The Recombinant Human F5 protein is a crucial tool for understanding coagulation processes and exploring potential therapeutic interventions in cardiovascular research. Coagulation factor V, also known as activated protein C cofactor, is an essential player in the blood clotting cascade, regulating the balance between procoagulant and anticoagulant activities.
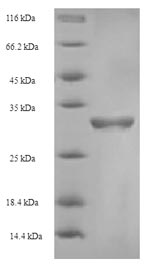
This product contains a partial sequence of the human F5 protein (1490-1614aa) expressed in E.coli, ensuring high-quality recombinant protein production. The N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO tag enables efficient purification and facilitates detection in downstream applications. With a purity greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE, our Recombinant Human F5 protein provides a reliable reagent for your cardiovascular research needs. Supplied as a lyophilized powder, this product is readily reconstituted for immediate use in your experiments.