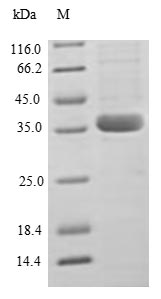
Recombinant Human C-C motif chemokine 2 (CCL2) is produced in E. coli and contains the complete mature protein sequence, covering amino acids 24 to 99. The protein carries an N-terminal GST tag, which helps with purification and detection processes. SDS-PAGE analysis confirms that the product achieves greater than 90% purity, which appears to deliver reliable results for research work. This reagent is intended for research use only and contains minimal endotoxin contamination.
CCL2, commonly called monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), serves as an important chemokine that draws monocytes, memory T cells, and dendritic cells toward inflammatory sites. It likely plays a central role in immune response control and has become a frequent subject of study in inflammatory disease research and immune system investigations. This makes it particularly useful for understanding how cells migrate and communicate through signaling networks.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Human CCL2 is a chemokine that requires precise folding, proper disulfide bond formation (with 2 conserved disulfide bonds), and specific tertiary structure for its functional activity in monocyte chemotaxis and receptor binding. The E. coli expression system cannot provide the necessary eukaryotic folding environment or oxidative conditions for correct disulfide bond formation. The large N-terminal GST tag (∼26 kDa) combined with the CCL2 mature protein (∼8 kDa) creates a chimeric protein where the tag constitutes approximately 75% of the total molecular mass (35.7 kDa). This massive size disparity will severely sterically interfere with receptor binding sites and dimerization interfaces. While the protein may be soluble, the probability of correct folding with functional chemotactic activity is extremely low.
This GST-CCL2 fusion protein (35.7 kDa) is fundamentally unsuitable for functional CCL2 research due to the severe steric hindrance caused by the massive GST tag (constituting ~75% of the protein mass). The tag dominance will prevent receptor binding, alter protein behavior in all assays, and likely induce immune responses. The only limited application is antibody development against linear epitopes, though most antibodies will target the GST domain. For reliable CCL2 research, use tag-free protein (8 kDa) produced in mammalian systems or chemically synthesized with proper disulfide bonds.