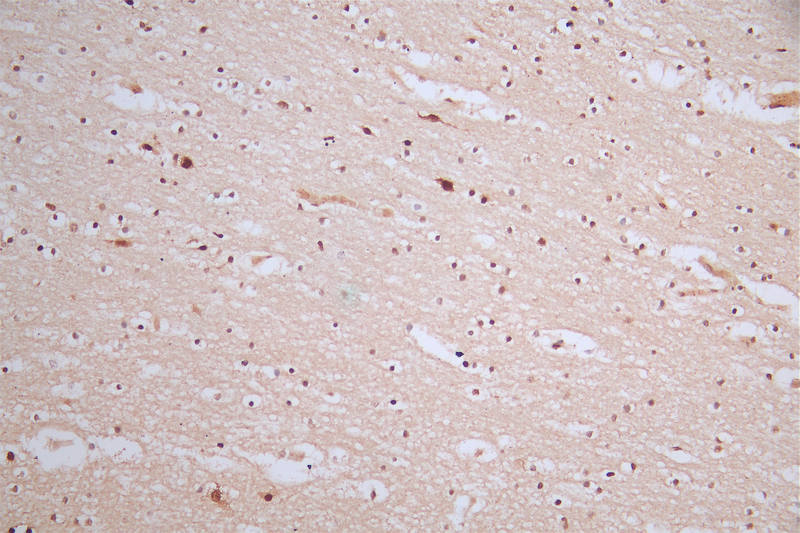
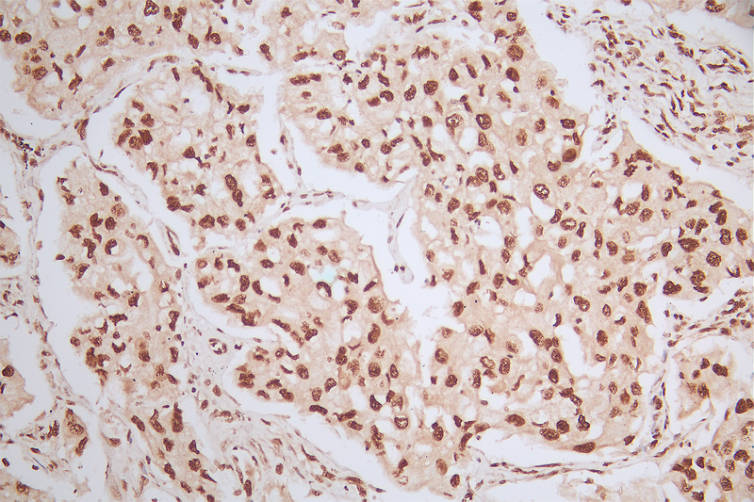
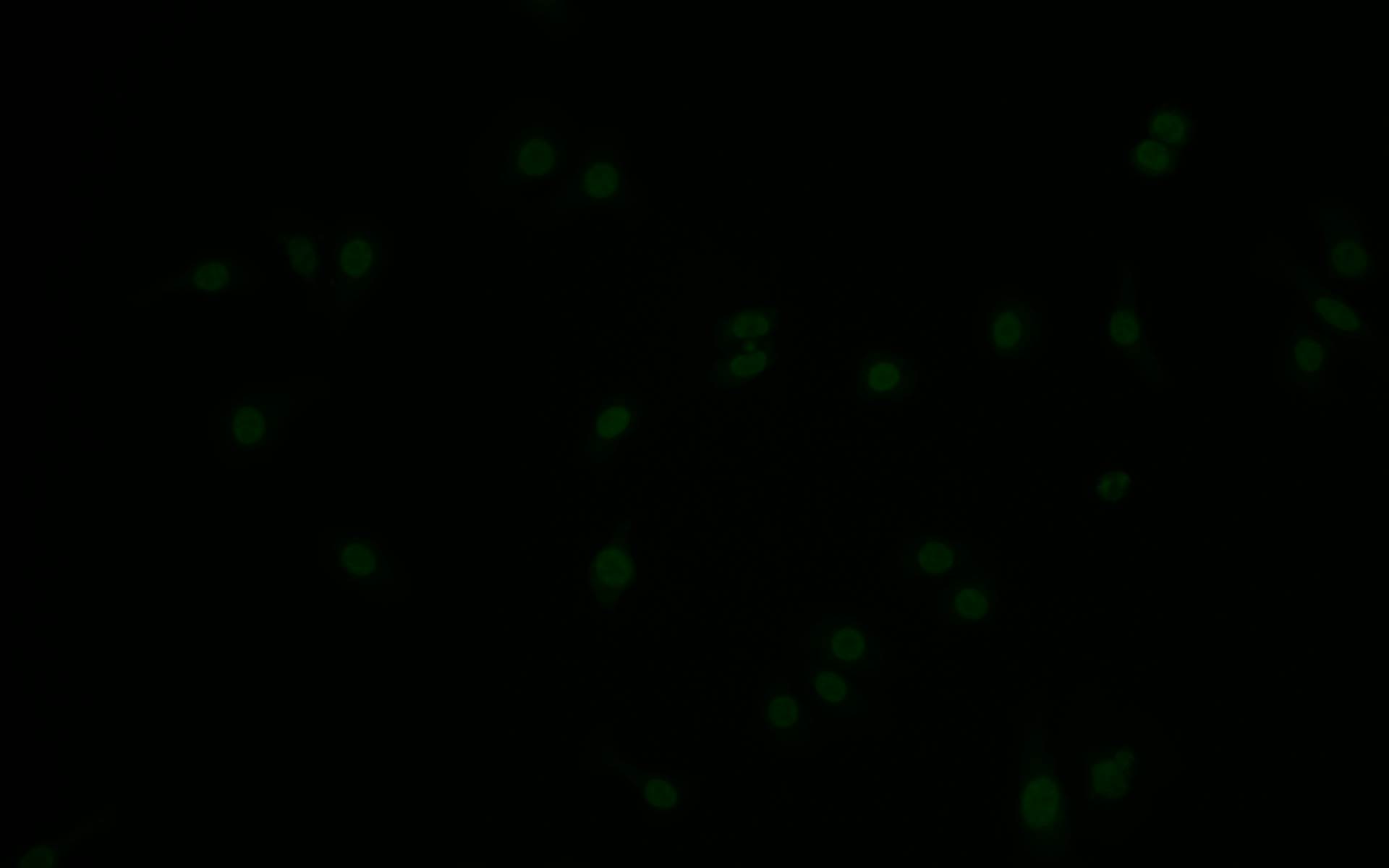
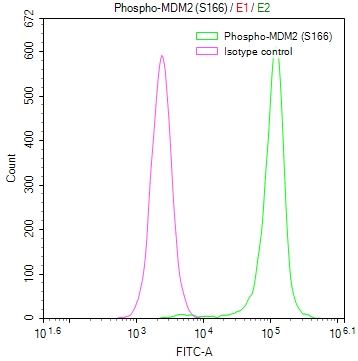
To produce the phospho-MDM2 (S166) recombinant monoclonal antibody, in vitro expression systems are harnessed, involving the cloning of DNA sequences of MDM2 antibodies obtained from immunoreactive rabbits. The immunogen used is a synthesized peptide derived from the human MDM2 protein that is phosphorylated at S166. Subsequently, the genes encoding the MDM2 antibodies are inserted into plasmid vectors, and these recombinant plasmid vectors are transfected into host cells to facilitate antibody expression. Post-expression, the phospho-MDM2 (S166) recombinant monoclonal antibody undergoes affinity-chromatography purification and is extensively tested for functionality in ELISA, IHC, IF, and FC applications, confirming its reactivity with the human MDM2 protein phosphorylated at S166.
MDM2 is a critical regulator of the tumor suppressor protein p53. Phosphorylation at S166 reduces MDM2's ability to target p53 for degradation, allowing p53 to accumulate and execute its functions in response to cellular stress and DNA damage.