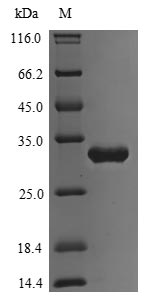
Recombinant Escherichia coli Transcriptional regulatory protein PhoP is produced using a yeast expression system, which appears to support proper protein folding and post-translational modifications. The protein comes as a full-length construct featuring an N-terminal 6xHis tag and a C-terminal Myc tag - these tags help with purification and detection processes. SDS-PAGE analysis indicates purity levels exceeding 90%, suggesting it may be well-suited for research applications.
PhoP acts as a transcriptional regulatory protein in Escherichia coli and likely plays an important role in how bacteria respond to environmental changes. Working alongside PhoQ, it forms part of a two-component system that controls genes related to magnesium transport and virulence factors. Scientists often examine PhoP to better understand how bacteria adapt and cause disease, which could have broader implications for antibiotic resistance patterns and microbial ecology.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Escherichia coli PhoP is a bacterial response regulator that requires precise folding, dimerization, and phosphorylation for its transcriptional regulatory activity. While the yeast expression system provides a eukaryotic environment that supports proper folding, it may not fully replicate the bacterial-specific folding requirements. The dual N-terminal 6xHis-tag and C-terminal Myc-tag may sterically interfere with the protein's functional domains or dimerization interface. While the full-length protein (1-223aa) contains all functional domains, the probability of correct folding with functional activity requires experimental validation.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies Using Pull-Down Assays
This application's reliability depends on proper folding validation. Bacterial response regulator interactions require precise tertiary and quaternary structure. If correctly folded (verified), the protein is suitable for identifying physiological interaction partners (e.g., PhoQ, DNA). If misfolded/unverified, the risk of non-specific binding or interaction failure makes results biologically misleading.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
Antibody development primarily relies on antigenic sequence recognition. If correctly folded (verified), the protein excels for generating conformation-sensitive antibodies. If misfolded/unverified, it remains suitable for producing antibodies against linear epitopes of PhoP.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Stability Studies
These studies are essential for determining folding status and protein quality. If correctly folded (verified), characterization provides insights into dimerization stability and functional properties. If misfolded/unverified, analysis yields physical property data for this specific preparation.
4. ELISA-Based Quantitative Assays
Immunoassays depend on epitope recognition rather than functional conformation. If correctly folded (verified), the protein serves as an excellent standard for quantitative detection. If misfolded/unverified, it remains suitable as an immunoassay standard for detecting immunoreactive material.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The yeast expression system provides eukaryotic folding conditions, but experimental validation is essential before functional applications for this bacterial response regulator. Begin with Application 3 (Biochemical Characterization) to assess folding quality through size-exclusion chromatography (dimerization check), circular dichroism spectroscopy, and phosphorylation response assays. If correct folding and phosphorylation capability are verified, proceed cautiously with Applications 1, 2 (conformational antibodies), and 4 for interaction studies, antibody development, and quantitative assays. If misfolding is detected, limit applications to linear epitope antibody production (Application 2) and basic biophysical characterization, avoiding all functional interaction studies. For reliable PhoP research, consider using protein expressed in bacterial systems or validating functionality with phosphorylation assays and DNA-binding tests.