and activation of primary B-lymphocytes. When antigen presenting cells (APC) activate T-cell receptor (TCR), a serie of phosphorylations lead to the recruitment of ZAP70 to the doubly phosphorylated TCR component CD3Z through ITAM motif at the plasma membrane. This recruitment serves to localization to the stimulated TCR and to relieve its autoinhibited conformation. Release of ZAP70 active conformation is further stabilized by phosphorylation mediated by LCK. Subsequently, ZAP70 phosphorylates at least 2 essential adapter proteins: LAT and LCP2. In turn, a large number of signaling molecules are recruited and ultimately lead to lymphokine production, T-cell proliferation and differentiation. Furthermore, ZAP70 controls cytoskeleton modifications, adhesion and mobility of T-lymphocytes, thus ensuring correct delivery of effectors to the APC. ZAP70 is also required for TCR-CD3Z internalization and degradation through interaction with the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL and adapter proteins SLA and SLA2. Thus, ZAP70 regulates both T-cell activation switch on and switch off by modulating TCR expression at the T-cell surface. During thymocyte development, ZAP70 promotes survival and cell-cycle progression of developing thymocytes before positive selection (when cells are still CD4/CD8 double negative). Additionally, ZAP70-dependent signaling pathway may also contribute to primary B-cells formation and activation through B-cell receptor (BCR).