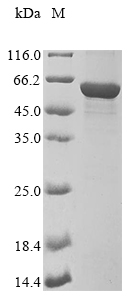
Just like other recombinant proteins, the production of this recombinant Mouse Vim protein began with appropriate cDNA and PCR methods, and then the Vim expression plasmids were built. Following sequence determination of the constructs, plasmids were transformed into E.coli for the expression of the recombinant Mouse Vim protein. N-terminal 10xHis tag & C-terminal Myc tag was used in the process. And we finally get the protein of interest with purity of 85%+.
Vim is a gene encoding a protein named vimentin in mouse. Other specieses, such as human, also have vimentin protein. It has been reported that vimentin, a cytoskeleton filament that is expressed only in mesenchymal cells after birth. It is re-expressed in epithelial cells in vivo under pathological conditions and in vitro in primary culture. This protein is involved in many biological processes, such as astrocyte development, regulation of mRNA stability, regulation of mRNA stability, etc. Recombinant vim A can be used to researching the interaction of proteins, such as plectin and vim.