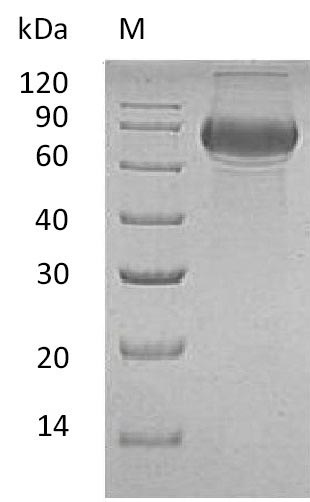
The recombinant human B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 is an active protein. It is produced in mammalian cells. The gene encoding the CD19 protein (20-291aa) into an expression vector with a C-terminal hFc-tag gene and introducing it into mammalian cells. These cells are cultured under conditions that induce protein expression. Once sufficient growth is achieved, the cells are lysed to release the recombinant CD19 protein, which is purified via affinity chromatography. The purity of the recombinant CD19 protein is assessed using SDS-PAGE, exceeding 95%. Its endotoxin content is less than 1.0 EU/μg as determined by the LAL method. A functional ELISA assay is performed to verify the CD19 protein's activity, ensuring it retains its intended function post-purification.
Human CD19 is a vital cell-surface marker for B lymphocytes. Its expression is restricted to B cells and follicular dendritic cells [1][2]. CD19 is expressed during early pre-B-cell differentiation and persists until terminal differentiation into plasma cells [3][4]. The CD19 molecule is highly homologous between humans and mice, featuring a conserved cytoplasmic domain and an immunoglobulin-like extracellular domain [4]. In normal peripheral blood, CD19 is expressed on the cell membrane in 5-20% of the total lymphocyte population [5]. Furthermore, CD19 integrates B-cell receptor (BCR) and TTLR9 signaling in human B cells through the CD19/PI3K/AKT/BTK axis [6]. CD19 is a promising target for immunotherapy due to its expression both on normal and neoplastic B cells [7].
References:
[1] M. Fujimoto, J. Poe, M. Hasegawa, & T. Tedder, Cd19 amplification of b lymphocyte ca2+ responses, Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 276, no. 48, p. 44820-44827, 2001. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m107559200
[2] R. Kumar, B lymphocyte antigen cd19,, p. 1-10, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-6438-9_101837-1
[3] K. Wang, G. Wei, & D. Liu, Cd19: a biomarker for b cell development, lymphoma diagnosis and therapy, Experimental Hematology and Oncology, vol. 1, no. 1, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1186/2162-3619-1-36
[4] Z. Kozmík, S. Wang, P. Dörfler, B. Adams, & M. Busslinger, The promoter of the cd19 gene is a target for the b-cell-specific transcription factor bsap, Molecular and Cellular Biology, vol. 12, no. 6, p. 2662-2672, 1992. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.12.6.2662-2672.1992
[5] A. Tamashevski, Y. Harmaza, R. Viter, D. Jevdokimovs, R. Poplausks, E. Slobozhaninaet al., Zinc oxide nanorod based immunosensing platform for the determination of human leukemic cells, Talanta, vol. 200, p. 378-386, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.03.064
[6] H. Morbach, J. Schickel, C. Cunningham‐Rundles, M. Conley, İ. Reisli, J. Francoet al., Cd19 controls toll-like receptor 9 responses in human b cells, Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, vol. 137, no. 3, p. 889-898.e6, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.08.040
[7] Q. Zheng, Z. Wang, H. Zhang, Q. Huang, J. Madsen, D. Sachset al., Diphtheria toxin‐based anti‐human cd19 immunotoxin for targeting human cd19+ tumors, Molecular Oncology, vol. 11, no. 5, p. 584-594, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12056