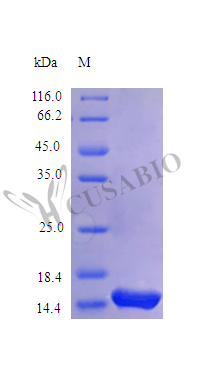
Recombinant Rhesus Macaque Interleukin-4 protein (IL4) is produced in E. coli with the full-length mature protein expressed from amino acids 25 to 153. This product is tag-free and achieves a high purity level exceeding 96%, confirmed by SDS-PAGE analysis. The protein demonstrates full biological activity, with an ED50 of less than 1.0 ng/ml in a cell proliferation assay using human TF-1 cells. Endotoxin levels remain below 1.0 EU/µg, determined by the LAL method.
Interleukin-4 (IL-4) appears to be a key cytokine involved in immune response regulation, primarily influencing the differentiation of naive helper T cells to Th2 cells. It plays what seems to be a critical role in promoting B-cell differentiation and antibody production. IL-4 is likely integral to understanding allergic inflammatory responses and has significant implications in research focused on immune modulation and related disorders.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. Cell Proliferation and Viability Assays in Primate Cell Models
This recombinant rhesus macaque IL-4 protein is confirmed to be biologically active (ED₅₀ < 1.0 ng/ml in human TF-1 cells) and suitable for studying IL-4-mediated cellular responses in primate models. The high purity (>96%) and low endotoxin levels ensure reliable results in dose-response studies. However, researchers should note that while it shows activity on human TF-1 cells, its performance on specific rhesus macaque primary cells should be validated, as species-specific differences in IL-4 receptor affinity may exist.
2. Cytokine Signaling Pathway Analysis
The biologically active IL-4 protein is appropriate for studying IL-4 receptor binding and downstream signaling cascades (STAT6 phosphorylation, JAK activation) in primate research models. The tag-free design eliminates potential interference with receptor binding. However, since the protein is expressed in E. coli and lacks mammalian glycosylation, signaling kinetics may differ slightly from native IL-4 in some cellular contexts. Comparative studies with human IL-4 should account for potential species-specific signaling differences.
3. Antibody Development and Validation Studies
This high-purity rhesus macaque IL-4 protein serves as an excellent antigen for developing species-specific antibodies. The mature protein sequence (25-153aa) represents the natural form, making it ideal for generating antibodies that recognize native IL-4 in rhesus samples. However, researchers should validate antibody specificity against both recombinant and native rhesus IL-4 to ensure recognition of properly folded protein in biological samples.
4. Comparative Cytokine Function Studies
The protein enables valid comparative studies between human and rhesus macaque IL-4 systems. The demonstrated activity on human TF-1 cells provides a baseline for cross-species reactivity assessment. However, direct functional comparisons should include validation in rhesus-specific cellular models to account for potential differences in receptor binding affinity or signaling potency between the species.
5. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
This recombinant IL-4 is suitable for studying interactions with IL-4 receptors and binding partners. The tag-free format and confirmed bioactivity ensure reliable results in binding assays (SPR, BLI). However, for novel interaction partners identified, validation with mammalian-expressed IL-4 is recommended to account for potential differences due to the absence of post-translational modifications in the E. coli-expressed protein.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This E. coli-expressed rhesus macaque IL-4 protein is a highly reliable research tool suitable for all proposed applications, with its biological activity confirmed through standardized proliferation assays. For immediate use, employ it in primate cell culture studies and signaling pathway analysis, noting that while it demonstrates cross-reactivity with human cells, validation in rhesus-specific models is recommended for species-specific conclusions. When developing antibodies, this protein is ideal for immunization and assay development, but resulting antibodies should be validated against native rhesus IL-4 when possible. For comparative studies with human IL-4, include parallel dose-response experiments to quantify any functional differences. The high purity and low endotoxin levels ensure minimal interference in sensitive cellular assays. While the E. coli expression system produces a non-glycosylated form, the confirmed bioactivity indicates proper folding for receptor engagement and biological function. Always include appropriate controls and validate key findings in biologically relevant systems.