The ACTB gene encodes the protein beta - actin. It is also commonly known as cytoplasmic beta - actin. Beta - actin is a crucial component of the cytoskeleton, playing a vital role in cell structure maintenance, cell motility, and muscle contraction. It participates in several important signaling pathways such as the Wnt and Rho signaling pathways.
Mutations or dysregulation of beta - actin are associated with various diseases, including some types of cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. In terms of drug development, targeting beta - actin has shown potential in treating cancer, though it is still in the research stage. Current studies aim to find specific agents that can precisely modulate its function.
Popular Product:
Recombinant Human Actin, cytoplasmic 1 (ACTB), partial (CSB-EP001207HU1)
Validated Data
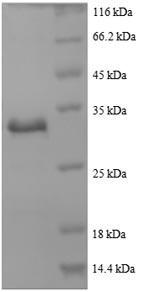
(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
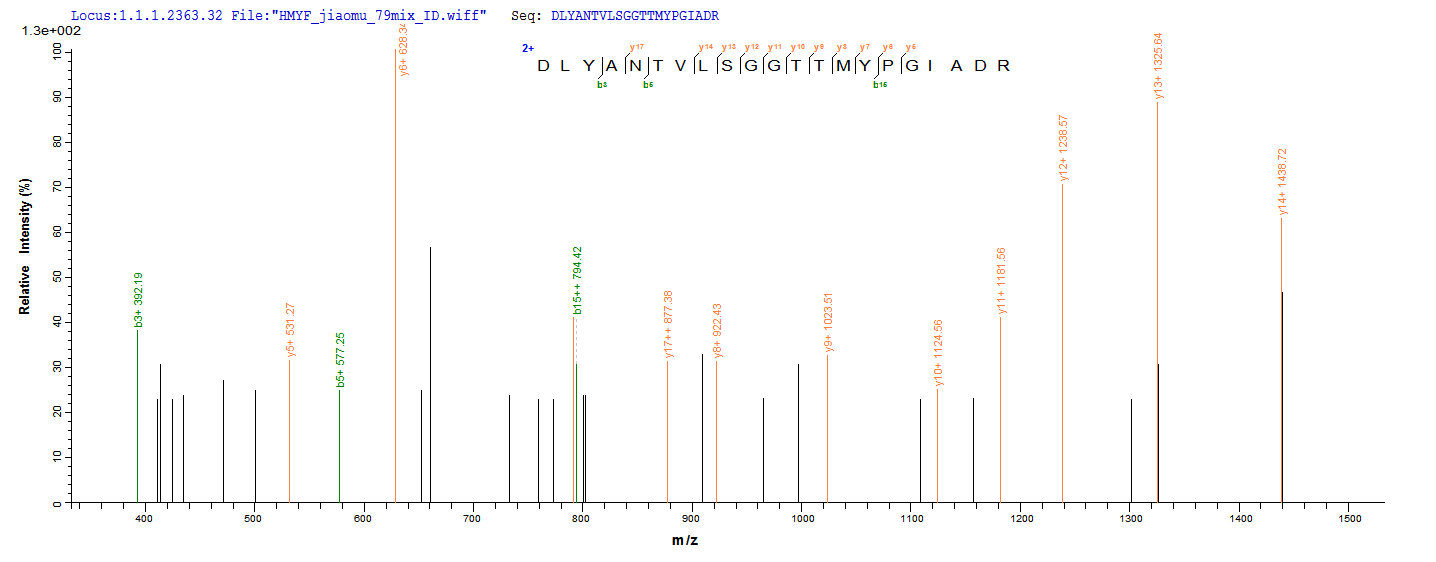
Based on the SEQUEST from database of E.coli host and target protein, the LC-MS/MS Analysis result of CSB-RP016294h could indicate that this peptide derived from E.coli-expressed Homo sapiens (Human) ACTB.
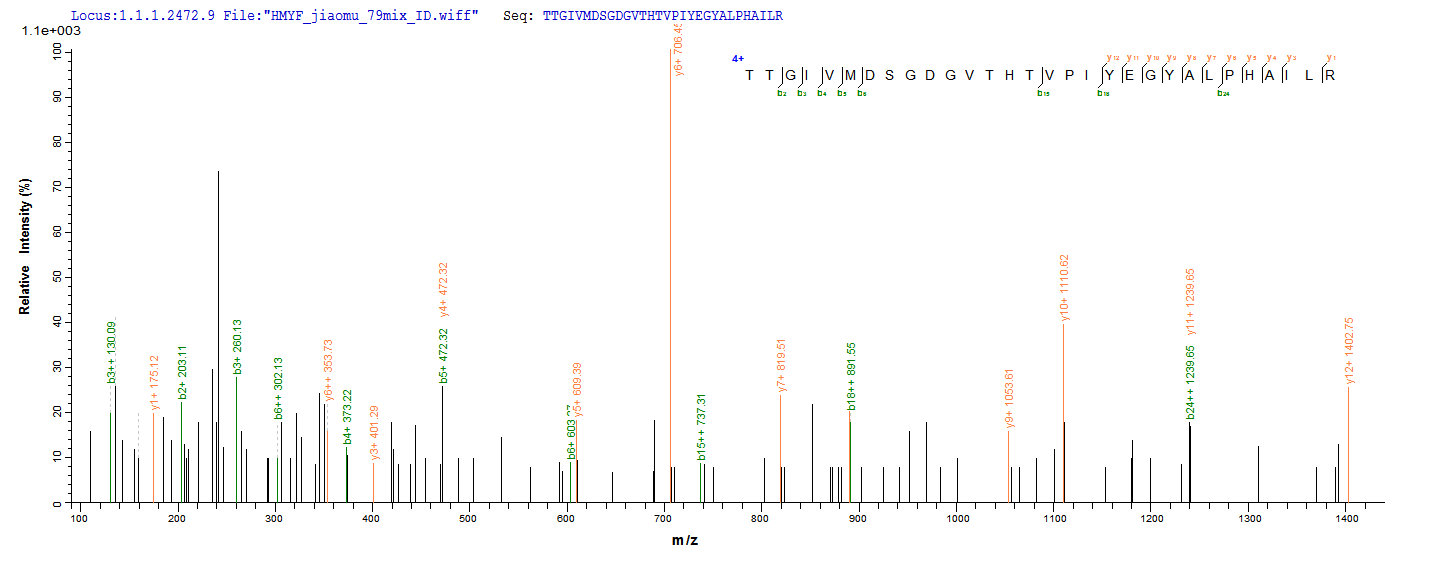
Based on the SEQUEST from database of E.coli host and target protein, the LC-MS/MS Analysis result of CSB-RP016294h could indicate that this peptide derived from E.coli-expressed Homo sapiens (Human) ACTB.
