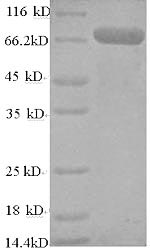
Amino acids 1-522 form the expressed segment for recombinant Human TRAF6. The calculated molecular weight for this TRAF6 protein is 75.6 kDa. This protein is generated in a e.coli-based system. The TRAF6 coding gene included the N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO tag, which simplifies the detection and purification processes of the recombinant TRAF6 protein in following stages of expression and purification.
TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) is a crucial signaling mediator within the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily and Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling pathways. TRAF6 is a multi-functional protein involved in various cellular processes, including immune response, inflammation, and bone metabolism. Its main function is to serve as an adaptor protein, facilitating the activation of downstream signaling cascades in response to receptor activation. TRAF6 plays a key role in the activation of NF-κB and MAPK pathways, leading to the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and other immune-related genes. In addition to its role in immunity, TRAF6 has implications for bone homeostasis through its involvement in RANKL-mediated osteoclast differentiation. Dysregulation of TRAF6 signaling has been linked to autoimmune diseases, inflammatory disorders, and bone-related conditions, making it a significant target for therapeutic interventions.