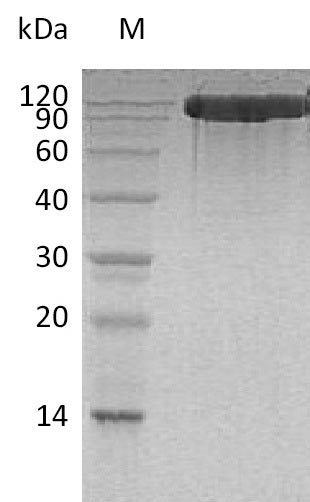
Producing recombinant human Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) involves several steps starting with isolating the target gene fused with a C-terminal 6xHis-tag gene. The target gene encodes the 18-740aa of the human ACE2. This fused gene is cloned into an expression vector and introduced into mammalian cells via transformation. The mammalian cells express the protein, which is collected from the cell lysate. Purification of the protein is typically achieved using affinity chromatography. The final step involves validating the recombinant ACE2 protein's functionality through various biochemical assays to ensure it meets the required standards. Its purity is greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE. It contains less than 1.0 EU/μg of endotoxin as determined by the LAL method. This recombinant ACE2 protein has also been validated as an active protein in BLI assay, in which the SARS-C0V-2 S Protein RBD-mFc on AMC Biosensor can bind Human ACE-2-His with an affinity constant of 2.06 nM.
Human ACE2 is a zinc metalloprotease that was first discovered in 2000 and shares substantial homology with human ACEs [1]. ACE2 is a crucial component of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) that can catalyze the cleavage of angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9 [2][3]. Structurally, the human ACE2 contains an extracellular N-terminal peptidase domain, a C-terminal collectrin-like domain, a single transmembrane helix, and an intracellular segment [4]. ACE2 plays a significant role in diseases such as COVID-19, where it serves as the functional host receptor for the virus [5]. Studies have shown that viruses like SARS-CoV and 2019-nCoV can invade human cells by binding to ACE2 [6]. ACE2 is widely expressed in various human tissues, including the respiratory, cardiovascular, digestive, and urinary systems, rendering these organs susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection [7][8].
References:
[1] A. Chenna, V. Konala, S. Bose, S. Roy, B. Madhira, V. Gayamet al., Acute kidney injury in a case series of patients with confirmed covid-19 (coronavirus disease 2019): role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and renin-angiotensin system blockade, Case Reports in Nephrology, vol. 2020, p. 1-8, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8811931
[2] R. Magazine, B. Chogtu, & A. Bhat, Role of angiotensin converting enzyme-2 and its modulation in disease: exploring new frontiers, Medicine and Pharmacy Reports, vol. 96, no. 2, p. 146-153, 2023. https://doi.org/10.15386/mpr-2345
[3] C. Tikellis, C. Johnston, J. Forbes, W. Burns, L. Burrell, J. Risvaniset al., Characterization of renal angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in diabetic nephropathy, Hypertension, vol. 41, no. 3, p. 392-397, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.0000060689.38912.cb
[4] C. Caillet-Saguy and N. Wolff, Pdz-containing proteins targeted by the ace2 receptor, Viruses, vol. 13, no. 11, p. 2281, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13112281
[5] X. Zou, K. Chen, J. Zou, P. Han, J. Hao, & Z. Han, Single-cell rna-seq data analysis on the receptor ace2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-ncov infection, Frontiers of Medicine, vol. 14, no. 2, p. 185-192, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-020-0754-0
[6] A. Mohamadzadeh and D. Mohamadzadeh, Bilateral acute anterior uveitis and optic nerve edema as a manifestation of coronavirus disease‐2019 (covid‐19): a case report, Clinical Case Reports, vol. 11, no. 6, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccr3.7473
[7] Y. Dai, F. Hu, H. Li, H. Huang, D. Wang, & Y. Liang, A profiling analysis on the receptor ace2 expression reveals the potential risk of different type of cancers vulnerable to sars-cov-2 infection, Annals of Translational Medicine, vol. 8, no. 7, p. 481-481, 2020. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2020.03.61
[8] Y. Wang, Y. Wang, W. Luo, L. Huang, J. Xiao, F. Liet al., A comprehensive investigation of the mrna and protein level of ace2, the putative receptor of sars-cov-2, in human tissues and blood cells, International Journal of Medical Sciences, vol. 17, no. 11, p. 1522-1531, 2020. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.46695