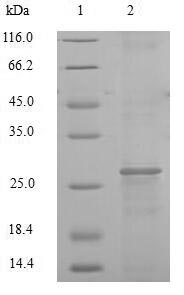
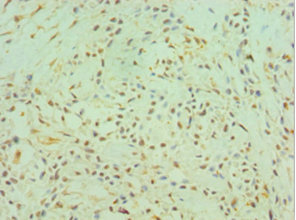
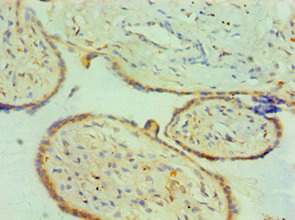
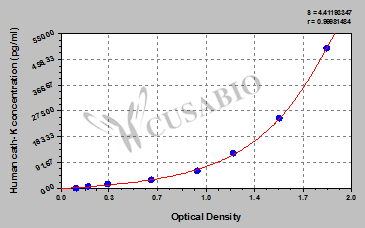
- Home
- Products
Kits
- ELISA Kits
- Exosome Isolation Kits
- ELISA Kits For Food Safety & Drug Residues
- Plasmid DNA Purification Maxiprep Kit
- HCP Detection ELISA Kit
Antibodies- Recombinant Antibodies
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Polyclonal Antibodies
- Secondary Antibodies
- Tag/Control Antibodies
- Small Molecular Antibodies
- ChIP Antibodies
- Antibody Pairs
- Custom Antibodies
- Modified Histone Antibodies
- Biosimilar Antibodies
Hot Categories- Mini Sample ELISA kit
- Inflammatory Factor ELISA Detection Panel
- Rare Species Antibodies
- Anti-CAR Linker Antibody
- Monkeypox Virus Research Related Products
- Anti-payload Antibodies
- Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Antibodies
- Flow Cytometry Antibodies
- IS Series Cytokine Detection ELISA Kit
- Recombinant DT3C protein
- Chemokine Receptors
- G protein-Coupled Receptor
- Recombinant Antibodies for Drug Discovery
- Recombinant Proteins for ADCs
- New Products Launch
- CRO Service
Quote for CRO Service Specialized CRO Services Protein Expression Services
- Transmembrane Protein Expression Service*
- E.coli Expression System
- Yeast Expression System
- In vitro E.coli Expression System
- Insect Baculovirus Expression System
- Mammalian Cell Expression System
- Pathways
- Technical Resources
- About Us
- Contact