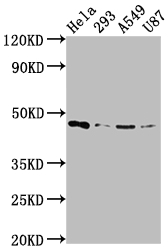
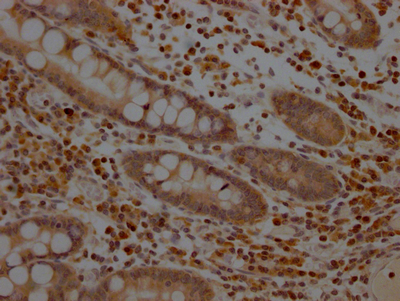
MAP2K1, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1, alias MEK1, MAPKK1, is a bispecific protein kinase, a member of the MAP kinase kinase kinase family, which is encoded by its own genes in human cells.MAP2K1 plays a key role in extracellular signaling, especially in its function in the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signaling pathway, which is involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. MAP2K1 plays a key role in extracellular signaling, especially in the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signaling pathway, which is involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, etc. MAP2K1 acts by receiving the phosphorylation signals from the upstream RAF kinase, which phosphorylates and activates the downstream ERK1/2, and then transmits the signals to the nucleus and affects the expression of genes.
The biological significance of MAP2K1 is very broad, and it is involved in the regulation of a variety of cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, transcriptional regulation, and development.The activity of MAP2K1 is critical for cellular response to a variety of external and internal signals. In addition, aberrant function of MAP2K1 has been associated with a variety of diseases, especially closely related to tumor development. For example, mutations in genes such as Raf and MEK1 may lead to the sustained activation of the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signaling pathway, which is considered to be one of the important causes of the infinite proliferative properties of tumors. Therefore, MEK1/MEK2 is often used as a target for tumor therapy in ERK signaling pathway research to develop novel anti-tumor drugs, such as selumetinib, an oral MEK inhibitor.