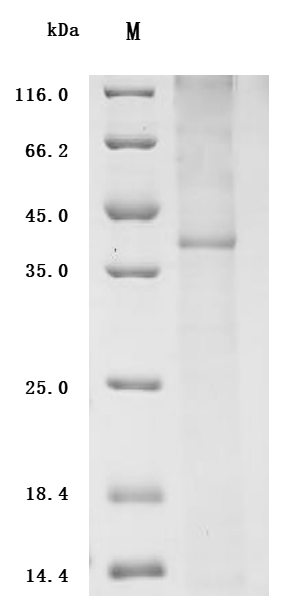
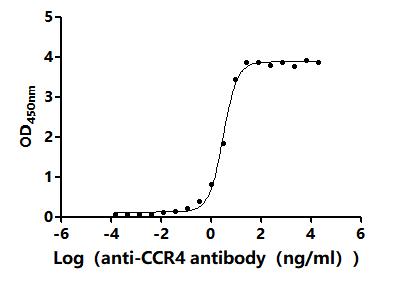
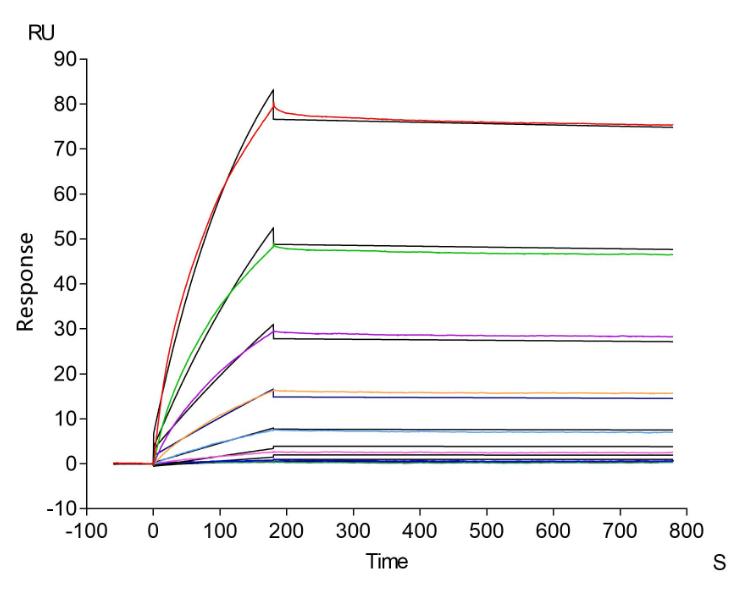
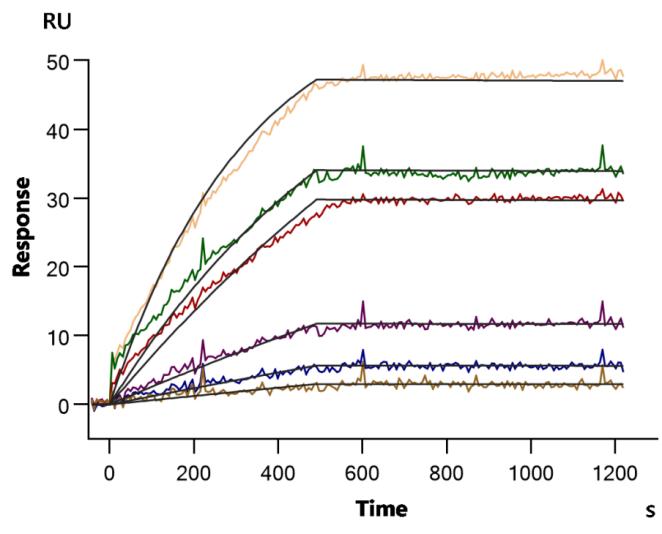
The recombinant human CCR4 protein is expressed from an in vitro E.coli expression system via the CCR4 cDNA clone corresponding to the 1-360aa of human CCR4 with an N-terminal 10xHis-tag. Its purity is greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE. Its biological activity has been validated through three applications including ELISA, SPR assay, and MetaSPR assay. In a functional ELISA, this recombinant CCR4 protein can bind the anti-CCR4 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA004843MA01HU), with the EC50 of 2.803-3.369 ng/mL. In the SPR assay, this CCR4 protein captured on a CM5 chip can bind the human CCR4 monoclonal antibody (CSB-RA004843MA01HU) with an affinity constant of 3.16 nM. It can bind the human CCR4 monoclonal antibody (CSB-RA004843MA01HU) captured on Protein A Chip with an affinity constant of 1.71 nM as detected by MetaSPR assay.
