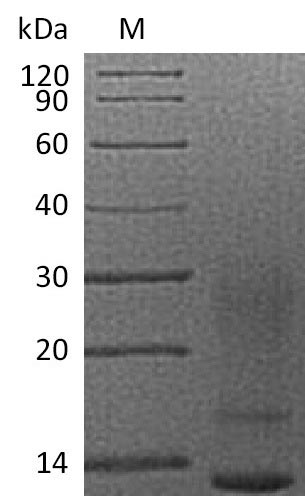
The recombinant human IL13 protein is an active protein. It is generated in mammalian cells. The target gene corresponding to the 35-146aa of human IL13 is first co-cloned into a suitable vector with a C-terminal 6xHis-tag gene and introduced into mammalian cells. The mammalian cells are grown to express the protein, which is harvested from the cell lysate. Purification is carried out using affinity chromatography technique. Purity is analyzed with SDS-PAGE, exceeding 95%. It contains less than 0.01 EU/µg of endotoxin as determined by the LAL method. The activity of the purified IL13 protein is validated in a cell proliferation assay using TF‑1 human erythroleukemic cells, with the ED50 of 1.5-4.5 ng/ml.
IL13 is a type II cytokine that plays a crucial role in various biological processes, particularly in the context of allergic asthma and cancer immunotherapy. IL13 shares receptor components and signaling pathways with IL-4, and it has been identified as a central mediator of allergic asthma. Studies have shown that IL13 is necessary and sufficient for the expression of allergic asthma [1].
IL13 has also been investigated in pulmonary fibrosis and granuloma formation. IL13-PE, a recombinant chimeric fusion protein containing human IL13 and a mutated Pseudomonas exotoxin, has been utilized to target IL13 receptor-expressing tumor cells [2]. Furthermore, IL13 is secreted by multiple subsets of immune cells and plays a role in promoting neck cell expansion and metaplasia in the gastric mucosa [3]. It has been implicated in promoting metaplasia development during chronic gastritis by acting directly on gastric epithelial cells [3].
References:
[1] M. Wills‐Karp, J. Luyimbazi, X. Xu, B. Schofield, T. Neben, C. Karpet al., Interleukin-13: central mediator of allergic asthma, Science, vol. 282, no. 5397, p. 2258-2261, 1998. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.282.5397.2258
[2] K. Blease, J. Schuh, C. Jakubzick, N. Lukacs, S. Kunkel, B. Joshiet al., Stat6-deficient mice develop airway hyperresponsiveness and peribronchial fibrosis during chronic fungal asthma, American Journal of Pathology, vol. 160, no. 2, p. 481-490, 2002. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64867-5
[3] C. Noto, S. Hoft, K. Bockerstett, N. Jackson, E. Ford, L. Vestet al., Il13 acts directly on gastric epithelial cells to promote metaplasia development during chronic gastritis, Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, vol. 13, no. 2, p. 623-642, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.09.012