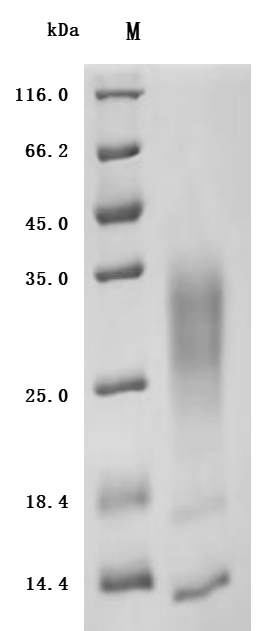
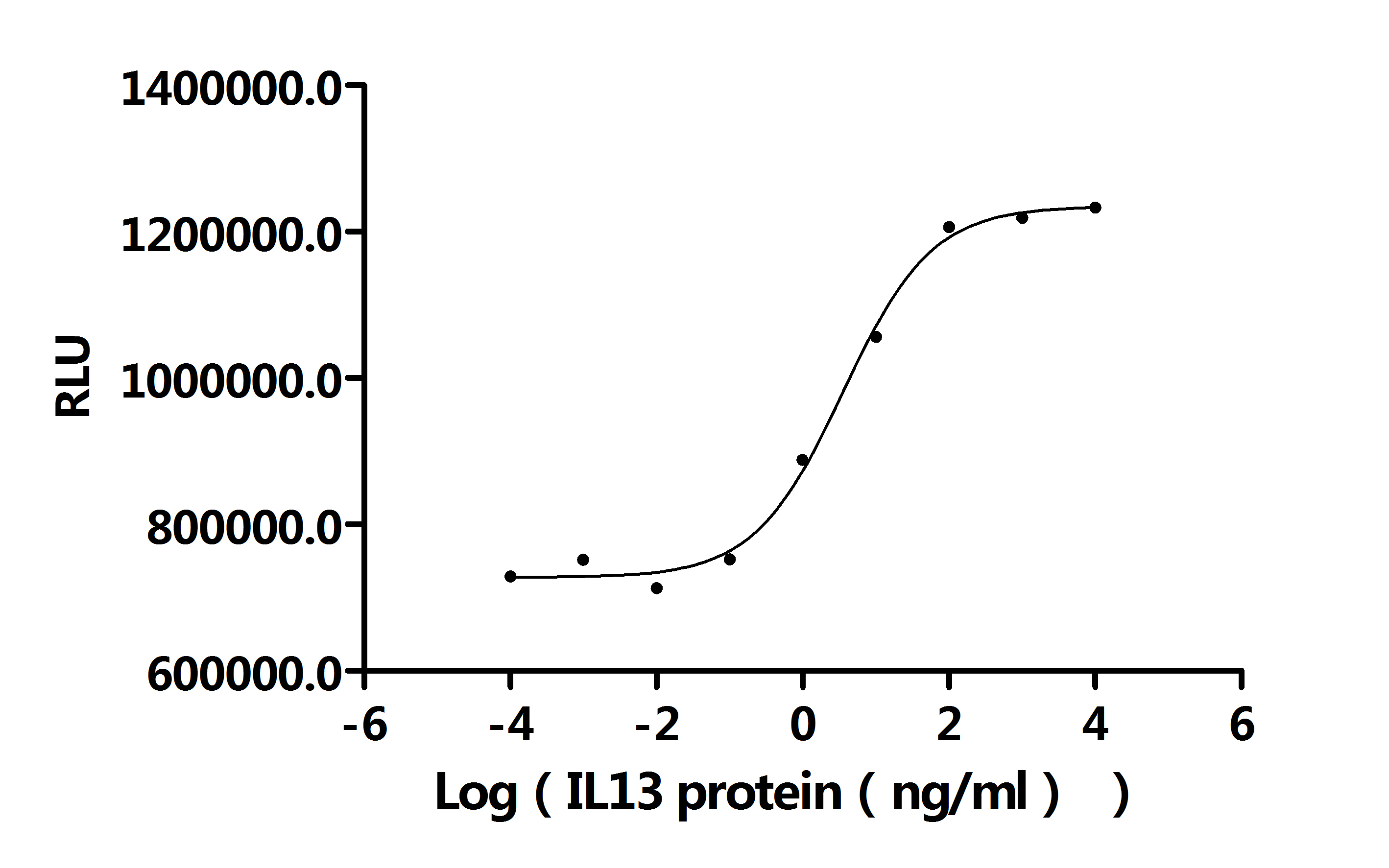
The recombinant human IL13 protein is produced by the HEK293 cell expression system. It is expressed with sequence (Gly21-Asn132) of human IL13 fused with a 10xHis tag at the C-terminus. The purity of this recombinant IL13 protein is over 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE. Its endotoxin is less than 1.0 EU/ug as measured by the LAL method. It has been validated to be biologically active in a proliferation assay. The ED50 as accessed by the dose-dependent stimulation of the proliferation of TF-1 cells is 2.045-6.215 ng/mL.