ACTB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody (CSB-RA000091M1m)
Validated Data
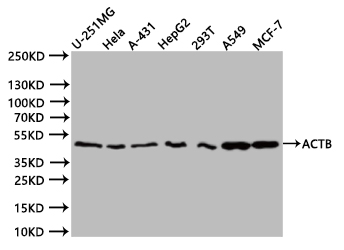
Western Blot
Positive WB detected in:U251 whole cell lysate (20µg), Hela whole cell lysate (20µg), HepG2 whole cell lysate (20µg), 293T whole cell lysate (20µg), A549 whole cell lysate (20µg), MCF7 whole cell lysate (20µg)
All lanes: ACTB antibody at 1:1000
Secondary
Goat polyclonal to mouse IgG at 1/40000 dilution
Predicted band size:42 kDa
Observed band size:42 kDa
Exposure time:20s
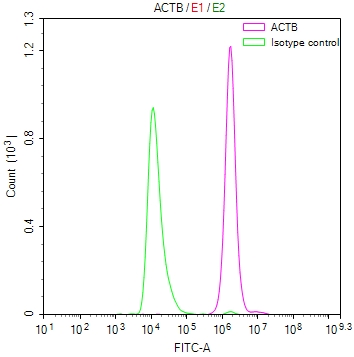
Overlay Peak curve showing Hela cells stained with CSB-RA000091M1m (red line) at 1:100. The cells were fixed in 4% formaldehyde and permeated by 0.2% TritonX-100. Then 10% normal goat serum to block non-specific protein-protein interactions followed by the antibody (1ug/1*106cells) for 45min at 4℃. The secondary antibody used was FITC-conjugated Goat Antimouse IgG(H+L) at 1:200 dilution for 35min at 4℃.Control antibody (green line) was mouse IgG (1ug/1*106cells) used under the same conditions. Acquisition of >10,000 events was performed.
The following ACTB reagents supplied by CUSABIO are manufactured under a strict quality control system. Multiple applications have been validated and solid technical support is offered.
ACTB Proteins
ACTB Proteins for Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
ACTB Proteins for Bos taurus (Bovine)
ACTB Proteins for Gallus gallus (Chicken)
ACTB Proteins for Ovis aries (Sheep)
ACTB Proteins for Mus musculus (Mouse)
ACTB Proteins for Homo sapiens (Human)
ACTB Proteins for Equus caballus (Horse)
ACTB Proteins for Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
ACTB Proteins for Oryzias latipes (Japanese rice fish) (Japanese killifish)
ACTB Proteins for Oreochromis mossambicus (Mozambique tilapia) (Tilapia mossambica)
ACTB Proteins for Cyprinus carpio (Common carp)
ACTB Proteins for Ctenopharyngodon idella (Grass carp) (Leuciscus idella)
ACTB Proteins for Camelus dromedarius (Dromedary) (Arabian camel)
ACTB Proteins for Chlorocebus pygerythrus (Vervet monkey) (Cercopithecus pygerythrus)
ACTB Proteins for Phytophthora infestans (Potato late blight fungus) (Botrytis infestans)
ACTB Proteins for Xenopus borealis (Kenyan clawed frog)
ACTB Proteins for Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) (Cricetulus barabensis griseus)
ACTB Proteins for Trichosurus vulpecula (Brush-tailed possum)
ACTB Proteins for Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
ACTB Proteins for Salmo salar (Atlantic salmon)
ACTB Proteins for Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog)
ACTB Proteins for Bos mutus grunniens (Wild yak) (Bos grunniens)
ACTB Proteins for Spermophilus citellus (European suslik) (Citellus citellus)
ACTB Proteins for Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
ACTB Proteins for Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee)
ACTB Proteins for Pongo abelii (Sumatran orangutan) (Pongo pygmaeus abelii)
ACTB Proteins for Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis)
ACTB Proteins for Sus scrofa (Pig)
ACTB Proteins for Cavia porcellus (Guinea pig)
ACTB Proteins for Chlorocebus aethiops (Green monkey) (Cercopithecus aethiops)
ACTB Proteins for Mesocricetus auratus (Golden hamster)
ACTB Proteins for Sigmodon hispidus (Hispid cotton rat)









