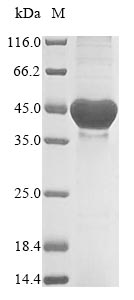
Recombinant Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B Quinolinate synthase (nadA) is expressed in E. coli, spanning amino acids 1-370. It comes with an N-terminal 6xHis-tag that makes purification more straightforward. The protein appears to maintain purity levels above 85% based on SDS-PAGE analysis, which should provide reliable experimental results. This product is meant for research use only and contains minimal endotoxin levels, making it appropriate for various biochemical assays and studies.
The nadA gene encodes quinolinate synthase, an enzyme that participates in NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) biosynthesis—a critical coenzyme for cellular metabolism. In Neisseria meningitidis, this protein likely plays a key role in synthesizing quinolinic acid, which serves as a precursor to NAD. Studying this enzyme may provide valuable insights into bacterial NAD biosynthesis, metabolic regulation, and potentially new antibiotic targets.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
As both the source organism (N. meningitidis) and expression system (E. coli) are prokaryotic, the protein has a reasonable probability of correct folding since both systems share similar requirements for protein synthesis and folding. Quinolinate synthase is an enzyme that requires proper folding for its catalytic activity in NAD biosynthesis. No experimental validation data (e.g., enzymatic activity assays, structural analysis) are provided. Therefore, while the probability of correct folding is higher than for eukaryotic proteins expressed in E. coli, the protein's folding status and bioactivity cannot be confirmed without experimental verification.
1. Biochemical Characterization of NAD Biosynthesis Pathway
If the recombinant NadA is correctly folded and functional, it can be used to study the NAD biosynthesis pathway through enzymatic assays, as proper folding is essential for catalytic activity. The 6xHis tag facilitates purification for detailed kinetic studies. However, if misfolded or inactive (unverified), such assays would yield invalid kinetic parameters and incorrect conclusions about the enzyme's catalytic properties and role in bacterial NAD metabolism.
2. Antibody Development and Immunological Studies
This application is suitable regardless of folding status. The recombinant NadA can serve as an effective antigen for antibody generation since antibodies primarily recognize linear epitopes. The high purity minimizes cross-reactivity issues during antibody production. However, if misfolded, generated antibodies may not optimally recognize conformation-dependent epitopes of the native protein in bacterial systems.
3. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
If properly folded, the His-tagged NadA could be used in pull-down assays to identify genuine interaction partners within NAD biosynthesis pathways, as native conformation is necessary for biologically relevant protein interactions. However, if misfolded, there is risk of non-specific binding or failure to recognize true biological partners, compromising the validity of identified interaction networks.
4. Structural and Biophysical Analysis
If correctly folded, the recombinant protein is suitable for structural studies to understand NadA's three-dimensional architecture, as these techniques rely on native conformation for meaningful insights. However, if misfolded, structural data would misrepresent the native enzyme's conformation, and the His-tag might interfere with crystallization or NMR analysis.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This recombinant NadA has a reasonable probability of correct folding due to the prokaryotic origin and expression system compatibility, but experimental validation remains essential before any application. The recommended action plan includes: first verifying protein folding and bioactivity through enzymatic assays measuring quinolinate synthase activity with appropriate substrates, complemented by biophysical characterization (size-exclusion chromatography, circular dichroism); if validation confirms proper folding and function, proceed with applications while recognizing that the His-tag might still affect some properties; if the protein is misfolded or inactive, consider optimization of expression conditions or use of alternative purification/refolding protocols to recover functionality.