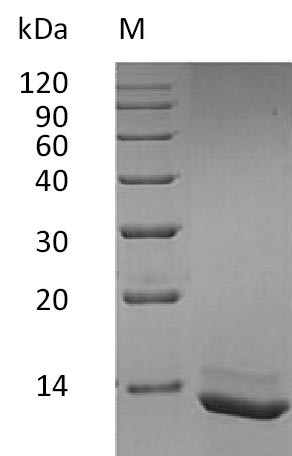
Recombinant Human Interleukin-15 (IL15) is expressed in E. coli and represents the full length of the mature protein, spanning amino acids 49-162. This tag-free protein is produced with a purity exceeding 95%, as verified by SDS-PAGE analysis. It demonstrates biological activity, with an effective dose (ED50) in a cell proliferation assay using CTLL-2 mouse cytotoxic T cells ranging from 40 to 200 pg/ml. The endotoxin level is maintained below 1.0 EU/µg, as determined by the LAL method.
Interleukin-15 (IL15) appears to be a central player in immune response regulation. This cytokine is particularly important for the proliferation and survival of natural killer (NK) cells and CD8+ T cells, which may contribute significantly to adaptive immunity. Researchers studying immune cell function, cancer immunotherapy, and vaccine development often turn to IL15 for insights into potential therapeutic strategies.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. T Cell Proliferation and Activation Studies
This recombinant IL-15 is confirmed to be highly bioactive (ED₅₀ 40-200 pg/ml in CTLL-2 cells) and suitable for T cell studies. However, as it is expressed in E. coli, it lacks glycosylation, which may affect protein stability or in vivo half-life compared to native IL-15. Researchers should validate its activity in human primary T cells and NK cells to ensure cross-reactivity, as CTLL-2 is a mouse cell line and may not fully represent human immune responses. The high purity and low endotoxin support reliable results in sensitive assays.
2. Natural Killer Cell Functional Assays
The protein is appropriate for NK cell studies, but its activity should be validated in primary human NK cells, as the ED₅₀ was determined in mouse CTLL-2 cells (a T cell line), which may not directly translate to NK cell biology. The E. coli expression produces non-glycosylated IL-15, which could influence NK cell activation or survival kinetics. Dose-response curves should be established specifically for human NK cells to ensure physiological relevance.
3. Cytokine Signaling Pathway Analysis
The biologically active IL-15 is suitable for signaling studies (e.g., JAK-STAT pathway activation). The tag-free design avoids tag-related artifacts. However, the non-glycosylated form may alter signaling dynamics (e.g., receptor binding affinity or signal duration) compared to glycosylated IL-15. Researchers should confirm phosphorylation events and downstream responses in human immune cells to ensure native-like signaling.
4. Antibody Development and Validation
This IL-15 serves as a good antigen for antibody development due to its full-length mature sequence, but antibodies generated against this E. coli-expressed, non-glycosylated protein may not recognize glycosylated epitopes on native IL-15. Comprehensive validation should include testing against mammalian-expressed or natural IL-15 from biological sources to ensure broad epitope coverage and physiological relevance. The bioactivity supports functional neutralization assays.
5. Immunotherapy Mechanism Studies
The protein can be used in preclinical immunotherapy research, but the E. coli expression and lack of glycosylation may limit in vivo applications due to potential immunogenicity or rapid clearance. For in vitro co-culture studies, it is suitable, but for animal models, consider using mammalian-expressed IL-15 to avoid species-specific immune responses. The low endotoxin is beneficial for complex assays, but in vivo efficacy should be validated with glycosylated forms.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This recombinant human IL-15 expressed in E. coli is a highly potent tool for in vitro studies, as evidenced by its low ED₅₀ in CTLL-2 cells, but researchers must account for its non-glycosylated state and prokaryotic expression system. For immediate use, employ it at picogram-level concentrations (40-200 pg/ml) based on the ED₅₀, but validate dose-response relationships in human primary T cells and NK cells to ensure cross-species reactivity and physiological relevance. When studying signaling pathways, the tag-free design is advantageous, but comparing key kinetics with mammalian-expressed IL-15 to address potential glycosylation-related differences. For antibody development, use this protein for immunization, but rigorously validate antibodies against glycosylated IL-15 to ensure recognition of native epitopes. In immunotherapy research, restrict initial studies to in vitro models and transition to mammalian-expressed IL-15 for in vivo work to avoid immunogenicity. Always include controls for non-specific effects (e.g., endotoxin, vehicle) and prioritize validation in human cell systems to bridge the gap between mouse CTLL-2 data and human immunology.