The human CCR4 protein is a critical component of the CCR4-NOT complex, which plays a significant role in various cellular processes, including mRNA degradation, transcription regulation, and RNA silencing. As a member of the G-protein coupled receptor family, CCR4 is predominantly expressed on T lymphocytes, particularly Th2 cells, where it serves as a specific marker and is involved in immune responses, including those related to atopic dermatitis and other inflammatory diseases [1]. The CCR4 protein interacts with several chemokines, notably CCL17 and CCL22, which are known to attract CCR4-expressing cells, thereby influencing immune cell trafficking and function [2].
In addition to its role in immune responses, human CCR4 exhibits enzymatic activity as part of the CCR4-NOT complex, specifically functioning as a deadenylase. This activity is crucial for the removal of poly(A) tails from mRNA, a process that is essential for mRNA degradation and regulation of gene expression [3][4]. The CCR4-NOT complex, which includes other proteins such as Caf1 and various Not proteins, is involved in multiple aspects of RNA metabolism, including mRNA transport, decapping, and quality control [5][6]. The deadenylation activity of CCR4 is particularly important in maintaining cellular homeostasis and regulating the stability of mRNAs, such as those encoding the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27, which is vital for cell cycle regulation [7].
Moreover, the CCR4 protein is implicated in various diseases, including cancers and autoimmune disorders, due to its role in modulating immune responses and influencing cell proliferation [8]. The understanding of CCR4's functions has led to the exploration of therapeutic strategies targeting CCR4-expressing cells, particularly in the context of immunotoxins designed to selectively eliminate these cells in cancer treatment [8].
References:
[1] G. Yang, X. Chen, Y. Sun, C. Ma, & Q. Ge. Chemokine-like factor 1 (clfk1) is over-expressed in patients with atopic dermatitis, International Journal of Biological Sciences, vol. 9, no. 8, p. 759-765, 2013. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.6291
[2] D. Wågsäter, O. Dienus, S. Löfgren, A. Hugander, & J. Dimberg. Quantification of the chemokines ccl17 and ccl22 in human colorectal adenocarcinomas, Molecular Medicine Reports, 2008. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.1.2.211
[3] M. Maryati, B. Airhihen, & G. Winkler. The enzyme activities of caf1 and ccr4 are both required for deadenylation by the human ccr4–not nuclease module, Biochemical Journal, vol. 469, no. 1, p. 169-176, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20150304
[4] M. Nousch, N. Techritz, D. Hampel, S. Millonigg, & C. Eckmann. The ccr4-not deadenylase complex constitutes the major poly(a) removal activity inc. elegans, Journal of Cell Science, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.132936
[5] P. Rangasamy, G. Kandasamy, & A. Pradhan. Ccr4-not complex nuclease caf1 is a novel shuttle factor involved in the degradation of ubiquitin-modified proteins by 26s proteasome,, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.13.093104
[6] N. Lau, A. Kolkman, F. Schaik, K. Mulder, W. Pijnappel, A. Heck, et al. Human ccr4–not complexes contain variable deadenylase subunits, Biochemical Journal, vol. 422, no. 3, p. 443-453, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj20090500
[7] M. Morita, T. Suzuki, T. Nakamura, K. Yokoyama, T. Miyasaka, & T. Yamamoto. Depletion of mammalian ccr4b deadenylase triggers elevation of the p27kip1 mrna level and impairs cell growth, Molecular and Cellular Biology, vol. 27, no. 13, p. 4980-4990, 2007. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.02304-06
[8] Z. Wang, W. Min, H. Zhang, H. Chen, S. Germana, C. Huang, et al. Diphtheria‐toxin based anti‐human ccr4 immunotoxin for targeting human ccr4+ cells in vivo, Molecular Oncology, vol. 9, no. 7, p. 1458-1470, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2015.04.004