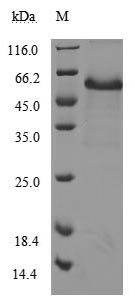
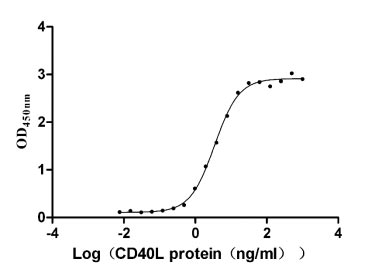
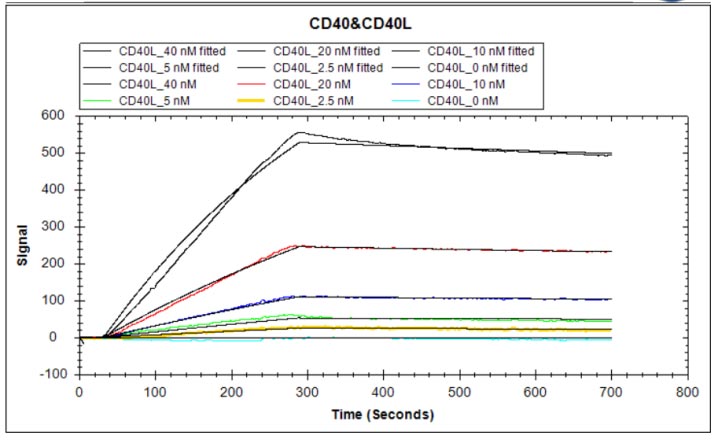
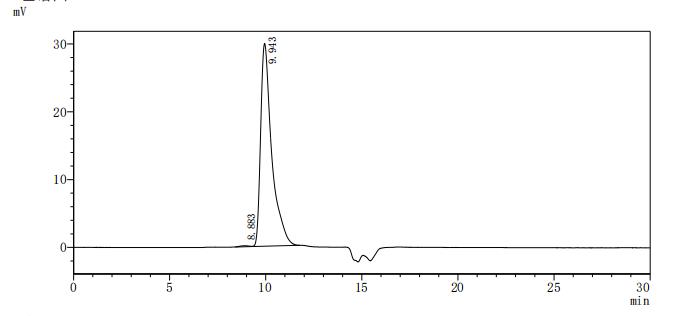
The recombinant human CD40 protein is produced by expressing a plasmid in mammalian cells that encodes the amino acid sequence from 21 to 193 of the human CD40. A hFc-tag is attached to the C-terminus of the protein. SDS-PAGE analysis measures the purity of this CD40 protein at greater than 95%, while LAL testing confirms its endotoxin levels are below 1.0 EU/μg. ELISA validates its biological activity, with this CD40 protein binding to CD40L (CSB-MP004937HU3) at an EC50 between 3.112 and 3.858 ng/mL. In the LSPR assay, this human CD40 protein captured on the COOH chip binds to the human CD40L protein (CSB-MP004937HU3) with an affinity constant of 2.06 nM.
Human TNFRSF5 (CD40) is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein primarily expressed on various immune cells, including B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and macrophages [1][2]. It plays a crucial role in the immune system. CD40 is essential for mediating costimulatory signals that enhance the activation and differentiation of B cells, thereby facilitating effective immune responses [3].
Upon binding of its ligand CD40L (CD154), CD40 undergoes conformational changes that lead to the recruitment of intracellular adaptor proteins known as TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs), which initiate downstream signaling cascades [4][5]. This signaling is crucial for processes such as B cell proliferation, isotype switching, and the generation of memory B cells, which are vital for long-term immunity [5]. Furthermore, CD40 signaling is implicated in the regulation of cytokine production, influencing the inflammatory response and the development of various immune-mediated conditions [2].
CD40 has also been implicated in various pathological conditions, including cancer and autoimmune diseases. Aberrant CD40 signaling can contribute to tumor progression by promoting an inflammatory microenvironment that supports tumor growth and metastasis [6]. In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), CD40 expression has been associated with clinical outcomes, suggesting that it may serve as a potential therapeutic target [7]. Moreover, CD40 is involved in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy, where its activation leads to enhanced inflammatory responses in retinal cells [8].
References:
[1] F. Dimitrakopoulos, Α. Κοττόρου, A. Antonacopoulou, Ν. Παναγόπουλος, C. Scopa, M. Kalofonou, et al. Expression of immune system-related membrane receptors cd40, rank, baffr and ltβr is associated with clinical outcome of operated non-small-cell lung cancer patients, Journal of Clinical Medicine, vol. 8, no. 5, p. 741, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050741
[2] C. Antoniades, C. Bakogiannis, D. Tousoulis, A. Antonopoulos, & C. Stefanadis. The cd40/cd40 ligand system, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, vol. 54, no. 8, p. 669-677, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2009.03.076
[3] C. Qi, H. Ma, M. Fei, K. Qian, B. Shen, C. Wu, et al. A novel mutation in cd40 and its functional characterization, Human Mutation, vol. 30, no. 6, p. 985-994, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.20967
[4] Z. Song, R. Jin, S. Yu, A. Nanda, D. Granger, & G. Li. Crucial role of cd40 signaling in vascular wall cells in neointimal formation and vascular remodeling after vascular interventions, Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis and Vascular Biology, vol. 32, no. 1, p. 50-64, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1161/atvbaha.111.238329
[5] L. Lu, W. Cook, L. Lin, & R. Noelle. Cd40 signaling through a newly identified tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 2 (traf2) binding site, Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 278, no. 46, p. 45414-45418, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m309601200
[6] L. Shorts, J. Weiss, J. Lee, R. Li, J. Subleski, T. Back, et al. Stimulation through cd40 on mouse and human renal cell carcinomas triggers cytokine production, leukocyte recruitment, and antitumor responses that can be independent of host cd40 expression, The Journal of Immunology, vol. 176, no. 11, p. 6543-6552, 2006. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.176.11.6543
[7] F. Dimitrakopoulos, A. Antonacopoulou, Α. Κοττόρου, M. Kalofonou, Ν. Παναγόπουλος, D. Dougenis, et al. Genetic variations of cd40 and ltβr genes are associated with increased susceptibility and clinical outcome of non-small-cell carcinoma patients, Frontiers in Oncology, vol. 11, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.721577
[8] J. Portillo, Y. Corcino, Y. Miao, J. Tang, N. Sheibani, T. Kern, et al. Cd40 in retinal müller cells induces p2x7-dependent cytokine expression in macrophages/microglia in diabetic mice and development of early experimental diabetic retinopathy, Diabetes, vol. 66, no. 2, p. 483-493, 2016. https://doi.org/10.2337/db16-0051