IL13 is a cytokine that plays a pivotal role in the immune system, particularly in mediating type 2 immune responses. It is primarily produced by Th2 cells, mast cells, and eosinophils, and is known for its involvement in various physiological and pathological processes, including allergic reactions, asthma, and other inflammatory diseases [1][2]. IL13 shares structural similarities with IL4 and exhibits overlapping functions, particularly in promoting IgE class switching in B cells, which is crucial for allergic responses [1][2].
The IL13 protein exerts its effects by binding to specific receptors, IL13Rα1 and IL13Rα2. The interaction with these receptors activates downstream signaling pathways, notably the JAK1/STAT6 pathway, which mediates many of its biological effects, including the regulation of gene expression related to inflammation and immune responses [3][4]. Notably, IL13Rα2 acts as a decoy receptor, which can inhibit the signaling of IL13, thereby modulating its effects in various contexts, such as in inflammatory bowel disease [3].
Research has also highlighted the dual role of IL13 in inflammation. While it is known to promote anti-inflammatory responses, its dysregulation can lead to pathological conditions. Elevated levels of IL13 have been associated with autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammatory conditions, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [5]. Genetic polymorphisms in the IL13 gene have been linked to variations in susceptibility to these diseases, indicating that genetic factors may influence IL13 expression and function [5].
Furthermore, IL13 has been implicated in tissue remodeling and fibrosis, particularly in the lungs and gastrointestinal tract. It promotes the differentiation of macrophages towards an M2 phenotype, which is associated with tissue repair and fibrosis, thus playing a significant role in chronic inflammatory conditions [6][7]. In the context of cancer, engineered variants of IL13 have been developed for targeted therapies, particularly in tumors that overexpress IL13 receptors, showcasing its potential in immunotherapy [8].
References:
[1] C. Hoornaert, E. Luyckx, K. Reekmans, M. Dhainaut, C. Guglielmetti, D. Blon, et al. In vivo interleukin-13-primed macrophages contribute to reduced alloantigen-specific t cell activation and prolong immunological survival of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell implants, The International Journal of Cell Cloning, vol. 34, no. 7, p. 1971-1984, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.2360
[2] K. TENBROCK, A. SCHUBERT, L. STAPENHORST, M. KEMPER, J. GELLERMANN, K. TIMMERMANN, et al. Type i ige receptor, interleukin 4 receptor and interleukin 13 polymorphisms in children with nephrotic syndrome, Clinical Science, vol. 102, no. 5, p. 507, 2002. https://doi.org/10.1042/cs20010229
[3] T. Yau, J. Vadakekolathu, G. Foulds, G. Du, C. Polytarchou, B. Dickins, et al. Hyperactive chemotaxis contributes to anti-tnfα treatment resistance in inflammatory bowel disease,, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.15.456400
[4] N. Wood, M. Whitters, B. Jacobson, J. Witek, J. Sypek, M. Kasaian, et al. Enhanced interleukin (il)-13 responses in mice lacking il-13 receptor α 2, The Journal of Experimental Medicine, vol. 197, no. 6, p. 703-709, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20020906
[5] S. Liu, H. Chang, Y. Chang, H. Kuo, & Y. Tsai. Il13 promoter (−1055) polymorphism associated with leukocyte mitochondria dna copy number in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Cells, vol. 11, no. 23, p. 3787, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11233787
[6] C. Petersen, A. Meyer, C. Salvo, E. Choi, C. Schlegel, A. Petersen, et al. A signalling cascade of il-33 to il-13 regulates metaplasia in the mouse stomach, Gut, vol. 67, no. 5, p. 805-817, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-312779
[7] C. Noto, S. Hoft, K. Bockerstett, N. Jackson, E. Ford, L. Vest, et al. Il13 acts directly on gastric epithelial cells to promote metaplasia development during chronic gastritis, Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, vol. 13, no. 2, p. 623-642, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.09.012
[8] L. Stern, S. Gholamin, I. Moraga, X. Yang, S. Saravanakumar, J. Cohen, et al. Engineered il13 variants direct specificity of il13rα2-targeted car t cell therapy, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 119, no. 33, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2112006119